Abstract
Objective
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a rare autosomal recessive disease characterised by high plasma phenylalanine levels inducing, if untreated, serious neurological manifestations in children but also, rarely, in adults who stopped their diet. The objective of the study was to describe the neurological manifestations observed in adults with PKU.
Methods
We analysed cases reported in French reference centres for inborn errors of metabolism and cases already reported in the literature.
Results
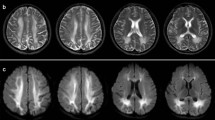
We report 8 new cases of neurological manifestations and 22 cases in the literature, which occurred in adult PKU patients, associated with chronic or rapid increase of phenylalanine levels, mostly when strict low-phenylalanine diet was stopped early in life. Neurological symptoms consisted in cerebellar ataxia, tremor, brisk reflexes, visual loss, sensory manifestations, and/or headaches. Visual loss was more frequent in the new cases (4/8) of the present series than in the literature (4/22). These neurological complications were associated with leucopathy on brain magnetic resonance imaging (27/29). The start of a low-phenylalanine diet improved or fully reversed neurological manifestations, even in patients with late diagnosis during adulthood.
Conclusion
Neurological manifestations can complicate PKU in adult patients with elevated phenylalanine levels, after long or short period of diet discontinuation. Neurologists should be aware of this diagnosis, and measure phenylalaninemia in case of neurological symptoms associated with non-specific leucopathy on brain MRI. PKU patients should be systematically encouraged to continue their diet and their medical follow-up to avoid neurological complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blau N, van Spronsen FJ, Levy HL (2010) Phenylketonuria. Lancet 376(9750):1417–1427
Scriver CR, Kaufman S, Eisensmith E, Woo SLC (1995) The hyperphenylalaninemias. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, vol 1. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1015–1075
Recommendations on the dietary management of phenylketonuria (1993) Report of Medical Research Council Working Party on Phenylketonuria. Arch Dis Child 68(3):426–427
van Spronsen FJ, van Wegberg AM, Ahring K, Bélanger-Quintana A, Blau N, Bosch AM et al (2017) Key European guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with phenylketonuria. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 8587:1–14
Thompson AJ, Youl BD, Kendall B, Lees AJ, Smith I, Brenton D et al (1990) Neurological deterioration in young adults with phenylketonuria. Lancet 336:602–605
Wood B (1976) Neurological disturbance in a phenylketonic child after discontinuation of dietary treatment. Dev Med Child Neurol 18:657–666
Villasana D, Butler IJ, Williams JC, Roongta SM (1989) Neurological deterioration in adult phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 12:451–457
McCombe PA, McLaughlin DB, Chalk JB, Brown NN, McGill JJ, Pender MP (1992) Spasticity and white matter abnormalities in adult phenylketonuria. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:359–361
Rubin SL, Piffer AL, Rougier MB, Delyfer MN, Korobelnik JF, Redonnet-Vernhet I et al (2013) Sight-threatening phenylketonuric encephalopathy in a young adult, reversed by diet. JIMD Rep 10:83–85
Daelman L, Sedel F, Tourbah A (2014) Progressive neuropsychiatric manifestations of phenylketonuria in adulthood. Rev Neurol (Paris) 170:280–287
Seki M, Takizawa T, Suzuki S, Shimizu T, Shibata H, Ishii T et al (2015) Adult phenylketonuria presenting with subacute severe neurologic symptoms. J Clin Neurosci 22:1361–1363
Tufekcioglu Z, Cakar A, Bilgic B, Hanagasi H, Gurvit H, Emre M (2016) Adult-onset phenylketonuria with rapidly progressive dementia and parkinsonism. Neurocase 22:273–275
Weglage J, Oberwittler C, Marquardt T, Schellscheidt J, Teeffelen-Heithoff A, Koch G et al (2000) Neurological deterioration in adult phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 23:83–84
Kasim S, Moo LR, Zschocke J, Jinnah HA (2001) Phenylketonuria presenting in adulthood as progressive spastic paraparesis with dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 71:795–797
Camdessanche JP, Jousserand G, Antoine JC (2010) Musty odour, mental retardation, and spastic paraplegia revealing phenylketonuria in adulthood. J Neurol 257:302–304
Rosini F, Rufa A, Monti L, Tirelli L, Federico A (2014) Adult-onset phenylketonuria revealed by acute reversible dementia, prosopagnosia and parkinsonism. J Neurol 261:2446–2448
Ishimaru K, Tamasawa N, Baba M, Matsunaga M, Takebe K (1993) Phenylketonuria with adult-onset neurological manifestation. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 33:961–5 (abstract)
Anwar MS, Waddell B, O'Riordan J (2013). Neurological improvement following reinstitution of a low phenylalanine diet after 20 years in established phenylketonuria. BMJ Case Rep
Evans AH, Costa DC, Gacinovic S, Katzenschlager R, O'sullivan JD, Heales S et al (2004) L-Dopa-responsive Parkinson's syndrome in association with phenylketonuria: In vivo dopamine transporter and D2 receptor findings. Mov Disord 19:1232–6
Cleary M, Walter JH, Wraith JE, Jenkins JP, Alani SM, Tyler K et al (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in phenylketonuria. Lancet 344:87–90
Bick U, Ullrich K, Stöber U, Möller H, Schuierer G, Ludolph AC et al (1993) White matter abnormalities in patients with treated hyperphenylalaninaemia: Magnetic resonance relaxometry and proton spectroscopy findings. Eur J Pediatr 152:1012–1020
Thompson AJ, Tillotson S, Smith I, Kendall B, Moore SG, Brenton DP (1993) Brain MRI changes in phenylketonuria: Associations with dietary status. Brain 116:811–821
van Spronsen FJ, Hoeksma M, Reijngoud DJ (2009) Brain dysfunction in phenylketonuria: is phenylalanine toxicity the only possible cause? J Inherit Metab Dis 32:46–51
Pilotto A, Blau N, Leks E, Schulte C, Deuschl C, Zipser C et al (2019) Cerebrospinal fluid biogenic amines depletion and brain atrophy in adult patients with phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 42:398–406
Brumm VL, Bilder D, Waisbren SE (2010) Psychiatric symptoms and disorders in phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 99:S59–63
Ten Hoedt AE, de Sonneville LM, Francois B, ter Horst NM, Janssen MC, Rubio-Gozalbo ME et al (2011) High phenylalanine levels directly affect mood and sustained attention in adults with phenylketonuria: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J Inherit Metab Dis 34:165–171
Moyle JJ, Fox AM, Arthur M, Bynevelt M, Burnett JR (2007) Meta-analysis of neuropsychological symptoms of adolescents and adults with PKU. Neuropsychol Rev 17:91–101
Anderson PJ, Leuzzi V (2010) White matter pathology in phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 99:S3–9
Leuzzi V, Tosetti M, Montanaro D, Carducci C, Artiola C, Carducci C et al (2007) The pathogenesis of the white matter abnormalities in phenylketonuria. A multimodal 3.0 tesla MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) study. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:209–216
Fonnesbeck CJ, McPheeters ML, Krishnaswami S, Lindegren ML, Reimschisel T (2013) Estimating the probability of IQ impairment from blood phenylalanine for phenylketonuria patients: a hierarchical meta-analysis. J Inherit Metab Dis 36:757–766
Waisbren SE, Noel K, Fahrbach K, Cella C, Frame D, Dorenbaum A et al (2007) Phenylalanine blood levels and clinical outcomes in phenylketonuria: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Mol Genet Metab 92:63–70
Jahja R, van Spronsen FJ, de Sonneville LMJ, van der Meere JJ, Bosch AM, Hollak CEM et al (2017) Long-term follow-up of cognition and mental health in adult phenylketonuria: a PKU-COBESO study. Behav Genet 47:486–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection was performed by PJ, SC, FF, and CD. Analyses of data were performed by PJ and SC. The first draft of the manuscript was written by PJ, SC, and TB, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest related to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaulent, P., Charriere, S., Feillet, F. et al. Neurological manifestations in adults with phenylketonuria: new cases and review of the literature. J Neurol 267, 531–542 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09608-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09608-2