Abstract.
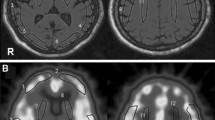
Cerebral blood flow and cerebrospinal fluid amino acids were investigated in patients with leukoaraiosis on magnetic resonance imaging. Ten patients with leukoaraiosis and without significant cerebral infarction and ten age-matched controls without abnormality on magnetic resonance imaging were studied. The regional cerebral blood flow was measured using the stable xenon computed tomography method. The blood flow was significantly lower in the leukoaraiosis area in the leukoaraiosis group than in the same area in the control group. The cerebrospinal fluid glutamate concentration was significantly higher in the leukoaraiosis group than in the control group. There was a significant negative correlation between the blood flow in the leukoaraiosis area and the cerebrospinal fluid glutamate concentration. The high concentration of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in patients with leukoaraiosis is considered to be related to ischaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 December 1997 Received in revised form: 14 April 1998 Accepted: 26 April 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oishi, M., Mochizuki, Y. Regional cerebral blood flow and cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in leukoaraiosis. J Neurol 245, 777–780 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050286
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050286