Abstract
Background
Diagnosis and disease monitoring of non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy (NSVN) are based on electrophysiological and clinical measures. However, these methods are insensitive to detect subtle differences of axonal injury. We here assessed the utility of a multiparametric MRI protocol to quantify axonal injury and neurogenic muscle damage in NSVN.
Methods
Ten NSVN patients and ten age-matched controls were investigated in this single-center prospective study. All participants were assessed by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the tibial nerve and multiecho Dixon MRI of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles. These data were correlated with clinical and electrophysiological data.
Results
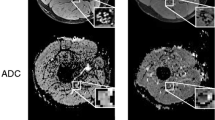
DTI scans of the tibial nerves of patients with NSVN showed significantly lower mean fractional anisotropy (FA) values (0.32 ± 0.02) compared to healthy controls (0.42 ± 0.01). FA values of NSVN patients correlated negatively with clinical measures of pain. Multiecho Dixon MRI scans revealed significantly higher intramuscular fat fractions in the soleus muscle (19.86 ± 6.18% vs. 5.86 ± 0.74%, p = 0.0015) and gastrocnemius muscle (26.09 ± 6.21% vs. 3.59 ± 0.82%, p = 0.0002) in NSVN patients compared to healthy controls.
Conclusion
Our data provide a proof of concept that MRI can render information about nerve integrity and muscle pathology in NSVN. Further studies are warranted to evaluate DTI and multiecho Dixon MRI as surrogate markers in NSVN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins MP, Dyck PJB, Gronseth GS et al (2010) Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline* on the classification, diagnosis, investigation, and immunosuppressive therapy of non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: executive summary. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8027.2010.00281.x
Schneider C, Wunderlich G, Bleistein J et al (2017) Lymphocyte antigens targetable by monoclonal antibodies in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88:756–760. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-315878
Üçeyler N, Geng A, Reiners K et al (2015) Non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy: single-center follow-up of 60 patients. J Neurol 262:2092–2100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7813-5
Chhabra A, Thakkar RS, Andreisek G et al (2013) Anatomic MR imaging and functional diffusion tensor imaging of peripheral nerve tumors and tumorlike conditions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:802–807. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3316
Ishikawa T, Asakura K, Mizutani Y et al (2017) MR neurography for the evaluation of CIDP. Muscle Nerve 55:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25368
Lichtenstein T, Sprenger A, Weiss K et al (2018) MRI biomarkers of proximal nerve injury in CIDP. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 5:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.502
Bäumer P, Pham M, Ruetters M et al (2014) Peripheral neuropathy: detection with diffusion-tensor imaging. Radiology 273:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14132837
Guggenberger R, Markovic D, Eppenberger P et al (2012) Assessment of median nerve with MR neurography by using diffusion-tensor imaging: normative and pathologic diffusion values. Radiology 265:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12111403
Idilman IS, Aniktar H, Idilman R et al (2013) Hepatic steatosis: quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology 267:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121360
Tang A, Tan J, Sun M et al (2013) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: MR imaging of liver proton density fat fraction to assess hepatic steatosis. Radiology 267:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120896
Mankodi A, Bishop CA, Auh S et al (2016) Quantifying disease activity in fatty-infiltrated skeletal muscle by IDEAL-CPMG in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord NMD 26:650–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2016.07.013
Fischer D, Hafner P, Rubino D et al (2016) The 6-minute walk test, motor function measure and quantitative thigh muscle MRI in Becker muscular dystrophy: a cross-sectional study. Neuromuscul Disord NMD 26:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2016.04.009
Lehmann HC, Zhang J, Mori S et al (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging to assess axonal regeneration in peripheral nerves. Exp Neurol 223:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.10.012
Morisaki S, Kawai Y, Umeda M et al (2011) In vivo assessment of peripheral nerve regeneration by diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging JMRI 33:535–542. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22442
Takagi T, Nakamura M, Yamada M et al (2009) Visualization of peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration: monitoring with diffusion tensor tractography. NeuroImage 44:884–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.09.022
Collins MP, Periquet MI (2008) Isolated vasculitis of the peripheral nervous system. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26:S118–S130
Kakuda T, Fukuda H, Tanitame K et al (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging of peripheral nerve in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a feasibility study. Neuroradiology 53:955–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0833-z
Collins MP, Mendell JR, Periquet MI et al (2000) Superficial peroneal nerve/peroneus brevis muscle biopsy in vasculitic neuropathy. Neurology 55:636. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.55.5.636
Gwathmey KG, Burns TM, Collins MP et al (2014) Vasculitic neuropathies. Lancet Neurol 13:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70236-9
Acknowledgements
We thank Jan Borggrefe for support in statistical analysis of interrater agreement and Claudia Müller for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS: study concept, conducting the study, data interpretation, drafting the manuscript. AS: study concept, conducting the study, analysis of data, drafting the manuscript. KW: study concept, technical assistance. KS: analysis of data. DM: study concept, drafting the manuscript for content. GRF: study concept, drafting the manuscript for content. TH: study concept. HCL: study concept, drafting the manuscript for content. TL: study concept, data analysis, drafting the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
KW is an employee of Philips Healthcare Germany since 10/2014. He reports personal fees from Philips Healthcare Germany, during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Philips Healthcare Germany, outside the submitted work. The other authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneider, C., Sprenger, A., Weiss, K. et al. MRI detects peripheral nerve and adjacent muscle pathology in non-systemic vasculitic neuropathy (NSVN). J Neurol 266, 975–981 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09224-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09224-0