Abstract
Objective
To estimate whether the risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) exceeds that of the general population.
Methods
We conducted a pooled analysis of cohort studies on COVID-19 in patients with MS published until July 31, 2021. We calculated the pooled crude death rate (CDR) and estimated the indirectly-adjusted age-standardized lethality ratio (SLR) to assess the risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with MS as compared to general population.
Results
Out of 520 articles, 18 fulfilled criteria for pooled analysis, with a total of 5634 patients (28.6% males, mean age 41.8 years). Of them, 111 died, yielding a CDR of 1.97% (95% confidence intervals [CIs] 1.61–2.33). The estimated SLR was 1.24 (95% CIs 1.01–1.48) after indirect age-standardization using case-fatality rates obtained from the detailed surveillance data available at the World Health Organization (WHO) website. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis and the analysis of temporal trends of SLR from March 2020 to July 2021 provided consistent findings.
Conclusions
Our pooled analysis suggests a 24%-increased risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with MS. These findings must be interpreted with caution, mainly because of the difficulties in COVID-19 case detection (especially in the first pandemic wave) and heterogeneity of the analyzed cohorts. Confirmation in larger population-based studies is warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The ongoing global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic [1] has raised concerns about a possible increased risk of death in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) [2]. Data available so far show comparable risk of morbidity [3] and prognosis [4] towards COVID-19 compared to the general population [1]. The lethality rate for COVID-19 among MS patients was estimated at around 3% [5], and in the general population worldwide around 2.4%, with mixed overall rates between countries and different age groups [6].
These two lethality rates are only apparently similar as patients with MS are expected to be younger and mostly females as compared with the general population in which instead age and male are two risk factors for worse COVID-19 outcome [5].
Despite the knowledge gain over the last few months, the risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with MS remains still unclear. Therefore, we conducted a pooled analysis of published cohort studies on COVID-19 in patients with MS to investigate whether their risk of death exceeds that of the general population.
Methods
Study design and registration
Our pooled analysis adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement [7] and the review protocol was registered in the PROSPERO database (Registration Number: CRD42021246205).
Search strategy
To identify studies on COVID-19 in patients with MS, we searched two medical (PubMed and Google Scholar) and one pre-print (MedRxiv) databases, using combinations of MeSH terms for articles published from January, the 1st 2020 until July 31, 2021, as follows: (multiple sclerosis) AND ((COVID-19) OR (coronavirus) OR (SARS-CoV-2)). The free-web tool Rayyan was used for screening and selecting relevant studies (http://www.rayyan.qcri.org).
To develop our literature search strategy, we applied the PI(E)COS framework [8], as follows: participants (P): people with MS; intervention (I): not applicable; exposure (E): COVID-19; control (C): not applicable; outcome (O): death due to COVID-19; study designs or settings (S): observational studies.
We selected only cohort studies, and excluded case series and case reports to minimize selection bias. To avoid the risk of missing relevant articles, we searched for additional papers through the bibliography of included articles and previously published reviews. Conference abstracts and articles written in languages other than English were not considered. To avoid the risk of duplicated data, we checked for authors and/or countries where data were collected. When two or more articles were from the same country, we included multiple studies only on the condition that there was no author overlap and that data were collected in different sites. We excluded studies supported by Pharma Industries.
To assess eligibility, two investigators (LP and SH) independently searched for articles, and agreement between them was required to include an article; disagreement was solved by a third author after reading the whole article (CT).
Data extraction
From each selected article, we extracted data on sample size, country of origin, date of database lock, number of death attributable to COVID-19 and age structure. When not reported, we derived an approximated age structure from the mean and standard deviation age by applying the normal distribution (after checking for normal data distribution).
Data analysis
We first calculated the pooled crude death rate (CDR) from all selected studies [9], and its relative 95% confidence intervals (CI), as follows:
We then estimated the age-standardized lethality ratio (SLR), and its 95% CIs [9], by an indirect standardization method [10], as follows:
To calculate the expected deaths attributable to COVID-19, we fixed as reference the age-specific case-fatality rates (CFRs) of COVID-19 obtained from the detailed surveillance data available on the World Health Organization (WHO) website (https://covid19.who.int). We used time- and country-restricted CFRs, i.e. we restricted the reference data collection to the time frames of the selected articles for each included country. In case of lack of data on a specific country or world region, we ran a free web search to obtain age-specific CFRs of COVID-19 from other sources.
A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was conducted by iteratively removing one article at a time to confirm that our findings were not driven by any single study.
Finally, we also projected the monthly changes of SLR in order to take into account that CFRs changed over time and across countries (mainly depending on differences in the extent of testing or in the contagion trajectory through the outbreak) [6].
Results
Search findings
The flow chart for study selection (according to PRISMA statement) is shown in the Fig. 1.
Our search retrieved 525 articles; after removing duplicates and screening from title and abstract, we assessed 140 full-text articles for eligibility. Of these, 18 articles [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28] met the eligibility criteria. Most of the data were collected during the first pandemic wave, with database lock set in April 2020 [23], May 2020 [14, 18, 22, 24], June 2020 [13, 15, 16, 19, 21], whereas data of the remaining studies were collected until September 2020 [26, 27], October 2020 [11], December 2020 [17, 25], February 2021 [12, 28], April 2021 [20].
Data were collected in different sites in Iran (three articles) [14, 15, 24] and United States (two articles) [18, 23]; two articles included data from different countries of Latin America [11] and North America [25]. The remaining articles were from Austria [17], Brazil [16], Chile [19], Czechia [28], France [22], Italy [27], Netherland [21], Poland [20], Saudi Arabia [12], Spain [13], Turkey [26]. Three articles included also data of 20 patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder that were removed from further analysis [11, 19].
Characteristics of participants
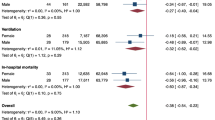
The pooled cohort consisted in 5634 patients. Their mean pooled age was 41.8 years and there were 1590 out of 5568 (28.6%) males (no data on sex ratio was reported in one article including 66 patients [14]). The Table 1 shows the main characteristics of included studies. Out of 5634 patients, 3968 (70.4%) received a COVID-19 diagnosis as confirmed at a positive reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) on nasal and/or pharyngeal swabs, whereas the remaining 1666 (29.6%) were suspected cases on the basis of clinical symptoms and signs.
Selected articles reported 111 deaths in 5634 patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, yielding a CDR of 1.97% (95% CIs 1.61–2.33). Overall, 873 patients required hospitalization, yielding a hospitalization rate of 15.5% (95% CIs 14.6–16.4).
Lethality of COVID-19 in patients with MS
The estimated SLR was 1.24 (95% CIs 1.01–1.48) after indirect standardization using time- and country-restricted data of general population. Most of the reference data were accessible on the detailed surveillance data at the WHO website [11, 13, 16, 17, 19,20,21,22, 26,27,28], whereas age-specific CFRs for Iran and Saudi Arabia were not available; therefore, we used data from Eastern Mediterranean Region as reference information [12, 14, 15, 24]. Reference data for articles conducted in United States [18, 23] and North America [25] were available at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/index.html).
The leave-one-out sensitivity analysis confirmed that this estimate did not change substantially even after iteratively removing one study at a time, thus indicating that the pooled result was not driven by any single study (see Table 2).
The Fig. 2 shows changes over time of the age-standardized SLR using the distribution of case-fatality rates by age; except for the first few months of the COVID-19 pandemic, the estimated SLR was steadily above 1.00, indicating an increased risk of death attributable to COVID-19 in patients with MS as compared to general population.
Standardised lethality ratio over time according to case fatality rates-distribution by age obtained from the detailed surveillance data available on the World Health Organization (WHO) website (https://covid19.who.int); note that a standardized lethality ratio > 1.0 indicates increased risk of death attributable to COVID-19 in patients with MS as compared to general population
Discussion
We explored whether the COVID-19-related risk of death of patients with MS exceeds that of the general population. For this purpose, we pooled available literature data and used indirect age-standardization to allow the comparison of lethality with the general population [10]. We found a 24%-increased risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with MS according to the standard population used as reference. Both the leave-one-out sensitivity analysis and the temporal trends over months in SLR provided consistent findings, except for the first pandemic wave when monitoring and tracking systems for COVID-19 cases were not fully established yet and strategies used for SARS-CoV-2 detection varied hugely across different countries [6].
The overall CFRs of COVID-19 in the general population differ between countries, are sex-dependent (greater risk in men than women) and age-dependent, with an exponential increase above 60 years. For this reason, despite the CDR similar to that of general population, the increased risk of death from COVID-19 observed in MS cohorts after age-standardization is not surprising as patients with MS are on average younger and predominantly women [5].
Other than male sex, older age, presence of comorbidity (shared with the general population) [4, 5], several MS-specific risk factors for a more severe COVID-19 course were suggested, namely worse disability level [13], progressive disease course [13, 15], lymphopenia [13, 28], steroid administration shortly before SARS-COV-2 infection [18, 27], current treatment with anti-CD20 agents [25, 27, 29]. Interestingly, current treatment with interferon beta formulations seems to exert a protective role on the COVID-19 severity [5]. However, other articles did not find any association between specific disease-modifying therapies and COVID-19 severity or lethality [13, 17, 21, 22, 23].
The possible detrimental effect of disease-modifying treatments on COVID-19 severity is a major concern during the pandemic, especially in relation to drug-induced lymphopenia. In this regard, not only anti-CD20 agents (namely ocrelizumab and rituximab), but also alemtuzumab, cladribine, dimethyl fumarate, fingolimod may potentially represent a risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcome. Nevertheless, none of the afore mentioned disease-modifying therapies, with except for anti-CD20 agents, has been associated with increased severity or lethality of COVID-19 until now [5]. Possible, not mutually exclusive, explanations are: (1) the more intense and prolonged B-cell depletion by anti-CD20 agents (as compared with the other immunosuppressant disease-modifying therapies) affecting the mature B‐cell response that is crucial for neutralizing SARS‐COV‐2 [30]; (2) the increased susceptibility to SARS-COV-2 infection in patients treated with anti-CD20 agents [29] that, in turn, may merely rise the chance of fatal outcome [31]; (3) the wider use of anti-CD20 agents in older patients with progressive disease course [13, 25]. However, the reasons why COVID-19 might result in an increased lethality in MS people than in general population deserves further research efforts that go beyond the scope of this study. Owing the mixed results from cohort studies conducted so far, mainly attributable to the small number of patients with fatal outcomes, sharing data initiatives were established to assess the determinants for COVID-19 severity in MS [32].
Our findings must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.
First, our estimations were standardized using data subjected to reporting delays, variation in data transmission and in case definition across different countries over time [6], mainly due to diverse testing strategies or shortage of diagnostic tests, especially during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Second, we pooled data from heterogeneous MS cohorts suffering from both referral bias towards more severe cases (for studies mainly based on suspected or confirmed cases) and the risk of including infections other than COVID-19 (for articles mainly based on suspected cases).
Thirdly, we could not applied an indirect sex- and age-standardized approach, as none article reported the structure by sex and age of the included MS cohorts. In this regard, we cannot exclude an underestimation of the SLR, considering the prevalence of female sex in MS population and the greater lethality of COVID-19 in men.
Notwithstanding these limitations, our findings suggest an increased risk of death from COVID-19 in patients with MS. Confirmation in larger population-based studies and identification of MS-specific risk factors are highly desirable.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (luca.prosperini@gmail.com) upon reasonable request.
References
Fauci AS, Lane HC, Redfield RR et al (2020) COVID-19—navigating the Uncharted. N Engl J Med 382(13):1268–1269
Sormani MP, Italian Study Group on COVID-19 infection in multiple sclerosis (2020) An Italian programme for COVID-19 infection in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 19(6):481–482
Evangelou N, Garjani A, dasNair R, et al (2021) Self-diagnosed COVID-19 in people with multiple sclerosis: a community-based cohort of the UK MS Register. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 92(1):107–109
Bsteh G, Bitschnau C, Hegen H et al (2020) Multiple sclerosis and COVID-19: how many are at risk? Eur J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14555
Barzegar M, Mirmosayyeb O, Gajarzadeh M et al (2021) COVID-19 among patients with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 8(4):e1001
World Health Organization (2021) Situation reports. www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports. Accessed on 31 Jul 2021
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Open Med 3(3):e123–e130
O’Sullivan D, Wilk S, Michalowski W et al (2013) Using PICO to align medical evidence with MDs decision making models. Stud Health Technol Inform 192:1057
Scalfari A, Knappertz V, Cutter G et al (2013) Mortality in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 81(2):184–192
Carson CA, Taylor HR, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P (1994) Age-standardization in epidemiological data. Int J Epidemiol 23(3):643–644
Alonso R, Silva B, Garcea O et al (2021) COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder patients in Latin America. Mult Scler Relat Disord 51:102886
Alshamrani F, Alnajashi H, AlJumah M et al (2021) Registry of patients with multiple sclerosis an COVID-19 infection in Saudi Arabia. Mult Scler Relat Disord 52:103004
Arrambide G, Llaneza-González MÁ, Costa-Frossard França L et al (2021) SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Multiple Sclerosis: Results of the Spanish Neurology Society Registry. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 8:e1024
Barzegar M, Mirmosayyeb O, Ghajarzadeh M et al (2020) Characteristics of COVID-19 disease in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler Relat Disord 45:102276
Bayat M, Fayyazpoor A, Haghighi AB et al (2020) SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with multiple sclerosis: a cross-sectional study. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.17.20214429
Brum DG, Neuroimmunology Brazilian Study Group Focused on COVID-19 and MS et al (2021) Incidence and clinical outcome of Coronavirus disease 2019 in a cohort of 11,560 Brazilian patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458520978354
Bsteh G, Assar H, Hegen H et al (2021) COVID-19 severity and mortality in multiple sclerosis are not associated with immunotherapy: insights from a nation-wide Austrian registry. PLoS ONE 16:e0255316
Chaudhry F, Bulka H, Rathnam AS et al (2020) COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis patients and risk factors for severe infection. J Neurol Sci 418:117147
Ciampi E, Uribe-San-Martín R, Soler B et al (2020) COVID-19 in MS and NMOSD: a multicentric online national survey in Chile. Mult Scler Relat Disord 45:102392
Czarnowska A, Brola W, Zajkowska O et al (2021) Clinical course and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in multiple sclerosis patients treated with disease-modifying therapies—the Polish experience. Neurol Neurochir Pol 55:11
Loonstra FC, Hoitsma E, van Kempen ZL et al (2020) COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis: the Dutch experience. Mult Scler 26:1256–1260
Louapre C, Collongues N, Stankoff B et al (2020) Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 77(9):1079–1088
Parrotta E, Kister I, Charvet L et al (2020) COVID-19 outcomes in MS: observational study of early experience from NYU Multiple Sclerosis Comprehensive Care Center. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 7:e835
Sahraian MA, Azimi A, Navardi S et al (2020) Evaluation of the rate of COVID-19 infection, hospitalization and death among Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 46:102472
Salter A, Fox RJ, Newsome SD et al (2021) Outcomes and Risk Factors Associated With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a North American Registry of Patients With Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 78(6):699–708
Sen S, Karabudak R, Schiavetti I et al (2021) The outcome of a national MS-Covid-19 study: what the Turkish MS cohort reveals? Mult Scler Relat Disord 52:102968
Sormani MP, De Rossi N, Schiavetti I et al (2021) Disease-Modifying Therapies and Coronavirus Disease 2019 Severity in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann Neurol 89:780–789
Stastna D, Menkyova I, Drahota J et al (2021) Multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and COVID-19: a pandemic year in Czechia. Mult Scler Relat Disord 54:103104
Reder AT, Centonze D, Naylor ML et al (2021) COVID-19 in patients with multiple sclerosis: associations with disease-modifying therapies. CNS Drugs 35:317–330
Sokal A, Chappert P, Barba-Spaeth G et al (2021) Maturation and persistence of the anti-SARS-CoV-2 memory B cell response. Cell 184:1201–1213
Centonze D, Rocca MA, Gasperini C et al (2021) Disease-modifying therapies and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in multiple sclerosis: an expert consensus. J Neurol 12:1−8
Peeters LM, Parciak T, Walton C et al (2020) COVID-19 in people with multiple sclerosis: a global data sharing initiative. Mult Scler 26(10):1157–1162
Funding
LP: consulting fees and/or speaker honoraria from Biogen, Celgene, Genzyme, Merck-Serono, Novartis and Teva; travel grants from Biogen, Genzyme, Novartis and Teva; research grants from the Italian MS Society (Associazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla) and Genzyme. CT: honoraria for speaking and travel grants from Biogen, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck Serono, Bayer-Schering, Teva, Genzyme, Almirall and Novartis. SH: travel funding and/or speaker honoraria from Biogen, Roche, Genzyme, Novartis, CSL Behring. SR: personal fees and non-financial support from Biogen, Genzyme, Merck-Serono, Novartis, and Teva. SG: honoraria for speaking and travel grants from Biogen, Sanofi-Aventis, Merck Serono, Bayer-Schering, Teva, Genzyme, Almirall and Novartis. CG: fees as invited speaker or travel expenses for attending meeting from Biogen, Merck-Serono, Teva, Sanofi, Novartis, Genzyme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Nothing to report relevant to the present study.
Ethical statement
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prosperini, L., Tortorella, C., Haggiag, S. et al. Increased risk of death from COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis: a pooled analysis of observational studies. J Neurol 269, 1114–1120 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10803-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10803-3