Abstract
Background and objectives
Weight gain is associated with imbalance in older people. In contrast, overweightness or mild obesity is less common in patients with chronic dizziness. This paradox may be, at least in part, related to differences in the body composition indices adopted in the previous studies. This study aimed to determine any association between the predicted body composition and chronic dizziness or imbalance of unknown causes.
Methods
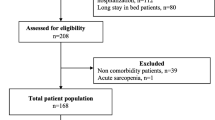
We measured the lean body mass, body fat mass, and appendicular skeletal mass in 9243 people who participated in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019–2021. Sarcopenia was defined according to the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia’s guidelines. Obesity was defined as a body fat percentage of ≥ 25% for men and ≥ 35% for women.
Results
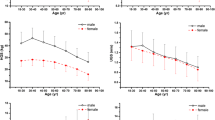
The participants with chronic dizziness had a lower body mass index than those without (p = 0.001). Furthermore, sarcopenia was more common in those with chronic dizziness. In contrast, the degree of obesity was comparable in both groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that sarcopenia was associated with a higher risk of chronic dizziness (odds ratio = 1.6, 95% confidence interval: 1.1–2.5; p = 0.026).
Discussion
Given the association of sarcopenia with chronic dizziness or imbalance, muscle mass may play a role in maintaining balance and stability. Physical exercise could be recommended to increase muscle mass in patients with chronic dizziness/imbalance and sarcopenia. Additional research is required to establish a causal relationship between chronic dizziness and sarcopenia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neuhauser HK (2016) The epidemiology of dizziness and vertigo. Handb Clin Neurol 137:67–82
Kim EJ, Song HJ, Lee HI, Kwon E, Jeong SH (2022) One-year prevalence and clinical characteristics in chronic dizziness: the 2019–2020 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Front Neurol 13:1016718
Neuhauser H, Von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F, Feldmann M, Ziese T, Lempert T (2005) Epidemiology of vestibular vertigo: a neurotologic survey of the general population. Neurology 65:898–904
Hue O, Simoneau M, Marcotte J, Berrigan F, Doré J, Marceau P, Marceau S, Tremblay A, Teasdale N (2007) Body weight is a strong predictor of postural stability. Gait Posture 26:32–38
Bermúdez Rey MC, Clark TK, Merfeld DM (2017) Balance screening of vestibular function in subjects aged 4 years and older: a living laboratory experience. Front Neurol 8:631
Tinetti ME (2003) Preventing falls in elderly persons. N Engl J Med 348:42–49
Fukuoka S, Kurita T, Dohi K, Masuda J, Seko T, Tanigawa T, Saito Y, Kakimoto H, Makino K, Ito M (2019) Untangling the obesity paradox in patients with acute myocardial infarction after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (detail analysis by age). Int J Cardiol 289:12–18
Thomas EL, Frost G, Taylor-Robinson SD, Bell JD (2012) Excess body fat in obese and normal-weight subjects. Nutr Res Rev 25:150–161
Oh K, Kim Y, Kweon S, Kim S, Yun S, Park S, Lee Y-K, Kim Y, Park O, Jeong EK (2021) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol Health 43:e2021025
Lebiedowska A, Hartman-Petrycka M, Blonska-Fajfrowska B (2021) How reliable is BMI? Bioimpedance analysis of body composition in underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese women. Ir J Med Sci 190:993–998
Oh YH, Choi S, Lee G, Son JS, Kim KH, Park SM (2021) Changes in body composition are associated with metabolic changes and the risk of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Med 10:745
Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (2019-2021). guidebook for Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANE). https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/knhanes/sub03/sub03_02_05.do (Korean)
Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. guidebook for conducting the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANE). https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_02_02.do?classType=4 (Korean)
Kim B-Y, Kang SM, Kang J-H, Kang SY, Kim KK, Kim K-B, Kim B, Kim SJ, Kim Y-H, Kim J-H (2021) 2020 Korean Society for the study of obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndrome 30:81
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Adult Alcohol Use Information. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/alcohol/alcohol_glossary.htm. Accessed 30 Jan 2021
Lee J, Lee C, Min J, Kang DW, Kim JY, Yang HI, Park J, Lee MK, Lee MY, Park I, Jae SY, Jekal Y, Jee SH, Jeon JY (2020) Development of the Korean Global Physical Activity Questionnaire: reliability and validity study. Glob Health Promot 27:44–55
World Health Organization (2012) Global physical activity questionnaire (GPAQ) analysis guide. WHO, Geneva
Lee G, Chang J, Hwang S-s, Son JS, Park SM (2020) Development and validation of prediction equations for the assessment of muscle or fat mass using anthropometric measurements, serum creatinine level, and lifestyle factors among Korean adults. Nurs Res Pract 15:95–105
Chen L-K, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung T-W, Chou M-Y, Iijima K, Jang HC, Kang L, Kim M, Kim S (2020) Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc 21(300–307):e302
WE Committee (1995) Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 854:312–344
Dixon JB (2010) The effect of obesity on health outcomes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316:104–108
Pi-Sunyer X (2009) The medical risks of obesity. Postgrad Med 121:21–33
Hruby A, Hu FB (2015) The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. Pharmacoeconomics 33:673–689
Kim AY, Lee JK, Kim SH, Choi J, Song JJ, Chae SW (2020) Is postural dysfunction related to sarcopenia? A population-based study. PLoS One 15:e0232135
McGregor RA, Cameron-Smith D, Poppitt SD (2014) It is not just muscle mass: a review of muscle quality, composition and metabolism during ageing as determinants of muscle function and mobility in later life. Longev Healthspan 3:1–8
Zhang Y, Guo J, Duanmu Y, Zhang C, Zhao W, Wang L, Cheng X, Veronese N, Cafarelli FP, Guglielmi G (2019) Quantitative analysis of modified functional muscle–bone unit and back muscle density in patients with lumbar vertebral fracture in Chinese elderly men: a case–control study. Aging Clin Exp Res 31:637–644
Newman A (2003) Health aging and body composition research group. Strength and muscle quality in a well-functioning cohort of older adults: the health aging and body composition study. JAGS 51:323–330
Yu R, Leung J, Woo J (2014) Incremental predictive value of sarcopenia for incident fracture in an elderly Chinese cohort: results from the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOs) Study. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15:551–558
Woo J, Leung J, Morley JE (2015) Defining sarcopenia in terms of incident adverse outcomes. J Am Med Dir Assoc 16:247–252
Yu R, Leung J, Woo J (2014) Sarcopenia combined with FRAX probabilities improves fracture risk prediction in older Chinese men. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15:918–923
Cho KH, Bok SK, Kim Y-J, Hwang SL (2012) Effect of lower limb strength on falls and balance of the elderly. Ann Rehabil Med 36:386–393
Brech GC, Freitas JSD, Gouvea M, Machado-Lima A, Bastos MF, Takayama L, Pereira R, Rodrigues M, Greve J, D’Andréa M (2021) Dynamic postural balance is mediated by anthropometry and body composition in older women. Acta Ortopéd Bras 29:87–91
Gadelha AB, Neri SGR, Oliveira RJd, Bottaro M, David ACd, Vainshelboim B, Lima RM (2018) Severity of sarcopenia is associated with postural balance and risk of falls in community-dwelling older women. Exp Aging Res 44:258–269
Cohen S, Nathan JA, Goldberg AL (2015) Muscle wasting in disease: molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14:58–74
Kawao N, Morita H, Obata K, Tatsumi K, Kaji H (2018) Role of follistatin in muscle and bone alterations induced by gravity change in mice. J Cell Physiol 233:1191–1201
Kawao N, Takafuji Y, Ishida M, Okumoto K, Morita H, Muratani M, Kaji H (2020) Roles of the vestibular system in obesity and impaired glucose metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS ONE 15:e0228685
Hammam E, Macefield VG (2017) Vestibular modulation of sympathetic nerve activity to muscle and skin in humans. Front Neurol 8:334
Butler AA (2006) The melanocortin system and energy balance. Peptides 27:281–290
Cone RD (2005) Anatomy and regulation of the central melanocortin system. Nat Neurosci 8:571–578
Shang D, Xiong J, Xiang H-B, Hao Y, Liu J-H (2015) Melanocortinergic circuits from medial vestibular nuclei to the kidney defined by transneuronal transport of pseudorabies virus. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:1996
Wang D, He X, Zhao Z, Feng Q, Lin R, Sun Y, Ding T, Xu F, Luo M, Zhan C (2015) Whole-brain mapping of the direct inputs and axonal projections of POMC and AgRP neurons. Front Neuroanat 9:40
Micarelli A, Viziano A, Granito I, Micarelli RX, Felicioni A, Alessandrini M (2021) Changes in body composition in unilateral vestibular hypofunction: relationships between bioelectrical impedance analysis and neuro-otological parameters. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278:2603–2611
Li Z, Tong X, Ma Y, Bao T, Yue J (2022) Prevalence of depression in patients with sarcopenia and correlation between the two diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13:128–144
Funding
This research was supported by Chungnam National University Hospital Research Fund, 2022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors are required to disclose financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.J., Jeong, H.S., Kwon, E. et al. Muscle mass and chronic dizziness: a cross-sectional study of a Korean population. J Neurol 271, 1213–1223 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-023-12014-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-023-12014-4