Abstract
Background
A recently developed digital tonometer for transpalpebral intraocular pressure (IOP) measurement, distributed by Corneal, Inc., allows the noninvasive measurement of IOP for screening purposes.
Method
We measured the IOP of 218 eyes in 109 patients of the Interdisciplinary Uveitis Center of the University of Heidelberg with intact corneal epithelium. IOPs were measured first with the TGDc-01 tonometer, and then by means of Goldmann tonometry. IOPs were recorded by two independent examiners. The mean of three measurements obtained with the TGDc-01 was taken, whereas only one measurement was performed with the Goldmann tonometer.
Results
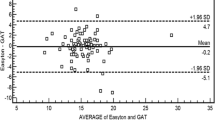
The mean difference between the TGDc-01 and Goldmann measurements was 3.7 mmHg. The standard deviation of the differences was ±4.06 mmHg. Thus measurements acquired with the TGDc-01 may range 4.4 mmHg above or 11.8 mmHg below the values given by Goldmann tonometry.
Conclusion
The IOP values obtained with the TGDc-01 were in poor agreement with Goldmann tonometry. We found a higher variation as well as a bias towards lower IOP values with the TGDc-01. It is a question of clinical judgement as to how far these deviating measurements can be accepted for screening purposes. Because the IOPs obtained with the TGDc-01 are generally lower and less accurate than those obtained with the Goldmann tonometer we believe that the TGDc-01 is not a reliable tool for IOP measurement in clinical routine.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Digital mobile tonometer for measurement of intraocular pressure through the eyelid: TGDc-01 “PRA”. Instruction booklet, Rjazan State Toolmaking Plant, 32 Kaljaeva Street, 390000 Rjazan, Russia
Draeger J, Stodtmeister R (2003) Ein “neues” Tonometer? Augenarzt 37:318–319
Mantha S, Roizen MF, Fleisher LA, Thisted R, Foss J (2000) Comparing methods of clinical measurements: reporting standards for Bland and Altman analysis. Anesth Analg 90:593–602
Martin M, Pache M, Flammer J (2003) Der portable Tonometer TGDc-01 und die Goldmann- und Lufttonometrie im Vergleich - eine Pilotstudie. In: Auffarth GU, Welt R, Demeler U (eds) Transactions, 17th Congress of the German Society for Intraocular Lens Implantation and Refractive Surgery (DGII). Biermann, Cologne, pp 126–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lösch, A., Scheuerle, A., Rupp, V. et al. Transpalpebral measurement of intraocular pressure using the TGDc-01 tonometer versus standard Goldmann applanation tonometry. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243, 313–316 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0971-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0971-2