Abstract
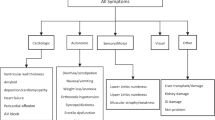
Hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis is a life-threatening, autosomal dominant, systemic amyloidosis caused by mutant transthyretin. In addition to ATTRV30M in endemic and non-endemic areas, more than 140 non-V30M mutations occur worldwide. The aim of this study was to analyze the clinical characteristics and genetic frequencies of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis. Diagnostic results and clinical manifestations of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis from April 1, 2012, to March 31, 2017, at Amyloidosis Medical Practice Center, Kumamoto University Hospital were analyzed. One hundred and four patients received a diagnosis of symptomatic hereditary ATTR amyloidosis. The following mutations of the TTR gene and their percentages were found: V30M in endemic areas, 10.6%; V30M in non-endemic areas, 51.0%; and non-V30M, 38.5%. The ages at onset of patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in non-endemic areas (66.6 ± 8.7 years) and those with non-V30M ATTR amyloidosis (55.8 ± 13.6 years) were significantly higher than those with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in endemic areas (37.0 ± 12.6 years). Of patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in endemic and non-endemic areas, and non-V30M ATTR amyloidosis, 63.6, 66.0, and 27.5% initially presented with polyneuropathy, respectively. Of patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in endemic areas, 81.8% had a family history of this disease. However, a significantly smaller percentage of patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis (30.0%) in non-endemic areas and non-V30M ATTR amyloidosis (34.0%) had a family history. Patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in non-endemic areas and patients with non-V30M ATTR amyloidosis occurred more frequently than previously believed, and their clinical manifestations were diverse.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sipe JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda SI, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, Westermark P (2016) Amyloid fibril proteins and amyloidosis: chemical identification and clinical classification International Society of Amyloidosis 2016 Nomenclature Guidelines. Amyloid 23(4):209–213
Kerschen P, Planté-Bordeneuve V (2016) Current and future treatment approaches in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol 18(12):53
Ando Y, Nakamura M, Araki S (2005) Transthyretin-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Arch Neurol 62(7):1057–1062
Araki S (1984) Type I familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Brain Dev 6(2):128–133
Andrade C (1952) A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain 75(3):408–427
Andersson R (1976) Familial amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. A clinical study based on patients living in northern Sweden. Acta Med Scand Suppl 590:1–64
Adams D, Cauquil C, Labeyrie C (2017) Familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol 30(5):481–489
Yamashita T, Hamidi Asl K, Yazaki M, Benson MD (2005) A prospective evaluation of the transthyretin Ile122 allele frequency in an African-American population. Amyloid 12(2):127–130
Yamashita T, Ando Y, Ueda M, Nakamura M, Okamoto S, Zeledon ME, Hirahara T, Hirai T, Ueda A, Misumi Y, Obayashi K, Inomata H, Uchino M (2008) Effect of liver transplantation on transthyretin Tyr114Cys-related cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 70(2):123–128
Planté-Bordeneuve V, Gorram F, Salhi H, Nordine T, Ayache SS, Le Corvoisier P, Azoulay D, Feray C, Damy T, Lefaucheur JP (2017) Long-term treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy with tafamidis: a clinical and neurophysiological study. J Neurol 264(2):268–276
Suhr OB, Coelho T, Buades J, Pouget J, Conceicao I, Berk J, Schmidt H, Waddington-Cruz M, Campistol JM, Bettencourt BR, Vaishnaw A, Gollob J, Adams D (2015) Efficacy and safety of patisiran for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: a phase II multi-dose study. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:109
Cortese A, Vita G, Luigetti M, Russo M, Bisogni G, Sabatelli M, Manganelli F, Santoro L, Cavallaro T, Fabrizi GM, Schenone A, Grandis M, Gemelli C, Mauro A, Pradotto LG, Gentile L, Stancanelli C, Lozza A, Perlini S, Piscosquito G, Calabrese D, Mazzeo A, Obici L, Pareyson D (2016) Monitoring effectiveness and safety of Tafamidis in transthyretin amyloidosis in Italy: a longitudinal multicenter study in a non-endemic area. J Neurol 263(5):916–924
Coelho T, Maia LF, da Silva AM, Cruz MW, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Suhr OB, Conceiçao I, Schmidt HH, Trigo P, Kelly JW, Labaudinière R, Chan J, Packman J, Grogan DR (2013) Long-term effects of tafamidis for the treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Neurol 260(11):2802–2814
Coelho T, Adams D, Silva A, Lozeron P, Hawkins PN, Mant T, Perez J, Chiesa J, Warrington S, Tranter E, Munisamy M, Falzone R, Harrop J, Cehelsky J, Bettencourt BR, Geissler M, Butler JS, Sehgal A, Meyers RE, Chen Q, Borland T, Hutabarat RM, Clausen VA, Alvarez R, Fitzgerald K, Gamba-Vitalo C, Nochur SV, Vaishnaw AK, Sah DW, Gollob JA, Suhr OB (2013) Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 369(9):819–829
Berk JL, Suhr OB, Obici L, Sekijima Y, Zeldenrust SR, Yamashita T, Heneghan MA, Gorevic PD, Litchy WJ, Wiesman JF, Nordh E, Corato M, Lozza A, Cortese A, Robinson-Papp J, Colton T, Rybin DV, Bisbee AB, Ando Y, Ikeda S, Seldin DC, Merlini G, Skinner M, Kelly JW, Dyck PJ, Diflunisal Trial Consortium (2013) Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 310(24):2658–2667
Coelho T, Maia LF, Martins da Silva A, Waddington Cruz M, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Lozeron P, Suhr OB, Campistol JM, Conceição IM, Schmidt HH, Trigo P, Kelly JW, Labaudinière R, Chan J, Packman J, Wilson A, Grogan DR (2012) Tafamidis for transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 79(8):785–792
Yamashita T, Ando Y, Okamoto S, Misumi Y, Hirahara T, Ueda M, Obayashi K, Nakamura M, Jono H, Shono M, Asonuma K, Inomata Y, Uchino M (2012) Long-term survival after liver transplantation in patients with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology 78(9):637–643
Conceição I, González-Duarte A, Obici L, Schmidt HH, Simoneau D, Ong ML, Amass L (2016) “Red-flag” symptom clusters in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 21(1):5–9
Ueda M, Misumi Y, Mizuguchi M, Nakamura M, Yamashita T, Sekijima Y, Ota K, Shinriki S, Jono H, Ikeda S, Suhr OB, Ando Y (2009) SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry evaluation of variant transthyretins for diagnosis and pathogenesis of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Clin Chem 55(6):1223–1227
Ando Y, Ohlsson PI, Suhr O, Nyhlin N, Yamashita T, Holmgren G, Danielsson A, Sandgren O, Uchino M, Ando M (1996) A new simple and rapid screening method for variant transthyretin-related amyloidosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 228(2):480–483
Koike H, Misu K, Ikeda S, Ando Y, Nakazato M, Ando E, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Sobue G, Study Group for Hereditary Neuropathy in Japan (2002) Type I (transthyretin Met30) familial amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: early- vs late-onset form. Arch Neurol 59(11):1771–1776
Koike H, Misu K, Sugiura M, Iijima M, Mori K, Yamamoto M, Hattori N, Mukai E, Ando Y, Ikeda S, Sobue G (2004) Pathology of early- vs late-onset TTR Met30 familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology 63(1):129–138
Ki Misu, Hattori N, Nagamatsu M, Si Ikeda, Ando Y, Nakazato M, Yi Takei, Hanyu N, Usui Y, Tanaka F, Harada T, Inukai A, Hashizume Y, Sobue G (1999) Late-onset familial amyloid polyneuropathy type I (transthyretin Met30-associated familial amyloid polyneuropathy) unrelated to endemic focus in Japan. Clinicopathological and genetic features. Brain 122(10):1951–1962
Yamashita T, Ueda M, Saga N, Nanto K, Tasaki M, Masuda T, Misumi Y, Oda S, Fujimoto A, Amano T, Takamatsu K, Yamashita S, Obayashi K, Matsui H, Ando Y (2016) Hereditary amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy caused by the novel variant transthyretin A36D. Amyloid 23(3):207–208
Koike H, Hashimoto R, Tomita M, Kawagashira Y, Iijima M, Tanaka F, Sobue G (2011) Diagnosis of sporadic transthyretin Val30Met familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a practical analysis. Amyloid 18(2):53–62
Planté-Bordeneuve V, Lalu T, Misrahi M, Reilly MM, Adams D, Lacroix C, Said G (1998) Genotypic-phenotypic variations in a series of 65 patients with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology 51(3):708–714
Conceição I, De Carvalho M (2007) Clinical variability in type I familial amyloid polyneuropathy (Val30Met): comparison between late- and early-onset cases in Portugal. Muscle Nerve 35(1):116–118
Okumura K, Yamashita T, Masuda T, Misumi Y, Ueda A, Ueda M, Obayashi K, Jono H, Yamashita S, Inomata Y, Ando Y (2016) Long-term outcome of patients with hereditary transthyretin V30M amyloidosis with polyneuropathy after liver transplantation. Amyloid 23(1):39–45
Ando Y, Coelho T, Berk JL, Cruz MW, Ericzon BG, Ikeda S, Lewis WD, Obici L, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Rapezzi C, Said G, Salvi F (2013) Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:31
Okamoto S, Wixner J, Obayashi K, Ando Y, Ericzon BG, Friman S, Uchino M, Suhr OB (2009) Liver transplantation for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: impact on Swedish patients’ survival. Liver Transpl 15(10):1229–1235
Holmgren G, Ericzon BG, Groth CG, Steen L, Suhr O, Andersen O, Wallin BG, Seymour A, Richardson S, Hawkins PN et al (1993) Clinical improvement and amyloid regression after liver transplantation in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Lancet 341(8853):1113–1116
Gustavsson A, Jahr H, Tobiassen R, Jacobson DR, Sletten K, Westermark P (1995) Amyloid fibril composition and transthyretin gene structure in senile systemic amyloidosis. Lab Investig 73(5):703–708
Westermark P, Sletten K, Johansson B, Cornwell GG 3rd (1990) Fibril in senile systemic amyloidosis is derived from normal transthyretin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(7):2843–2845
Ando Y, Tanaka Y, Ando E, Yamashita T, Nishida Y, Tashima K, Suga M, Uchino M, Ando M (1995) Effect of liver transplantation on autonomic dysfunction in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type I. Lancet 345(8943):195–196
Suhr OB, Larsson M, Ericzon BG, Wilczek HE, FAPWTRʼs investigators (2016) Survival after transplantation in patients with mutations other than Val30Met: extracts from the FAP world transplant registry. Transplantation 100(2):373–381
Sekijima Y, Wiseman RL, Matteson J, Hammarström P, Miller SR, Sawkar AR, Balch WE, Kelly JW (2005) The biological and chemical basis for tissue-selective amyloid disease. Cell 121(1):73–85
Ihse E, Rapezzi C, Merlini G, Benson MD, Ando Y, Suhr OB, Ikeda S, Lavatelli F, Obici L, Quarta CC, Leone O, Jono H, Ueda M, Lorenzini M, Liepnieks J, Ohshima T, Tasaki M, Yamashita T, Westermark P (2013) Amyloid fibrils containing fragmented ATTR may be the standard fibril composition in ATTR amyloidosis. Amyloid 20(3):142–150
Rajabally YA, Adams D, Latour P, Attarian S (2016) Hereditary and inflammatory neuropathies: a review of reported associations, mimics and misdiagnoses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(10):1051–1060
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This Institutional Review Board of the Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University (No. 1172, 1387) approved this study.
Informed consent
All patients gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, T., Ueda, M., Misumi, Y. et al. Genetic and clinical characteristics of hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis in endemic and non-endemic areas: experience from a single-referral center in Japan. J Neurol 265, 134–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8640-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8640-7