Abstract
Background
To determine the blink patterns of newscasters.
Methods
The blink patterns of 39 professional newscasters (24 Japanese and 19 non-Japanese, 19 men and 20 women, mean age: 34.5 ± 6.5 years) were analyzed by a blink analyzer in this observational case series. Sixty-four normal Japanese volunteers (35 men and 29 women, mean age: 31.2 ± 7.6 years) were used as lay normal controls.
Results
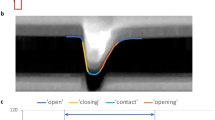
The maximum, mean, and coefficient of variation (CV) of interblinking time (IBT: the time between one blink and the next) in newscasters were 2.36 ± 0.90 s (P < 0.0005), 0.95 ± 0.27 s (P < 0.0005), and 0.76 ± 0.25 (P < 0.0005), respectively, while those of the controls were 8.87 ± 3.96 s, 4.01 ± 2.05 s, and 0.55 ± 0.21, respectively. The maximum, mean, and CV of the blinking time (BT: the length of time for each blink) of newscasters were 0.71 ± 0.43 s (P < 0.0005), 0.29 ± 0.11 s (P < 0.0005), and 0.55 ± 0.25 (P < 0.0005), respectively. The values were longer when compared with normal controls, which were also significantly different, 0.35 ± 0.12 s, 0.20 ± 0.04 s and 0.23 ± 0.09, respectively.
Conclusions
The six blink-related factors varied between newscasters and normal controls. Newscasters blink more often with greater irregularity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathers WD, Lane JA, Zimmerman MB (1996) Tear film changes associated with normal aging. Cornea 15:229–234 doi:10.1097/00003226–199605000–00001
Nakamori K, Odawara M, Nakajima T, Mizutani T, Tsubota K (1997) Blinking is controlled primarily by ocular surface conditions. Am J Ophthalmol 124:24–30
Tsubota K, Nakamori K (1995) Effects of ocular surface area and blink rate on tear dynamics. Arch Ophthalmol 113:155–158
Tsubota K, Hata S, Okusawa Y, Egami F, Ohtsuki T, Nakamori K (1996) Quantitative videographic analysis of blinking in normal subjects and patients with dry eye. Arch Ophthalmol 114:715–720
Tsubota K, Nakamori K (1993) Dry eyes and video display terminals. N Engl J Med 328:584 doi:10.1056/NEJM199302253280817
Mackintosh JH, Kumar R, Kitamura T (1983) Blink rate in psychiatric illness. Br J Psychiatry 143:55–57
Sandyk R (1990) The significance of eye blink rate in parkinsonism: a hypothesis. Int J Neurosci 51:99–103 doi:10.3109/00207459009000515
Stern JA, Walrath LC, Goldstein R (1984) The endogenous eyeblink. Psychophysiology 21:22–33 doi:10.1111/j.1469–8986.1984.tb02312.x
MacLean WE Jr, Lewis MH, Bryson-Brockmann WA, Ellis DN, Arendt RE, Baumeister AA (1985) Blink rate and stereotyped behavior: evidence for dopamine involvement. Biol Psychiatry 20:1321–1325 doi:10.1016/0006–3223(85)90117–9
Tsubota K, Egami F, Ohtsuki T, Shintani M (1999) Abnormal blinking of newscasters. Lancet 354:308 doi:10.1016/S0140–6736(99)02100–5
Blehm C, Vishnu S, Khattak A, Mitra S, Yee RW (2005) Computer vision syndrome: a review. Surv Ophthalmol 50:253–262 doi:10.1016/j.survophthal.2005.02.008
Hagan S, Lory B (1998) Prevalence of dry eye among computer users. Optom Vis Sci 75:712–713 doi:10.1097/00006324–199810000–00014
World Health Organization (1987) Visual display terminals and workers’ health. WHO Offset Publ 99:1–206
Acosta MC, Gallar J, Belmonte C (1999) The influence of eye solutions on blinking and ocular comfort at rest and during work at video display terminals. Exp Eye Res 68:663–669 doi:10.1006/exer.1998.0656
Tsubota K, Toda I, Nakamori K (1996) Poor illumination, VDTs and desiccated eyes. Lancet 347:768–769 doi:10.1016/S0140–6736(96)90122–1
Yaginuma Y, Yamada H, Nagai H (1990) Study of the relationship between lacrimation and blink in VDT work. Ergonomics 33:799–809 doi:10.1080/00140139008927186
Tsubota K, Hata S, Mori A, Nakamori K, Fujishima H (1997) Decreased blinking in dry saunas. Cornea 16:242–243 doi:10.1097/00003226–199703000–00022
Mori A, Oguchi Y, Okusawa Y, Ono M, Fujishima H, Tsubota K (1997) Use of high speed, high-resolution thermography to evaluate the tear film layer. Am J Ophthalmol 124:729–735
Lemp MA, Baudouin C, Baum J, Dogru M, Foulks GN, Kinoshita S et al (2007) The definition and classification of dry eye disease: Report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop. Ocul Surf 5:75–92
Stevens JR (1978) Eye blink and schizophrenia: psychosis or tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 135:223–226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, A., Egami, F., Nakamori, K. et al. Quantitative videographic analysis of blink patterns of newscasters. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 1449–1453 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0887-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0887-3