Abstract
Background
Malignant gliomas (MG) are aggressive brain tumours in adults. The standard of care is concurrent radiation plus temozolomide (TMZ) [chemo-radiotherapy (CRT)] followed by TMZ maintenance up to 6 months. TMZ is considered to have a low toxicity profile, but several studies reported occurrence of severe myelosuppression, especially during the concomitant phase. Toxicity may be prolonged, thus treatment should be discontinued.
Purpose
To evaluate the risk of recurrente myelotoxicity during adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) in patients who recovered from severe myelotoxicity during CRT.
Methods
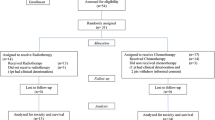
We retrospectively collected data on patients with MG who developed and recovered from severe myelotoxicity during CRT from eight Italian neuro-oncology centers.
Results
We included 87 patients. Histology was Glioblastoma (GBM) in 78 patients (89.7%); 60% of patients were female. After myelotoxicity recovery, 54 (62%) received treatment. The majority of them (82%, n = 44) received adjuvant TMZ and 18% (n = 10) others treatments. Out of 44 patients who received adjuvant TMZ, 34% experienced the re-occurrence of grade 3–4 myelotoxicity which required permanent CT discontinuation in 6 (13%) cases. Patients who received TMZ or other treatments had longer overall (OS) (adjusted HR 0.46, p = 0.008) and progression free survival (PFS) (adjusted HR 0.57, p = 0.034) than those who remained untreated.
Conclusion
Our study suggests that after severe myelotoxicity the majority of patients received treatment, particularly with TMZ. Only a fraction of patients experienced toxicity recurrence, suggesting that TMZ is well tolerated and had an impact on PFS and OS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, [V.V.]. The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Dixit S, Baker L, Walmsley V, Hingorani M (2012) Temozolomide-related idiosyncratic and other uncommon toxicities: a systematic review. Anticancer Drugs 23(10):1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e328356f5b0
Gerber DE, Grossman SA, Zeltzman M, Parisi MA, Kleinberg L (2007) The impact of thrombocytopenia from temozolomide and radiation in newly diagnosed adults with high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol 9(1):47–52. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2006-024 (Epub 2006 Nov 15)
Lombardi G, Caccese M, Bellu L, Pambuku A, Bergo E, Berti F, Gardiman MP, Della Puppa A, Denaro L, Dal Pos S, Zagonel V (2018) Good tolerability of maintenance temozolomide in glioblastoma patients after severe hematological toxicity during concomitant radiotherapy and temozolomide treatment: report of two cases. Anticancer Drugs 29(9):924–928. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000678 (PMID: 30080691)
Lombardi G, Rumiato E, Bertorelle R, Saggioro D, Farina P, Della Puppa A, Zustovich F, Berti F, Sacchetto V, Marcato R, Amadori A, Zagonel V (2015) Clinical and genetic factors associated with severe hematological toxicity in glioblastoma patients during radiation plus temozolomide treatment: a prospective study. Am J Clin Oncol 38(5):514–519. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e3182a790ea
Robins HI, Eickhoff J, Gilbert MR, Armstrong TS, Shi W, De Groot JF, Schultz CJ, Hunter GK, Valeinis E, Roach M, Youssef EF, Souhami L, Howard SP, Lieberman FS, Herman JG, Zhang P, Mehta MP (2019) The association between BMI and BSA-temozolomide-induced myelosuppression toxicities: a correlative analysis of NRG oncology RTOG 0525. Neurooncol Pract. 6(6):473–478. https://doi.org/10.1093/nop/npz006
Arulananda S, Lynam J, Sem Liew M, Wada M, Cher L, Gan HK (2018) Clinical correlates of severe thrombocytopenia from temozolomide in glioblastoma patients. Intern Med J 48(10):1206–1214. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.14000
Armstrong TS, Cao Y, Scheurer ME et al (2009) Risk analysis of severe myelotoxicity with temozolomide: the effects of clinical and genetic factors. Neurooncology 11:825–832
Yin AA, He YL, Etcheverry A et al (2019) Novel predictive epigenetic signature for temozolomide in non-G-CIMP glioblastomas. Clin Epigenetic 11(1):76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0670-9
Altinoz MA, Elmaci I, Bolukbasi FH, Ekmekci CG, Yenmis G, Sari R, Sav A (2017) A MGMT gene variants, temozolomide myelotoxicity and glioma risk. A concise literature survey including an illustrative case. J Chemother 29(4):238–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/1120009X.2017.1312752 (PMID: 28436299)
Becker-Schiebe ME, Wetzel M, Wetzel F, Christansen H, Hoffmann W (2015) Hematologic toxicity of temozolomide and radiation in glioblastoma patients—correlation with clinicopathological factors. Clin Med J1:63–69
Gupta T, Mohanty S, Moiyadi A, Jalali R (2013) Factors predicting temozolomide induced clinically significant acute hematologic toxicity in patients with high-grade gliomas: a clinical audit. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(9):1814–1819
Sabharwal A, Waters R, Danson S, Clamp A, Lorigan P, Thatcher N, Margison GP, Middleton MR (2011) Predicting the myelotoxicity of chemotherapy: the use of pretreatment O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase determination in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Melanoma Res 21(6):502–508. https://doi.org/10.1097/CMR.0b013e32832ccd58
Villano JL, Letarte N, Yu JM, Abdur S, Bressler LR (2012) Hematologic adverse events associated with temozolomide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69(1):107–113
Tinchon A, Oberndorfer S, Marosi C, Gleiss A, Geroldinger A, Sax C, Sherif C, Moser W, Grisold W (2015) Haematological toxicity of Valproic acid compared to Levetiracetam in patients with glioblastoma multiforme undergoing concomitant radio-chemotherapy: a retrospective cohort study. J Neurol 262(1):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7552-z (PMID: 25359262)
Handoko KB, Souverein PC, van Staa TP et al (2006) Risk of aplastic anemia in patients using antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 47:1232–1236
Ronning PA, Helseth E, Meling TR, Johannesen TB (2012) A population-based study on the effect of temozolomide in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol 14:1178–1184
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V, Jaques D, Budach V, Langer C, Murphy B, Cumberlin R, Coleman CN, Rubin P (2003) CTCAE v30: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13(3):176–181
Niewald M, Berdel C, Fleckenstein J, Licht N, Ketter R, Rube C (2011) Toxicity after radiochemotherapy for glioblastoma using temozolomide—a retrospective evaluation. Radiat Oncol 6:141
Lin AJ, Campian JL, Hui C, Rudra S, Rao YJ, Thotala D, Hallahan D, Huang J (2018) Impact of concurrent versus adjuvant chemotherapy on the severity and duration of lymphopenia in glioma patients treated with radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 136(2):403–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2668-5 (PMID: 29143923)
Williams M, Liu ZW, Woolf D, Hargreaves S, Michalarea V, Menashy R, Kooner I, Wilson E (2012) Change in platelet levels during radiotherapy with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide for the treatment of glioblastoma: a novel prognostic factor for survival. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138(10):1683–1688
Vaios EJ, Nahed BV, Muzikansky A, Fathi AT, Dietrich J (2016) Bone marrow response as a potential biomarker of outcomes in glioblastoma patients. J Neurosurg 14:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.7.JNS16609
Ho KG, Uhlmann EN, Wong ET, Uhlmann EJ (2020) Leukopenia is a biomarker for effective temozolomide dosing and predicts overall survival of patients with glioblastoma Mol. Clin Oncol 13(6):80. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2020.2150
Fontanilles M, Marguet F, Alexandru C, Langlois O, Veresezan O, Gilard V, David M, Laquerriere A, Hanzen C, Tennevet I, Di Fiore F, Clatot F (2019) Early platelet variation during concomitant chemo-radiotherapy predicts adjuvant temozolomide-induced thrombocytopenia in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Support Care Cancer 27(2):477–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4336-5 (PMID: 29978325)
Coffelt SB, Wellenstein MD, de Visser KE (2016) Neutrophils in cancer: neutral no more. Nat Rev Cancer 16(7):431–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.52
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21:309–322
Bowman RL, Klemm F, Akkari L, Pyonteck SM, Sevenich L, Quail DF, Dhara S, Simpson K, Gardner EE, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Brennan CW, Tabar V, Gutin PH, Joyce JA (2016) Macrophage Ontogeny Underlies Differences in Tumor-Specific Education in Brain Malignancies. Cell Rep. 17(9):2445–2459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.052
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of study: VV, AP. Acquisition data: AP, AF, GL, RR, PG, SR, LG, CS, EP, GS, GT. Data analysis: LP. Interpretation: AE, VV, AP. Drafting: VV, LP. Revising: AE, AP. Final approval: VV, AP. All authors read and approved submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Informed consent, in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villani, V., Anghileri, E., Prosperini, L. et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy after severe myelotoxicity during chemoradiation phase in malignant gliomas. Is it feasibile? Results from AINO study (Italian Association for Neuro-Oncology). J Neurol 268, 2866–2875 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10438-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10438-4