Abstract
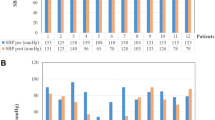
Nitric oxide (NO) is synthesised from the amino-acid l-arginine by the enzyme nitric oxide synthetase (NOS) and modulates a wide variety of neural, cardiovascular and hormonal processes. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction and impaired neurohormonal secretion characterise patients with primary chronic autonomic failure (AF). To investigate the role of NO, we studied the cardiovascular and neurohormonal effects of intravenous (i. v.) l-arginine (0.5 g/kg) in 20 patients with AF: [10 with multiple system atrophy (MSA) and 10 patients with pure autonomic failure (PAF)] and compared them with age-matched healthy normal subjects. Basal mean arterial pressure (MAP) was higher in MSA and PAF than controls (p < 0.02). Following l-arginine, MAP fell in MSA (mean: −39 ± 8 mmHg, 95 % CI −21 to −57, p < 0.05) and PAF (−37 ± 5, 95 % CI −26 to −58, p < 0.05) but not in controls. There were no significant changes in HR between the groups. Basal plasma noradrenaline (NA) was similar in controls and MSA, but lower in PAF (p < 0.05). Following l-arginine the percentage rise in plasma NA was similar in controls and MSA, but not in PAF (p < 0.05). Plasma insulin rose similarly in controls and MSA, but was higher in PAF (p < 0.05). Plasma glucose rose to a similar level in all groups. In conclusion, l-arginine, lowered BP in both MSA and PAF. In PAF a contributory factor may be increased insulin release, without a compensatory increase in sympatho-neural activity to counter its potential vasodilator effects. These studies suggest that reducing NO levels, as with NOS inhibitors, may be of benefit in the treatment of postural hypotension and possibly post-prandial hypotension in chronic primary AF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 May 2000, Received in revised form: 13 September 2000, Accepted: 22 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimber, J., Watson, L. & Mathias, C. Cardiovascular and neurohormonal responses to i. v. l-arginine in two groups with primary autonomic failure. J Neurol 248, 1036–1041 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150170022
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150170022