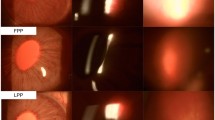
Abstract
Background
To investigate the effects of a new biodegradable dexamethasone drug delivery system, Surodex, in two experimental intraocular inflammation models; endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) and experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU).
Methods
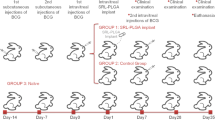
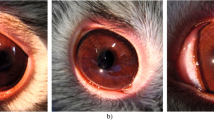
Surodex was inserted into the right anterior chambers (ACs) of rats. In the EIU experiment, protein concentration, cell infiltration, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the aqueous humor were measured 24 h after injection. Eyes were evaluated histopathologically. In the EAU experiment, firstly, Surodex was administered at various days after immunization. Then, Surodex was administered on day 9 and eyes were evaluated histopathologically. Intraocular cytokine levels (IFN-γ and IL-4) were investigated.
Results
In the EIU experiments, eyes with Surodex exhibited significantly reduced inflammation compared with contralateral controls. Protein concentrations, cell infiltrations, as well as MPO activity were reduced. In the EAU experiments, all rats with Surodex given on days 0 or 7 showed no or significantly reduced inflammation in both eyes. Rats treated on day 12 developed reduced inflammation only in the treated eyes. IFN-γ levels were significantly lower in the eyes with Surodex, whereas IL-4 was not detectable.
Conclusions
This new, biodegradable corticosteroid drug-delivery system is highly effective in suppressing intraocular inflammation, and should be a useful tool to manage uveitis in humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behar-Cohen FF, Parel JM, Pouliquen Y, Thillaye-Goldenberg B, Goureau O, Heydolph S, Courtois Y, De Kozak Y (1997) Iontophoresis of dexamethasone in the treatment of endotoxin-induced-uveitis in rats. Exp Eye Res 65:533–545
Chang DF, Wong V (1999) Two clinical trials of an intraocular steroid delivery system for cataract surgery. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 97:261–279
Charteris DG, Lightman SL (1992) Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production in vivo in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Immunology 75:463–467
Cheng CK, Berger AS, Pearson PA, Ashton P, Jaffe GJ (1995) Intravitreal sustained-release dexamethasone device in the treatment of experimental uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 36:442–453
Cousins SW, Guss RB, Howes EL Jr, Rosenbaum JT (1984) Endotoxin-induced uveitis in the rat: observations on altered vascular permeability, clinical findings, and histology. Exp Eye Res 39:665–676
Jaffe GJ, Ben-Nun J, Guo H, Dunn JP, Ashton P (2000) Fluocinolone acetonide sustained drug delivery device to treat severe uveitis. Ophthalmology 107:2024–2033
Jaffe GJ, Pearson PA, Ashton P (2000) Dexamethasone sustained drug delivery implant for the treatment of severe uveitis. Retina 20:402–403
Jaffe GJ, Yang CH, Guo H, Denny JP, Lima C, Ashton P (2000) Safety and pharmacokinetics of an intraocular fluocinolone acetonide sustained delivery device. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3569–3575
Jennings T, Rusin MM, Tessler HH, Cunha-Vaz JG (1988) Posterior sub-Tenon's injections of corticosteroids in uveitis patients with cystoid macular edema. Jpn J Ophthalmol 32:385–391
Mochizuki M, Nussenblatt RB, Kuwabara T, Gery L (1985) Effects of cyclosporine and other immunosuppressive drugs on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26:226–232
Tan DT, Chee SP, Lim L, Lim AS (1999) Randomized clinical trial of a new dexamethasone delivery system (Surodex) for treatment of post-cataract surgery inflammation. Ophthalmology 106:223–231
Tan DT, Chee SP, Lim L, Theng J, Van Ede M (2001) Randomized clinical trial of Surodex steroid drug delivery system for cataract surgery: anterior versus posterior placement of two Surodex in the eye. Ophthalmology 108:2172–2181
Acknowledgement. We sincerely thank Y. Ishii for his excellent preparation of histopathological specimens.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodama, M., Numaga, J., Yoshida, A. et al. Effects of a new dexamethasone-delivery system (Surodex) on experimental intraocular inflammation models. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 241, 927–933 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-003-0753-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-003-0753-2