Abstract
Background
In multiple sclerosis (MS), pronounced neurodegeneration manifests itself as cerebral gray matter (GM) atrophy, which is associated with cognitive and physical impairments. Microstructural changes in GM estimated by diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) may reveal neurodegeneration that is undetectable by conventional structural MRI and thus serve as a more sensitive marker of disease progression.
Objective
The primary objective was to investigate the relationships between morphological and diffusional properties in cerebral GM and physical and cognitive performance in relapsing–remitting MS (RRMS) patients. A secondary objective was to investigate the relationship between GM microstructure and white matter (WM) injury, estimated by the volume of WM lesions.
Methods
Sixty-seven RRMS patients performed the brief repeatable battery of neuropsychological tests (BRB-N), the 6-minute walk test (6MWT), the six spot step test (SSST), and underwent MRI scans using structural and DKI protocols. GM volumetrics and DKI measurements were analyzed in the cortex and deep GM structures using a general linear model with demographics, physical- and cognitive performance as covariates.
Results
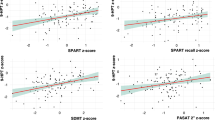
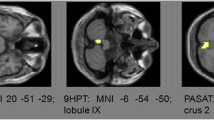
Mean diffusivity (MD) in the cortex was associated with the SSST, 6MWT, information processing, global cognitive performance, and volume of WM lesions. In addition, thalamic volume was associated with SSST (r2 = 0.21, 6MWT (r2 = 0.18), information processing (r2 = 0.21), and WM lesion volume (r2 = 0.60).
Conclusion
Cortical diffusion and thalamic volume are associated with walking and cognitive performance in RRMS patients and are highly affected by the presence of WM lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors will review requests for access to the data that support the findings of this study and access will be granted upon reasonable request.
References
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B et al (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2):292–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22366
Roosendaal SD, Bendfeldt K, Vrenken H et al (2011) Grey matter volume in a large cohort of MS patients: relation to MRI parameters and disability. Mult Scler J 17(9):1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458511404916
Eshaghi A, Prados F, Brownlee WJ et al (2018) Deep gray matter volume loss drives disability worsening in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 83(2):210–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25145
Debernard L, Melzer TR, Alla S et al (2015) Deep grey matter MRI abnormalities and cognitive function in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 234(3):352–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.10.004
Azevedo CJ, Cen SY, Khadka S et al (2018) Thalamic atrophy in multiple sclerosis: a magnetic resonance imaging marker of neurodegeneration throughout disease. Ann Neurol 83(2):223–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25150
Veraart J, Poot DHJ, Van Hecke W et al (2011) More accurate estimation of diffusion tensor parameters using diffusion kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 65(1):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22603
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1432–1440. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20508
Falangola MF, Jensen JH, Babb JS et al (2008) Age-related non-Gaussian diffusion patterns in the prefrontal brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 28(6):1345–1350. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21604
Ng SH, Hsu WC, Wai YY et al (2013) Sex dimorphism of cortical water diffusion in normal aging measured by magnetic resonance imaging. Front Aging Neurosci 5:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2013.00071
Bester M, Jensen JH, Babb JS et al (2015) Non-Gaussian diffusion MRI of gray matter is associated with cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler J 21(7):935–944. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458514556295
De Santis S, Bastiani M, Droby A et al (2018) Characterizing microstructural tissue properties in multiple sclerosis with diffusion MRI at 7 T and 3 T: the impact of the experimental design. Neuroscience 403:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.03.048
Langeskov-Christensen M, Grøndahl Hvid L, Nygaard MKE et al (2020) Efficacy of high-intensity aerobic exercise on brain MRI measures in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000011241
Langeskov-Christensen M, Eskildsen S, Stenager E et al (2018) Aerobic capacity is not associated with most cognitive domains in patients with multiple sclerosis—a cross-sectional investigation. J Clin Med. 7(9):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090272
Rao SM, Cognitive Function Study Group N (1990) A manual for the brief repeatable battery of neuropsychology tests in multiple sclerosis. National Multiple Sclerosis Society, New York
Nieuwenhuis MM, Van Tongeren H, Sørensen PS, Ravnborg M (2006) The Six Spot Step Test: a new measurement for walking ability in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12(4):495–500. https://doi.org/10.1191/1352458506ms1293oa
Goldman MD, Marrie RA, Cohen JA (2008) Evaluation of the six-minute walk in multiple sclerosis subjects and healthy controls. Mult Scler 14(3):383–390. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458507082607
Hansen B, Lund TE, Sangill R, Stubbe E, Finsterbusch J, Jespersen SN (2016) Experimental considerations for fast kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 76(5):1455–1468. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26055
Schmidt P, Gaser C, Arsic M et al (2012) An automated tool for detection of FLAIR-hyperintense white-matter lesions in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 59(4):3774–3783. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUROIMAGE.2011.11.032
Thaler C, Faizy T, Sedlacik J et al (2015) T1-Thresholds in black holes increase clinical-radiological correlation in multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 10(12):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144693
Aubert-Broche B, Fonov VS, García-Lorenzo D et al (2013) A new method for structural volume analysis of longitudinal brain MRI data and its application in studying the growth trajectories of anatomical brain structures in childhood. Neuroimage 82:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.065
Coupe P, Kervrann C, Barillot C, Yger P, Prima S, Hellier P (2008) An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-D magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 27(4):425–441. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2007.906087
Coupé P, Manjón JV, Gedamu E, Arnold D, Robles M, Collins DL (2010) Robust Rician noise estimation for MR images. Med Image Anal 14(4):483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2010.03.001
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998) A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17(1):87–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.668698
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peters TM, Evans AC (1994) Automatic 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18(2):192–205. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004728-199403000-00005
Avants BB, Tustison NJ, Stauffer M, Song G, Wu B, Gee JC (2014) The insight ToolKit image registration framework. Front Neuroinform 8:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2014.00044
Fonov VS, Manjón JV, Collins DL, Coupé P, Eskildsen SF (2011) Simultaneous segmentation and grading of anatomical structures for patient’s classification: application to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 59(4):3736–3747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.080
Coupé P, Manjón JV, Fonov V, Pruessner J, Robles M, Collins DL (2011) Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. Neuroimage 54(2):940–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUROIMAGE.2010.09.018
Eskildsen SF, Uldahl M, Ostergaard LR (2005) Extraction of the cerebral cortical boundaries from MRI for measurement of cortical thickness. In: Fitzpatrick JM, Reinhardt JM (eds) Proceedings of SPIE, vol 5747. Medical Imaging, San Diego, p 1400. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.595145
Eskildsen SF, Ostergaard LR (2006) Active surface approach for extraction of the human cerebral cortex from MRI. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 9(11):823–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/11866763
Veraart J, Novikov DS, Christiaens D, Ades-Aron B, Sijbers J, Fieremans E (2016) Denoising of diffusion MRI using random matrix theory. Neuroimage 142:394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.016
Kellner E, Dhital B, Kiselev VG, Reisert M (2016) Gibbs-ringing artifact removal based on local subvoxel-shifts. Magn Reson Med 76(5):1574–1581. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26054
Andersson JLR, Sotiropoulos SN (2016) An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 125:1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.019
Eskildsen SF, Østergaard LR (2008) Evaluation of five algorithms for mapping brain cortical surfaces. In: Proceedings—21st Brazilian symposium on computer graphics and image processing, SIBGRAPI 2008. IEEE, pp 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1109/SIBGRAPI.2008.16
Boringa JB, Lazeron RHC, Reuling IEW et al (2001) The brief repeatable battery of neuropsychological tests: normative values allow application in multiple sclerosis clinical practice. Mult Scler 7(4):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1191/135245801680209385
Sepulcre J, Vannotti S, Hernández R et al (2006) Cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis using the Brief Repeatable Battery-Neuropsychology test. Mult Scler 12(2):187–195. https://doi.org/10.1191/1352458506ms1258oa
Worsley K, Duerden E, Evans A et al (2009) SurfStat: a Matlab toolbox for the statistical analysis of univariate and multivariate surface and volumetric data using linear mixed effects models and random field theory. Neuroimage 47:S102. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(09)70882-1
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Found Stat Comput 1:409. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74686-7
Worsley KJ, Marrett S, Neelin P, Vandal AC, Friston KJ, Evans AC (1996) A unified statistical approach for determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Hum Brain Mapp 4(1):58–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1996)4:1%3c58::AID-HBM4%3e3.0.CO;2-O
Benjamini Y, Heller R (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29(4):1165–1188
Filippi M, Cercignani M, Inglese M, Horsfield MA, Comi G (2001) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 56(3):304–311. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.56.3.304
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G et al (2003) Assessment of normal-appearing white and gray matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 59(9):1406–1412. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.59.9.1406
Cercignani M, Inglese M, Pagani E, Comi G, Filippi M (2001) Mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy histograms of patients with multiple sclerosis. Am J Neuroradiol 22(5):952–958. papers3://publication/uuid/4F01DD03-295B-4F8E-B32E-27327AB8CFA5. Accessed 10 Apr 2019
Hannoun S, Durand-Dubief F, Confavreux C et al (2012) Diffusion tensor-MRI evidence for extra-axonal neuronal degeneration in caudate and thalamic nuclei of patients with multiple sclerosis. Am J Neuroradiol 33(7):1363–1368. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2983
Funding
This study was funded by Jascha Fonden, Fonden for Neurologisk Forskning, The Danish Multiple Sclerosis Society, Aase og Ejnar Danielsens Fond, Knud og Edith Eriksens Fond, Augustinus Foundation, Direktør Emil C. Hertz og Hustru Inger Hertz’s Fond, Else og Mogens Wedell-Wedellsborgs Fond, Karen A. Tolstrups Fond, and the Faculty of Health, Aarhus University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
UD has received research support, travel grants, and/or teaching honorary from Biogen Idec, Merck Serono, Novartis, Bayer Schering, and Sanofi Aventis as well as honoraria from serving on scientific advisory boards of Biogen Idec and Genzyme.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nygaard, M.K.E., Langeskov-Christensen, M., Dalgas, U. et al. Cortical diffusion kurtosis imaging and thalamic volume are associated with cognitive and walking performance in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 268, 3861–3870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10543-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10543-4