Abstract
Background
Induction of glucose-regulated protein (GRP)-78 in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a protective mechanism cells use to adapt to ER stress. We evaluated the expression of GRP-78 and its regulation by an oxidant tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBH) in human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells.
Methods
We used a carboxy-H2-DCFDA staining method to detect tBH-induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in RPE cells, and analyzed the expression of GRP-78 in normal human fetal and adult retinas and in cultured human RPE cells by immunohistochemistry. The effects of tBH (10–100 μM) on GRP-78 and on growth arrest and DNA damage inducible genes 153 (GADD153) protein and mRNA expression were studied using Western blot and real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results
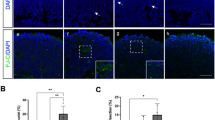
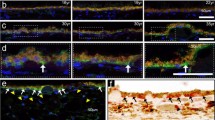
Sections of fetal retinas were negative for GRP-78. Adult retinas showed moderate cytoplasmic GRP-78 staining in the RPE and choroid. tBH-induced ROS accumulation in RPE cells showed partial colocalization with the ER. GRP-78 and GADD153 mRNA and protein expression in cultured RPE cells were significantly upregulated by treatment with tBH.
Conclusion
tBH increases oxidative stress, increases accumulation of ROS in the ER, and upregulates expression of GRP-78 and GADD153. This supports the connection between oxidative stress and ER stress, and suggests that GRP-78 may serve a protective role in the RPE response to oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes JA, Smoak IW (2000) Glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is elevated in embryonic mouse heart and induced following hypoglycemic stress. Anat Embryol (Berl) 202:67–74
Brewster JL, Linseman DA, Bouchard RJ, Loucks FA, Precht TA, Esch EA, Heidenreich KA (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and trophic factor withdrawal activate distinct signaling cascades that induce glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and a caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:242–253
Chen L, Gao X (2002) Neuronal apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurochem Res 27:891–898
Dey A, Kessova IG, Cederbaum AI (2006) Decreased protein and mRNA expression of ER stress proteins GRP-78 and GRP94 in HepG2 cells over-expressing CYP2E1. Arch Biochem Biophys 447:155–166
Forman MS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2003) “Unfolding” pathways in neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci 26:407–410
Ghribi O (2006) The role of the endoplasmic reticulum in the accumulation of beta-amyloid peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Mol Med 6:119–133
Ghribi O, Herman MM, DeWitt DA, Forbes MS, Savory J (2001) Abeta(1–42) and aluminum induce stress in the endoplasmic reticulum in rabbit hippocampus, involving nuclear translocation of GADD153 and NF-kappaB. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 96:30–38
Ghribi O, Herman MM, Pramoonjago P, Spaulding NK, Savory J (2004) GDNF regulates the A beta-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress response in rabbit hippocampus by inhibiting the activation of GADD153 and the JNK and ERK kinases. Neurobiol Dis 16:417–427
Gomer CJ, Ferrario A, Rucker N, Wong S, Lee AS (1991) Glucose regulated protein induction and cellular resistance to oxidative stress mediated by porphyrin photosensitization. Cancer Res 51:6574–6579
Guo ZH, Mattson MP (2000) In vivo 2-deoxyglucose administration preserves glucose and glutamate transport and mitochondrial function in cortical synaptic terminals after exposure to amyloid beta-peptide and iron: evidence for a stress response. Exp Neurol 166:173–179
Guyton KZ, Xu Q, Holbrook NJ (1996) Induction of the mammalian stess response gene GADD153 by oxidative stress:role of AP-1 element. Biochem J 314:547–554
Ha KN, Chen Y, Cai J, Sternberg P Jr (2006) Increased glutathione synthesis through an ARE-Nrf2-dependent pathway by zinc in the RPE: implication for protection against oxidative stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:2709–2715
Hashimoto M, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Masliah E (2003) Role of protein aggregation in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Neuromolecular Med 4:21–36
Hayashi T, Saito A, Okuno S, Ferrand-Drake M, Dodd RL, Chan PH (2005) Damage to the endoplasmic reticulum and activation of apoptotic machinery by oxidative stress in ischemic neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:41–53
Imaizumi K, Miyoshi K, Katayama T, Yoneda T, Taniguchi M, Kudo T, Tohyama M (2001) The unfolded protein response and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1536:85–96
Jin M, Yaung J, Kannan R, He S, Ryan SJ, Hinton DR (2005) Hepatocyte growth factor protects RPE cells from apoptosis induced by glutathione depletion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4311–4319
Kannan R, Jin M, Gamulescu MA, Hinton DR (2004) Ceramide-induced apoptosis: role of catalase and hepatocyte growth factor. Free Radic Biol Med 37:166–175
Kasahara E, Lin LR, Ho YS, Reddy VN (2005) SOD2 protects against oxidation-induced apoptosis in mouse retinal pigment epithelium: implications for age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:3426–3434
Katayama T, Imaizumi K, Manabe T, Hitomi J, Kudo T, Tohyama M (2004) Induction of neuronal death by ER stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 28:67–78
King A, Gottlieb E, Brooks DG, Murphy MP, Dunaief JL (2004) Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species mediate blue light-induced death of retinal pigment epithelial cells. Photochem Photobiol 79:470–475
Kline CL, Schrufer TL, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR (2006) Glucosamine-induced phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 is mediated by the protein kinase R-like endoplasmic-reticulum associated kinase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:1004–1014
Kudo T, Okumura M, Imaizumi K, Araki W, Morihara T, Tanimukai H, Kamagata E, Tabuchi N, Kimura R, Kanayama D, Fukumori A, Tagami S, Okochi M, Kubo M, Tanii H, Tohyama M, Tabira T, Takeda M (2006) Altered localization of amyloid precursor protein under endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344:525–530
Kuznetsov G, Bush KT, Zhang PL, Nigam SK (1996) Perturbations in maturation of secretory proteins and their association with endoplasmic reticulum chaperones in a cell culture model for epithelial ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8584–8589
Lai MT, Huang KL, Chang WM, Lai YK (2003) Geldanamycin induction of GRP-78 requires activation of reactive oxygen species via ER stress responsive elements in 9 L rat brain tumour cells. Cell Signal 15:585–595
Le Bras M, Rouy I, Brenner C (2006) The modulation of inter-organelle cross-talk to control apoptosis. Med Chem 2:1–12
Gilmore WJ, Kirby GM (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress due to altered cellular redox status positively regulates murine hepatic CYP2A5 expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:600–608
Lee AS (1992) Mammalian stress response: induction of the glucose-regulated protein family. Curr Opin Cell Biol 4:267–273
Lee AS (2001) The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci 26:504–510
Li B, Chen YH (2003) [The expression of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) in mouse brain during early development]. Shi Yan Sheng Wu Xue Bao 36:137–144
Liang FQ, Godley BF (2003) Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial DNA damage in human retinal pigment epithelial cells: a possible mechanism for RPE aging and age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res 76:397–403
Liang FQ, Green L, Wang C, Alssadi R, Godley BF (2004) Melatonin protects human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells against oxidative stress. Exp Eye Res 78:1069–1075
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Lu L, Hackett SF, Mincey A, Lai H, Campochiaro PA (2006) Effects of different types of oxidative stress in RPE cells. J Cell Physiol 206:119–125
Mattson MP (2006) Neuronal life-and-death signaling, apoptosis, and neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1997–2006
Miceli MV, Liles MR, Newsome DA (1994) Evaluation of oxidative processes in human pigment epithelial cells associated with retinal outer segment phagocytosis. Exp Cell Res 214:242–249
Onoue S, Kumon Y, Igase K, Ohnishi T, Sakanaka M (2005) Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153 increases transiently in the thalamus following focal cerebral infarction. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 134:189–197
Paschen W, Mengesdorf T, Althausen S, Hotop S (2001) Peroxidative stress selectively down-regulates the neuronal stress response activated under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. J Neurochem 76:1916–1924
Paz Gavilan M, Vela J, Castano A, Ramos B, del Rio JC, Vitorica J, Ruano D (2006) Cellular environment facilitates protein accumulation in aged rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 27:973–982
Price BD, Mannheim-Rodman LA, Calderwood SK (1992) Brefeldin A, thapsigargin, and AIF4- stimulate the accumulation of GRP-78 mRNA in a cycloheximide dependent manner, whilst induction by hypoxia is independent of protein synthesis. J Cell Physiol 152:545–552
Rao RV, Peel A, Logvinova A, del Rio G, Hermel E, Yokota T, Goldsmith PC, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2002) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: role of the ER chaperone GRP-78. FEBS Lett 514:122–128
Reddy RK, Mao C, Baumeister P, Austin RC, Kaufman RJ, Lee AS (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein GRP-78 protects cells from apoptosis induced by topoisomerase inhibitors: role of ATP binding site in suppression of caspase-7 activation. J Biol Chem 278:20915–20924
Roth F, Bindewald A, Holz FG (2004) Keypathophysiologic pathways in age-related macular disease. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:710–716
Roybal CN, Marmorstein LY, Vander Jagt DL, Abcouwer SF (2005) Aberrant accumulation of fibulin-3 in the endoplasmic reticulum leads to activation of the unfolded protein response and VEGF expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:3973–3979
Ryu EJ, Harding HP, Angelastro JM, Vitolo OV, Ron D, Greene LA (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 22:10690–10698
Sanges D, Marigo V (2006) Cross-talk between two apoptotic pathways activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress: differential contribution of caspase-12 and AIF. Apoptosis 11:1629–1641
Takuma K, Yan SS, Stern DM, Yamada K (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Sci 97:312–316
Tang J-R, Nakamura M, Okura T, Takata Y, Watanabe S, Yang Z-H, Liu J, Kitami Y, Hiwada K (2002) Mechanism of oxidative stress-induced GADD153 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:1255–1259
Walter L, Hajnoczky G (2005) Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum: the lethal interorganelle cross-talk. J Bioenerg Biomembr 37:191–206
Wang X, Wang B, Fan Z, Shi X, Ke ZJ, Luo J (20067) Thiamine deficiency induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurons. Neuroscience 135:1129–1139
Wassell J, Boulton M (1997) A role for vitamin A in the formation of ocular lipofuscin. Br J Ophthalmol 81:911–918
Yan SD, Schmidt AM, Stern D (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: inside, outside, upside down. Biochem Soc Symp 67:15–22
Yu Z, Luo H, Fu W, Mattson MP (1999) The endoplasmic reticulum stress-responsive protein GRP-78 protects neurons against excitotoxicity and apoptosis: suppression of oxidative stress and stabilization of calcium homeostasis. Exp Neurol 155:302–314
Zarbin MA (2004) Current concepts in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 122:598–614
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation and National Institutes for Health grant EY01545 and Core grant EY03040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
There are no commercial financial relationships to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Yaung, J., Kim, Y.H. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 677–683 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0770-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0770-2