Abstract
Objectives
The previous studies have shown that recurrent stroke (RS) adversely affects the life of survivors of ischemic stroke (IS). However, lifestyle associated with RS has received a little systematic study in Chinese Han patients. We aimed to perform a comprehensive assessment of lifestyle and the potential risk factors associated with RS in Chinese Han inpatients with first-ever acute ischemic stroke by conducting a long-term follow-up.
Methods
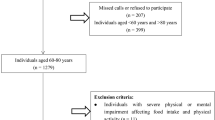
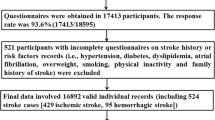
Using a prospective and longitudinal design, we recruited 421 patients with first-ever acute ischemic stroke who were consecutively admitted to the Acute Stroke Unit between November 2012 and January 2014. Demographic data, vascular risk factors, previous Rankin scale score, and etiology were collected at study intake. Multivariable Cox regression model was used to investigate the influencing factors for RS.
Results
Fifty-seven (13.5%) patients experienced RS during the 1-year follow-up period. Multivariable Cox regression analysis revealed that smoking [hazard ratio (HR), 2.153; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.263–3.671], high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) (HR 0.438; 95% CI 0.211–0.911), housework (HR 0.488; 95% CI 0.256–0.933), ischemic heart disease (IHD) (HR 2.998; 95% CI 1.281–7.020), daily consumption of fresh fruits (HR 0.477; 95% CI 0.278–0.819), and good sleep quality (HR 0.375; 95% CI 0.216–0.650) were associated with RS among stroke patients.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that healthy lifestyle (high fruit intake, smoking cessation, housework, and good sleep quality), higher HDL levels, and lack of IHD may be associated with a lower risk of RS in patients with first-onset IS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB (2016) Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 133:447–454
Ovbiagele B, Goldstein LB, Higashida RT, Howard VJ, Johnston SC, Khavjou OA, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Mohl S, Sacco RL, Saver JL, Trogdon JG (2013) Forecasting the future of stroke in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association and American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:2361–2375
Hardie K, Hankey GJ, Jamrozik K, Broadhurst RJ, Anderson C (2004) Ten-year risk of first recurrent stroke and disability after first-ever stroke in the Perth Community Stroke Study. Stroke 35:731–735
Zhu B, Liu H, Pan Y, Jing J, Li H, Zhao X, Liu L, Wang D, Johnston SC, Wang Z, Wang Y, Wang Y (2018) Elevated neutrophil and presence of intracranial artery stenosis increase the risk of recurrent stroke. Stroke 49:2294–2300
Aron AW, Staff I, Fortunato G, McCullough LD (2015) Prestroke living situation and depression contribute to initial stroke severity and stroke recovery. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24:492–499
Wangqin R, Wang X, Wang Y, Xian Y, Zhao X, Liu L, Li H, Meng X, Wang Y (2017) Risk factors associated with 90-day recurrent stroke in patients on dual antiplatelet therapy for minor stroke or high-risk TIA: a subgroup analysis of the CHANCE trial. Stroke Vasc Neurol 2:176–183
Wei W, Li S, San F, Zhang S, Shen Q, Guo J, Zhang L (2018) Retrospective analysis of prognosis and risk factors of patients with stroke by TOAST. Medicine 97:e0412
Raghuram K, Durgam A, Kohlnhofer J, Singh A (2018) Relationship between stroke recurrence, infarct pattern, and vascular distribution in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis. J Neurointerv Surg 10:1161–1163
Bai B, Yan Z, Hao Y, Zhang Z, Li G, Dekker J, Qiu C (2017) A randomised controlled multimodal intervention trial in patients with ischaemic stroke in Shandong, China: design and rationale. Lancet 390:S13–S13
Tu WJ, Zeng XW, Deng A, Zhao SJ, Luo DZ, Ma GZ, Wang H, Liu Q (2017) Circulating FABP4 (fatty acid–binding protein 4) is a novel prognostic biomarker in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 48:1531
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB (2016) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 133:e38–e360
Adams JHP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh REE (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Huang Z, Zhang X, Zhang H, Ye R, Xiong Y (2015) Reduced endothelial progenitor cells in extracranial arterial stenosis but not intracranial arterial stenosis. J Vasc Surg 62:1539–1545
Lee E, Choi K, Ryu J, Jeon S, Lee S, Park S, Park S, Lee J, Choo S, Chung C, Jung S, Kang D, Kim JS, Kwon SU (2011) Stroke risk after coronary artery bypass graft surgery and extent of cerebral artery atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:1811–1818
Toole JF, Malinow MR, Chambless LE, Spence JD, Pettigrew LC, Howard VJ, Sides EG, Wang CH, Stampfer M (2004) Lowering homocysteine in patients with ischemic stroke to prevent recurrent stroke, myocardial infarction, and death: the Vitamin Intervention for Stroke Prevention (VISP) randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291:565–575
Fletcher GF, Landolfo C, Niebauer J, Ozemek C, Arena R, Lavie CJ (2018) Promoting physical activity and exercise: JACC health promotion series. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:1622–1639
Noma, KKihara, Y, Higashi Y (2017) Outstanding effect of physical exercise on endothelial function even in children and adolescents. Circ J 81:637–639
Tsoupras, ALordan, R, Zabetakis I (2018) Inflammation, not cholesterol, is a cause of chronic disease. Nutrients 10:604
Molnar MZ, Lu JL, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP (2016) Association of incident restless legs syndrome with outcomes in a large cohort of US veterans. J Sleep Res 25:47–56
Clasadonte J, Scemes E, Wang Z, Boison D, Haydon PG (2017) Connexin 43-mediated astroglial metabolic networks contribute to the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle. Neuron 95:1365–1380.e5
Itani O, Jike M, Watanabe N, Kaneita Y (2017) Short sleep duration and health outcomes: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Sleep Med 32:246–256
Sterr A, Kuhn M, Nissen C, Ettine D, Funk S, Feige B, Umarova R, Urbach H, Weiller C, Riemann D (2018) Post-stroke insomnia in community-dwelling patients with chronic motor stroke: physiological evidence and implications for stroke care. Sci Rep 8:8409
Kim KT, Moon H, Yang J, Sohn S, Hong J, Cho YW (2017) The prevalence and clinical significance of sleep disorders in acute ischemic stroke patients—a questionnaire study. Sleep Breath 21:759–765
Carlisi CO, Hilbert K, Guyer AE, Ernst M (2017) Sleep-amount differentially affects fear-processing neural circuitry in pediatric anxiety: a preliminary fMRI investigation. Cognit Affect Behav Neurosci 17:1098–1113
Huang WS, Muo CH, Chang SN, Chang YJ, Tsai CH, Kao CH (2014) Benzodiazepine use and risk of stroke: a retrospective population-based cohort study. Psychiat Clin Neuros 68:255–262
Owolabi M, Sarfo F, Howard VJ, Irvin MR, Gebregziabher M, Akinyemi R, Bennett A, Armstrong K, Tiwari HK, Akpalu A, Wahab KW, Owolabi L, Fawale B, Komolafe M, Obiako R, Adebayo P, Manly JM, Ogbole G, Melikam E, Laryea R, Saulson R, Jenkins C, Arnett DK, Lackland DT, Ovbiagele B, Howard G (2017) Stroke in indigenous Africans, African Americans, and European Americans. Stroke 48:1169–1175
Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ, Appel LJ, Braun LT, Chaturvedi S, Creager MA, Culebras A, Eckel RH, Hart RG, Hinchey JA, Howard VJ, Jauch EC, Levine SR, Meschia JF, Moore WS, Nixon JV, Pearson TA (2011) Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 42:517–584
Lin MP, Ovbiagele B, Markovic D, Towfighi A (2016) Association of secondhand smoke with stroke outcomes. Stroke 47:2828–2835
Teuschl Y, Matz K, Firlinger B, Dachenhausen A, Tuomilehto J, Brainin M, Group AS (2017) Preventive effects of multiple domain interventions on lifestyle and risk factor changes in stroke survivors: evidence from a two-year randomized trial. Int J Stroke 12:976–984
Du H, Li L, Bennett D, Guo Y, Key TJ, Bian Z, Sherliker P, Gao H, Chen Y, Yang L, Chen J, Wang S, Du R, Su H, Collins R, Peto R, Chen Z (2016) Fresh fruit consumption and major cardiovascular disease in China. New Engl J Med 374:1332–1343
Hu D, Huang J, Wang Y, Zhang D, Qu Y (2014) Fruits and vegetables consumption and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Stroke 45:1613–1619
Grassi D, Desideri G, Di Giosia P, De Feo M, Fellini E, Cheli P, Ferri L, Ferri C (2013) Tea, flavonoids, and cardiovascular health: endothelial protection. Am J Clin Nutr 98:1660S–1666S
Suen J, Thomas J, Kranz A, Vun S, Miller M (2016) Effect of flavonoids on oxidative stress and inflammation in adults at risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Healthcare 4:69
Liu RH (2003) Health benefits of fruit and vegetables are from additive and synergistic combinations of phytochemicals. Am J Clin Nutr 78:517S–520S
Amarenco P, Lavallee PC, Labreuche J, Ducrocq G, Juliard JM, Feldman L, Cabrejo L, Meseguer E, Guidoux C, Adrai V, Ratani S, Kusmierek J, Lapergue B, Klein IF, Gongora-Rivera F, Jaramillo A, Abboud H, Olivot JM, Mazighi M, Touboul PJ, Steg PG (2013) Coronary artery disease and risk of major vascular events after cerebral infarction. Stroke 44:1505–1511
Expert Panel On Detection, E. A. T. O., Expert Panel On Detection, E. A. T. O. (2001) executive summary of the third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 285:2486–2497
Bowman L, Hopewell JC, Chen F, Wallendszus K, Stevens W, Collins R, Wiviott SD, Cannon CP, Braunwald E, Sammons E, Landray MJ (2017) Effects of anacetrapib in patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease. New Engl J Med 377:1217–1227
Fang X, Liu H, Zhang X, Zhang H, Qin X, Ji X (2016) Metabolic syndrome, its components, and diabetes on 5-year risk of recurrent stroke among mild-to-moderate ischemic stroke survivors: a multiclinic registry study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:626–634
Feingold KR, Grunfeld C (2016) Effect of inflammation on HDL structure and function. Curr Opin Lipidol 27:521–530
Ruiz M, Frej C, Holmer A, Guo LJ, Tran S, Dahlback B (2017) High-density lipoprotein-associated apolipoprotein m limits endothelial inflammation by delivering sphingosine-1-phosphate to the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37:118–129
Jr FEH (2015) Regression modelling strategies: with applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal regression, and Survival Analysis. Springer, New York
Pan Y, Song T, Chen R, Li H, Zhao X, Liu L, Wang C, Wang Y, Wang Y (2016) Socioeconomic deprivation and mortality in people after ischemic stroke: the China National Stroke Registry. Int J Stroke 11:557–564
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (201707010436), Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital Medical Scientific Research Projects (YY2016-005), and Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province, China (20173024; 20181012). We want to thank Xiang Yang Zhang of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston for her advice on Methods and Results sections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares that there is no competing interest.
Ethical standards
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, and conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, with all participants in this study providing written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, ZX., Lin, XL., Lu, HK. et al. Lifestyles correlate with stroke recurrence in Chinese inpatients with first-ever acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol 266, 1194–1202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09249-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09249-5