Abstract
Background
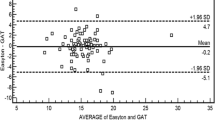
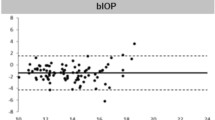
Disposable tonometers are increasingly being adopted partly because of concerns over the transmission of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and partly for convenience. Recently, we have found one such tonometer (Tonojet by Luneau Ophthalmologie, France) underestimated the intraocular pressure (IOP).
Methods
We hypothesized that this underestimation was caused by a difference in the surface property of the tonometers. A tensiometer was used to measure the suction force resulting from interfacial tension between a solution of lignocaine and fluorescein and the tonometers.
Results
The results showed that the suction force was significantly greater for the Goldmann compared to the Tonojet.
Conclusions
The magnitude of this force was too small to account for the difference in IOP measurements. The Tonojet was less hydrophilic than the Goldmann, and the contact angle of the fluid was therefore greater. For a given tear film, less hydrophilic tonometers will tend to have thicker mires, and this may lead to underestimation of the IOP. When such disposable tonometers are used, it is recommended care should be taken to reject readings from thick mires.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This is a 2% sodium hypochlorite solution. The active ingredients include sodium hypochlorite 2% w/w and sodium chloride 16.5% w/w.
As measured by Vernier calipers.
References
Baddon ACJ, Osborne S, Quah SA, Batterbury M, Wong D. Comparison of Luneau SA Disposable and Goldmann Applanation Tonometer readings. Eye. DOI EYE-05-423R
Bhatnagar A, Gupta AK (2005) Disposable devices for measuring intraocular pressure: a clinical study to assess their accuracy. Eye 19:752–754
Desai SP, Sivakumar S, Fryers PT (2001) Evaluation of a disposable prism for applanation tonometry. Eye 15:279–282
Kim P, Lertsumitkul S, Clark M, Gardner L, Macken P (2004) Accuracy of the Tonosafe disposable tonometer head compared to the Goldmann tonometer alone. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 32:364–367
Liu C, Brown NND, Meenan BJ (2005) Statistical analysis of the effect of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) operating parameters on the surface processing of poly(methylmethacrylate) film. Surface Sci 575:273–286
Maldonado MJ, Rodriguez-Galietero A, Cano-Parra J, Menezo JL, Diaz-LLopis M (1996) Goldmann applanation tonometry using sterile disposable silicone tonometer shields. Ophthalmology 103:815–821
Schmalenburg KE, Buettner HM, Uhrich KE (2004) Microprinting of proteins on oxygen plasma-activated poly(methylmethacrylate). Biomaterials 25:1851–1857
Whitacre MM, Stein R (1993) Sources of error with use of Goldmann-type tonometers. Surv Ophthalmol 38(1):1–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osborne, S.F., Williams, R., Batterbury, M. et al. Does the surface property of a disposable applanation tonometer account for its underestimation of intraocular pressure when compared with the Goldmann tonometer?. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245, 555–559 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0380-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-006-0380-9