Abstract
Background and objective
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used for treating dystonia, commonly targeting the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optimal stimulation parameters are required to achieve satisfying results. However, recommended parameters for STN-DBS remain to be identified. In this review, we aimed to assess the optimal stimulation parameters by analyzing previously published STN-DBS data of patients with dystonia.
Methods
We examined the STN-DBS stimulation parameters used in studies on dystonia selected on the PubMed/Medline database.
Results
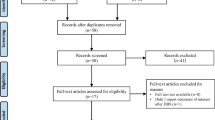
Of the 86 publications retrieved from the PubMed/Medline database, we included 24, which consisted of data from 94 patients and 160 electrodes. Overall, the following average stimulation parameters were observed: amplitude, 2.59 ± 0.67 V; pulse width, 83.87 ± 34.70 μs; frequency, 142.08 ± 37.81 Hz. The average improvement rate was 64.72 ± 24.74%. The improvement rate and stimulation parameters were linearly dependent. The average improvement rate increased by 3.58% at each 10-Hz increase in frequency. In focal and segmental dystonia, the improvement rate and stimulation parameters were linearly dependent. The improvement rate increased by 6.06% and decreased by 2.14% at each 10-Hz increase in frequency and pulse width, respectively. Seventeen publications (83 patients) mentioned stimulation-related adverse effects, including dyskinesia (17), depression (8), transient dysarthria (5), weight gain (4), transient dysphasia (3), transient paresthesia (2), and sustained hyperkinesia (2).
Conclusions
The optimal stimulation parameter for STN-DBS varies across patients. Our findings may be useful for DBS programming based on the specific dystonia subtypes, especially for patients with focal and segmental dystonia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steeves TD, Day L, Dykeman J, Jette N, Pringsheim T (2012) The prevalence of primary dystonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 27(14):1789–1796. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25244
Albanese A, Bhatia K, Bressman SB, Delong MR, Fahn S, Fung VS, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Jinnah HA, Klein C, Lang AE, Mink JW, Teller JK (2013) Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov Disord 28(7):863–873. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25475
Neychev VK, Gross RE, Lehéricy S, Hess EJ, Jinnah HA (2011) The functional neuroanatomy of dystonia. Neurobiol Dis 42(2):185–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.026
Balint B, Bhatia KP (2014) Dystonia: an update on phenomenology, classification, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Opin Neurol 27(4):468–476. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0000000000000114
Malek N (2019) Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurol India 67(4):968–978. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.266268
Cury RG, Kalia SK, Shah BB, Jimenez-Shahed J, Prashanth LK, Moro E (2018) Surgical treatment of dystonia. Expert Rev Neurother 18(6):477–492. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1478288
Elble RJ, Shih L, Cozzens JW (2018) Surgical treatments for essential tremor. Expert Rev Neurother 18(4):303–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1445526
Vidailhet M, Vercueil L, Houeto JL, Krystkowiak P, Benabid AL, Cornu P, Lagrange C, Tézenas du Montcel S, Dormont D, Grand S, Blond S, Detante O, Pillon B, Ardouin C, Agid Y, Destée A, Pollak P (2005) Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N Engl J Med 352(5):459–467. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa042187
Lin S, Wu Y, Li H, Zhang C, Wang T, Pan Y, He L, Shen R, Deng Z, Sun B, Ding J, Li D (2019) Deep brain stimulation of the globus pallidus internus versus the subthalamic nucleus in isolated dystonia. J Neurosurg 132(3):721. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.12.Jns181927
Bagatti D, D’Ammando A, Franzini A, Messina G (2019) Deep brain stimulation of the caudal zona incerta and motor thalamus for postischemic dystonic tremor of the left upper limb: case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 125:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.183
Horisawa S, Arai T, Suzuki N, Kawamata T, Taira T (2019) The striking effects of deep cerebellar stimulation on generalized fixed dystonia: case report. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.11.Jns182180
Guridi J, Rodriguez-Rojas R, Carmona-Abellán M, Parras O, Becerra V, Lanciego JL (2018) History and future challenges of the subthalamic nucleus as surgical target: Review article. Mov Disord 33(10):1540–1550. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.92
Deng Z, Pan Y, Zhang C, Zhang J, Qiu X, Zhan S, Li D, Sun B (2018) Subthalamic deep brain stimulation in patients with primary dystonia: A ten-year follow-up study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 55:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.05.024
Deng ZD, Li DY, Zhang CC, Pan YX, Zhang J, Jin H, Zeljec K, Zhan SK, Sun BM (2017) Long-term follow-up of bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation for refractory tardive dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 41:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.05.010
Tormenti MJ, Tomycz ND, Coffman KA, Kondziolka D, Crammond DJ, Tyler-Kabara EC (2011) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for dopa-responsive dystonia in a 6-year-old child. J Neurosurg Pediatr 7(6):650–653. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.3.Peds10402
Schjerling L, Hjermind LE, Jespersen B, Madsen FF, Brennum J, Jensen SR, Løkkegaard A, Karlsborg M (2013) A randomized double-blind crossover trial comparing subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation for dystonia. J Neurosurg 119(6):1537–1545. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.8.Jns13844
Kim JB, Shirley M, Albert L, Ahmed MR (2013) Accuracy of deep brain stimulation electrode placement using intraoperative computed tomography without microelectrode recording. J Neurosurg 119(2):301–306. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.4.JNS122324
Yianni J, Nandi D, Shad A, Bain P, Gregory R, Aziz T (2004) Increased risk of lead fracture and migration in dystonia compared with other movement disorders following deep brain stimulation. J Clin Neurosci 11(3):243–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2003.10.003
Rolston JD, Englot DJ, Starr PA, Larson PS (2016) An unexpectedly high rate of revisions and removals in deep brain stimulation surgery: analysis of multiple databases. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 33:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.09.014
Moro E, Poon Y-YW, Lozano AM, Saint-Cyr JA, Lang AE (2006) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation: improvements in outcome with reprogramming. Arch Neurol 63(9):1266–1272. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.63.9.1266
Magown P, Andrade RA, Soroceanu A, Kiss ZHT (2018) Deep brain stimulation parameters for dystonia: a systematic review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 54:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.04.017
Dayal V, Limousin P, Foltynie T (2017) Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: the effect of varying stimulation parameters. J Parkinsons Dis 7(2):235–245. https://doi.org/10.3233/jpd-171077
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 81870887).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YW, CZ and YW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, C., Sun, B. et al. Parameters for subthalamic deep brain stimulation in patients with dystonia: a systematic review. J Neurol 269, 197–204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-10372-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-10372-x