Abstract
Background
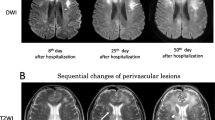
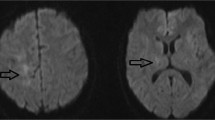
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a subacute onset demyelinating disease caused by JC virus and characterized by multifocal involvement of the subcortical white matter and cerebellar hemispheres or peduncles on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, non-HIV PML patients with brain lesions limited to the cerebellum and brainstem have not been well characterized.
Methods
We report a 68-year-old man with systemic lupus erythematosus under treatment with immunosuppressants who developed non-HIV PML with brain lesions limited to the cerebellum and brainstem and successfully treated with a combination of mefloquine and mirtazapine. We performed a literature review to characterize patients with non-HIV PML with brain lesions limited to the cerebellum and brainstem.
Results
Eight cases with non-HIV brainstem/cerebellar form PML were identified including our case. All cases had compromised status related underlying diseases. Four (50%) had a good prognosis. Five cases were treated, including 3 with favourable outcomes. Between the good prognosis group (n = 4) and the poor prognosis group (n = 4), treatment status for PML and the interval between the initial manifestation and diagnosis did not differ. Among those who performed contrast-enhanced brain imaging, lesion enhancement was related to good prognosis (good prognosis group vs. poor prognosis group; 100% vs. 0%).
Conclusion
PML should be considered in the differential diagnosis of brain lesions limited to the cerebellum and brainstem in immunocompromised patients. The presence of immune response against JC virus and inflammatory reactions may indicate good prognosis in non-HIV brainstem/cerebellar form PML



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagawa Y, Ueno A, Ikeda J, Ishii W, Shishido-Hara Y, Sekijima Y (2018) Two patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with immune response against JC virus showing good long-term outcome by combination therapy of mefloquine, mirtazapine, and risperidone. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 58:324–331
Antinori A, Cingolani A, Lorenzini P, Giancola ML, Uccella I, Bossolasco S, Grisetti S, Moretti F, Vigo B, Bongiovanni M, Del Grosso B, Arcidiacono MI, Fibbia GC, Mena M, Finazzi MG, Guaraldi G, Ammassari A, d'Arminio Monforte A, Cinque P, De Luca A, Italian Registry Investigative Neuro ASG (2003) Clinical epidemiology and survival of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy: data from the Italian Registry Investigative Neuro AIDS (IRINA). J Neurovirol 9(Suppl 1):47–53
Anttila SA, Leinonen EV (2001) A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev 7:249–264
Aotsuka Y, Uzawa A, Nishimura K, Kojima K, Yamaguchi M, Makino T, Nakamichi K, Saijo M, Kuwabara S (2016) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy localized in the cerebellum and brainstem associated with idiopathic CD4(+) T lymphocytopenia. Intern Med 55:1645–1647
Arai Y, Tsutsui Y, Nagashima K, Shinmura Y, Kosugi T, Wakai M, Nishikage H, Yamamoto J (2002) Autopsy case of the cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy without immunodeficiency. Neuropathology 22:48–56
Barraud de Lagerie S, Comets E, Gautrand C, Fernandez C, Auchere D, Singlas E, Mentre F, Gimenez F (2004) Cerebral uptake of mefloquine enantiomers with and without the P-gp inhibitor elacridar (GF1210918) in mice. Br J Pharmacol 141:1214–1222
Beppu M, Kawamoto M, Nukuzuma S, Kohara N (2012) Mefloquine improved progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Intern Med 51:1245–1247
Berger JR, Aksamit AJ, Clifford DB, Davis L, Koralnik IJ, Sejvar JJ, Bartt R, Major EO, Nath A (2013) PML diagnostic criteria: consensus statement from the AAN neuroinfectious disease section. Neurology 80:1430–1438
Berger JR, Levy RM, Flomenhoft D, Dobbs M (1998) Predictive factors for prolonged survival in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 44:341–349
Bernal-Cano F, Joseph JT, Koralnik IJ (2007) Spinal cord lesions of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patient. J Neurovirol 13:474–476
Bossolasco S, Calori G, Moretti F, Boschini A, Bertelli D, Mena M, Gerevini S, Bestetti A, Pedale R, Sala S, Sala S, Lazzarin A, Cinque P (2005) Prognostic significance of JC virus DNA levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Infect Dis 40:738–744
Brew BJ, Davies NW, Cinque P, Clifford DB, Nath A (2010) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and other forms of JC virus disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:667–679
Brooks BR, Walker DL (1984) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin 2:299–313
Du Pasquier RA, Koralnik IJ (2003) Inflammatory reaction in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: harmful or beneficial? J Neurovirol 9(Suppl 1):25–31
Hirayama M, Nosaki Y, Matsui K, Terao S, Kuwayama M, Tateyama H, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y (2012) Efficacy of mefloquine to progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy initially presented with parkinsonism. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114:728–731
Irie T, Kasai M, Abe N, Seto K, Naohara T, Kawamura K, Higa T, Sano K, Takahashi H, Nagashima K (1992) Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient with chronic renal failure. Intern Med 31:218–223
Ito D, Yasui K, Hasegawa Y, Nakamichi K, Katsuno M, Takahashi A (2016) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions confirmed by repeated CSF-JC virus tests and coexistence of JC virus granule cell neuronopathy. Report of a case. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 56:481–485
Kishida S, Tanaka K (2010) Mefloquine treatment in a patient suffering from progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after umbilical cord blood transplant. Intern Med 49:2509–2513
Kobayashi Z, Akaza M, Numasawa Y, Ishihara S, Tomimitsu H, Nakamichi K, Saijo M, Morio T, Shimizu N, Sanjo N, Shintani S, Mizusawa H (2013) Failure of mefloquine therapy in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: report of two Japanese patients without human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Neurol Sci 324:190–194
Marzocchetti A, Tompkins T, Clifford DB, Gandhi RT, Kesari S, Berger JR, Simpson DM, Prosperi M, De Luca A, Koralnik IJ (2009) Determinants of survival in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology 73:1551–1558
Moenster RP, Jett RA (2012) Mirtazapine and mefloquine therapy for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Am J Health Syst Pharm 69:496–498
Morales H, Tomsick T (2015) Middle cerebellar peduncles: Magnetic resonance imaging and pathophysiologic correlate. World J Radiol 7:438–447
Morimoto A, Ueno H, Fujii H, Nakamura T, Nakamichi K, Saijo M, Yukitake M, Matsumoto M (2013) Ineffective mefloquine therapy in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy complicated with malignant lymphoma: finding and usefulness of susceptibility-weighted imaging. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 53:843–847
Nakamichi K, Mizusawa H, Yamada M, Kishida S, Miura Y, Shimokawa T, Takasaki T, Lim CK, Kurane I, Saijo M (2012) Characteristics of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy clarified through internet-assisted laboratory surveillance in Japan. BMC Neurol 12:121
Nishigori R, Warabi Y, Shishido-Hara Y, Nakamichi K, Nakata Y, Komori T, Isozaki E (2019) Inflammatory cerebellar PML with a CD4/CD8 ratio of 2.9 showed a favorable prognosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Intern Med. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.3038-19
Ohnuki E, Asayama S, Asayama T, Nakamichi K, Saijo M, Kosaka S (2016) A case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with chronic renal failure, whose JC virus in cerebrospinal fluid disappeared after mefloquine-mirtazapine dual therapy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 56:705–708
Parr J, Horoupian DS, Winkelman AC (1979) Cerebellar form of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). Can J Neurol Sci 6:123–128
Phan-Ba R, Lommers E, Tshibanda L, Calay P, Dubois B, Moonen G, Clifford D, Belachew S (2012) MRI preclinical detection and asymptomatic course of a progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy (PML) under natalizumab therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:224–226
Rocha AJ, Littig IA, Nunes RH, Tilbery CP (2013) Central nervous system infectious diseases mimicking multiple sclerosis: recognizing distinguishable features using MRI. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 71:738–746
Rueger MA, Miletic H, Dorries K, Wyen C, Eggers C, Deckert M, Faetkenheuer G, Jacobs AH (2006) Long-term remission in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy caused by idiopathic CD4+ T lymphocytopenia: a case report. Clin Infect Dis 42:e53–56
Sahraian MA, Radue EW, Eshaghi A, Besliu S, Minagar A (2012) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a review of the neuroimaging features and differential diagnosis. Eur J Neurol 19:1060–1069
Shah R, Bag AK, Chapman PR, Cure JK (2010) Imaging manifestations of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Radiol 65:431–439
Shishido-Hara Y (2010) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies: a review of clinical, neuropathological, and virological aspects of JC virus-induced demyelinating disease. Acta Neuropathol 120:403–417
Shishido-Hara Y, Higuchi K, Ohara S, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ, Uchihara T (2008) Promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies provide a scaffold for human polyomavirus JC replication and are disrupted after development of viral inclusions in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 67:299–308
Tan CS, Koralnik IJ (2010) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and other disorders caused by JC virus: clinical features and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol 9:425–437
Tan IL, McArthur JC, Clifford DB, Major EO, Nath A (2011) Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in natalizumab-associated PML. Neurology 77:1061–1067
Uchino A, Sawada A, Takase Y, Kudo S (2004) Symmetrical lesions of the middle cerebellar peduncle: MR imaging and differential diagnosis. Magn Reson Med Sci 3:133–140
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient for his participation in this study. We wish to thank Dr. Nobuaki Funata, Department of Pathology, Tokyo Metropolitan Cancer and Infectious Diseases Center, Komagome Hospital for his help with pathological diagnosis.
Funding
This work was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for the Research Committee of Prion Disease and Slow Virus Infection, Research on Policy Planning and Evaluation for Rare and Intractable Diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (Grant Number H29-Nanchitou (Nan)-Ippan-036) and by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 17K09768).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript and contributed to the design of the study and interpretation of data. MH, KS and HF drafted the manuscript. MH, TU, HM, SA, SK, Y S–H, KN and MS contributed to the diagnosis and treatment of the patient. TU, Y S–H, TN and KH revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamaguchi, M., Suzuki, K., Fujita, H. et al. Successful treatment of non-HIV progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: case report and literature review. J Neurol 267, 731–738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09629-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09629-x