Abstract
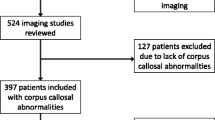
Corpus callosum abnormality (CCA) outcomes are quite unpredictable and variable, from asymptomatic forms to mild or severe neurodevelopment disorders. The aim of this study was to examine clinical outcomes in CCA patients. The study included 61 children and adolescents in whom brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans showed CCA, isolated or associated to other central nervous system lesions. All patients underwent anamnesis, physical and neurological examination, routine laboratory tests, electroencephalogram (EEG), and MRI scans. In all participants, the intelligence quotient (IQ) was determined. We divided the participants into two subgroups: the first subgroup included patients with an isolated CCA, and the second subgroup included patients with CCA associated with extra-callosal brain lesions (complex CCA). We found that CCA were associated with elevated frequency to intellectual disability (ID), other neurodevelopment disorders, epilepsy, and isolated EEG anomalies. Mild ID (p = 0.003) was more frequent in the isolated subgroup, while epilepsy (p = 0.036) and pre-perinatal risk factors (p = 0.023) were more frequent in the complex CCA subgroup. Although the role of the CC in the interhemispheric communication is known, neurological and neurodevelopment outcomes of CCA are extremely variable and unpredictable. The presence of extra-callosal brain anomalies is one of the major prognostic factor, and probably, they have an important impact on the clinical outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
- ADHD:
-
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- ASD:
-
Autism spectrum disorders
- CC:
-
Corpus callosum
- CCA:
-
Corpus callosum abnormalities
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- HCC:
-
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum
- ID:
-
Intellectual disability
- IQ:
-
Intelligence quotient
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- pACC:
-
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
- PCA:
-
Post-conceptional age
- tACC:
-
Total agenesis of the corpus callosum
- WISC-IV:
-
Wechsler intelligence scale for children–fourth edition, Italian version
References
Innocenti GM (1986) Postnatal development of corticocortical connections. Ital J Neurol Sci Suppl 5:25–28
Gazzaniga MS (2000) Cerebral specialization and interhemispheric communication: does the corpus callosum enable the human condition? Brain J Neurol 123(Pt 7):1293–1326
Edwards TJ, Sherr EH, Barkovich AJ, Richards LJ (2014) Clinical, genetic and imaging findings identify new causes for corpus callosum development syndromes. Brain J Neurol 137(Pt 6):1579–1613. doi:10.1093/brain/awt358
Wahl M, Lauterbach-Soon B, Hattingen E, Jung P, Singer O, Volz S, Klein JC, Steinmetz H, Ziemann U (2007) Human motor corpus callosum: topography, somatotopy, and link between microstructure and function. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 27(45):12132–12138. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2320-07.2007
Wahl M, Strominger Z, Jeremy RJ, Barkovich AJ, Wakahiro M, Sherr EH, Mukherjee P (2009) Variability of homotopic and heterotopic callosal connectivity in partial agenesis of the corpus callosum: a 3T diffusion tensor imaging and Q-ball tractography study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(2):282–289. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1361
Paul LK (2011) Developmental malformation of the corpus callosum: a review of typical callosal development and examples of developmental disorders with callosal involvement. J Neurodev Disord 3(1):3–27. doi:10.1007/s11689-010-9059-y
Bloom JS, Hynd GW (2005) The role of the corpus callosum in interhemispheric transfer of information: excitation or inhibition? Neuropsychol Rev 15(2):59–71. doi:10.1007/s11065-005-6252-y
Rakic P, Yakovlev PI (1968) Development of the corpus callosum and cavum septi in man. J Comp Neurol 132(1):45–72. doi:10.1002/cne.901320103
Fame RM, MacDonald JL, Macklis JD (2011) Development, specification, and diversity of callosal projection neurons. Trends Neurosci 34(1):41–50. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2010.10.002
Rash BG, Richards LJ (2001) A role for cingulate pioneering axons in the development of the corpus callosum. J Comp Neurol 434(2):147–157
Hofer S, Frahm J (2006) Topography of the human corpus callosum revisited—comprehensive fiber tractography using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 32(3):989–994. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.044
Luders E, Thompson PM, Toga AW (2010) The development of the corpus callosum in the healthy human brain. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30(33):10985–10990. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5122-09.2010
Dobyns WB, Berry-Kravis E, Havernick NJ, Holden KR, Viskochil D (1999) X-linked lissencephaly with absent corpus callosum and ambiguous genitalia. Am J Med Genet 86(4):331–337
Sztriha L, Johansen JG, Al-Gazali LI (2005) Extreme microcephaly with agyria-pachygyria, partial agenesis of the corpus callosum, and pontocerebellar dysplasia. J Child Neurol 20(2):170–172
Paul LK, Brown WS, Adolphs R, Tyszka JM, Richards LJ, Mukherjee P, Sherr EH (2007) Agenesis of the corpus callosum: genetic, developmental and functional aspects of connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(4):287–299. doi:10.1038/nrn2107
Schell-Apacik CC, Wagner K, Bihler M, Ertl-Wagner B, Heinrich U, Klopocki E, Kalscheuer VM, Muenke M, von Voss H (2008) Agenesis and dysgenesis of the corpus callosum: clinical, genetic and neuroimaging findings in a series of 41 patients. Am J Med Genet Part A 146A(19):2501–2511. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32476
de Ligt J, Willemsen MH, van Bon BW, Kleefstra T, Yntema HG, Kroes T, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Koolen DA, de Vries P, Gilissen C, del Rosario M, Hoischen A, Scheffer H, de Vries BB, Brunner HG, Veltman JA, Vissers LE (2012) Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N Engl J Med 367(20):1921–1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1206524
O’Driscoll MC, Black GC, Clayton-Smith J, Sherr EH, Dobyns WB (2010) Identification of genomic loci contributing to agenesis of the corpus callosum. Am J Med Genet Part A 152A(9):2145–2159. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33558
Grogono JL (1968) Children with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Dev Med Child Neurol 10(5):613–616
Jeret JS, Serur D, Wisniewski KE, Lubin RA (1987) Clinicopathological findings associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum. Brain Dev 9(3):255–264
Al-Hashim AH, Blaser S, Raybaud C, MacGregor D (2016) Corpus callosum abnormalities: neuroradiological and clinical correlations. Dev Med Child Neurol 58(5):475–484. doi:10.1111/dmcn.12978
Hanna RM, Marsh SE, Swistun D, Al-Gazali L, Zaki MS, Abdel-Salam GM, Al-Tawari A, Bastaki L, Kayserili H, Rajab A, Boglarka B, Dietrich RB, Dobyns WB, Truwit CL, Sattar S, Chuang NA, Sherr EH, Gleeson JG (2011) Distinguishing 3 classes of corpus callosal abnormalities in consanguineous families. Neurology 76(4):373–382. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318208f492
Neal JB, Filippi CG, Mayeux R (2015) Morphometric variability of neuroimaging features in children with agenesis of the corpus callosum. BMC Neurol 15:116. doi:10.1186/s12883-015-0382-5
Palmer EE, Mowat D (2014) Agenesis of the corpus callosum: a clinical approach to diagnosis. Am J Med Genet Part C Semin Med Genet 166C(2):184–197. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31405
Tang PH, Bartha AI, Norton ME, Barkovich AJ, Sherr EH, Glenn OA (2009) Agenesis of the corpus callosum: an MR imaging analysis of associated abnormalities in the fetus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(2):257–263. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1331
Unterberger I, Bauer R, Walser G, Bauer G (2016) Corpus callosum and epilepsies. Seizure 37:55–60. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2016.02.012
Sotiriadis A, Makrydimas G (2012) Neurodevelopment after prenatal diagnosis of isolated agenesis of the corpus callosum: an integrative review. Am J Obstet Gynecol 206(4):337. e331–337. e335. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2011.12.024
Santo S, D’Antonio F, Homfray T, Rich P, Pilu G, Bhide A, Thilaganathan B, Papageorghiou AT (2012) Counseling in fetal medicine: agenesis of the corpus callosum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol Off J Int Soc Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 40(5):513–521. doi:10.1002/uog.12315
Wechsler D (2004) The Wechsler intelligence scale for children—fourth edition. Pearson, London
Roid GH, Miller LJ (1997) Leiter international performance scale—revised: examiner’s manual. Stoelting Co, Wood Dale
Hinkley LB, Marco EJ, Findlay AM, Honma S, Jeremy RJ, Strominger Z, Bukshpun P, Wakahiro M, Brown WS, Paul LK, Barkovich AJ, Mukherjee P, Nagarajan SS, Sherr EH (2012) The role of corpus callosum development in functional connectivity and cognitive processing. PLoS One 7(8):e39804. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039804
Siffredi V, Anderson V, Leventer RJ, Spencer-Smith MM (2013) Neuropsychological profile of agenesis of the corpus callosum: a systematic review. Dev Neuropsychol 38(1):36–57. doi:10.1080/87565641.2012.721421
Lau YC, Hinkley LB, Bukshpun P, Strominger ZA, Wakahiro ML, Baron-Cohen S, Allison C, Auyeung B, Jeremy RJ, Nagarajan SS, Sherr EH, Marco EJ (2013) Autism traits in individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum. J Autism Dev Disord 43(5):1106–1118. doi:10.1007/s10803-012-1653-2
Njiokiktjien C, Valk J, Ramaekers G (1988) Malformation or damage of the corpus callosum? A clinical and MRI study. Brain Dev 10(2):92–99
Frazier TW, Hardan AY (2009) A meta-analysis of the corpus callosum in autism. Biol Psychiatry 66(10):935–941. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.022
Travers BG, Adluru N, Ennis C, Tromp do PM, Destiche D, Doran S, Bigler ED, Lange N, Lainhart JE, Alexander AL (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging in autism spectrum disorder: a review. Autism Res 5(5):289–313. doi:10.1002/aur.1243
Aoki Y, Abe O, Nippashi Y, Yamasue H (2013) Comparison of white matter integrity between autism spectrum disorder subjects and typically developing individuals: a meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging tractography studies. Mol Autism 4(1):25. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-4-25
Barbeau EB, Lewis JD, Doyon J, Benali H, Zeffiro TA, Mottron L (2015) A greater involvement of posterior brain areas in interhemispheric transfer in autism: fMRI, DWI and behavioral evidences. NeuroImage Clin 8:267–280. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2015.04.019
Hynd GW, Hall J, Novey ES, Eliopulos D, Black K, Gonzalez JJ, Edmonds JE, Riccio C, Cohen M (1995) Dyslexia and corpus callosum morphology. Arch Neurol 52(1):32–38
Valera EM, Faraone SV, Murray KE, Seidman LJ (2007) Meta-analysis of structural imaging findings in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 61(12):1361–1369. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.06.011
Hutchinson E, Pulsipher D, Dabbs K, y Gutierrez AM, Sheth R, Jones J, Seidenberg M, Meyerand E, Hermann B (2010) Children with new-onset epilepsy exhibit diffusion abnormalities in cerebral white matter in the absence of volumetric differences. Epilepsy Res 88(2–3):208–214. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.11.011
Pastura G, Doering T, Gasparetto EL, Mattos P, Araujo AP (2015) Exploratory analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: evidence of abnormal white matter structure. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. doi:10.1007/s12402-015-0185-y
Dougherty CC, Evans DW, Myers SM, Moore GJ, Michael AM (2016) A comparison of structural brain imaging findings in autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychol Rev 26(1):25–43. doi:10.1007/s11065-015-9300-2
Taylor M, David AS (1998) Agenesis of the corpus callosum: a United Kingdom series of 56 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(1):131–134
Groppel G, Gallmetzer P, Prayer D, Serles W, Baumgartner C (2009) Focal lesions in the splenium of the corpus callosum in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 50(6):1354–1360. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01800.x
Kim SE, Lee JH, Chung HK, Lim SM, Lee HW (2014) Alterations in white matter microstructures and cognitive dysfunctions in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Eur J Neurol 21(5):708–717. doi:10.1111/ene.12301
Meng L, Xiang J, Kotecha R, Rose D, Zhao H, Zhao D, Yang J, Degrauw T (2010) White matter abnormalities in children and adolescents with temporal lobe epilepsy. Magn Reson Imaging 28(9):1290–1298. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.046
Kim H, Harrison A, Kankirawatana P, Rozzelle C, Blount J, Torgerson C, Knowlton R (2013) Major white matter fiber changes in medically intractable neocortical epilepsy in children: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Epilepsy Res 103(2–3):211–220. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.07.017
Ji GJ, Zhang Z, Xu Q, Zang YF, Liao W, Lu G (2014) Generalized tonic-clonic seizures: aberrant interhemispheric functional and anatomical connectivity. Radiology 271(3):839–847. doi:10.1148/radiol.13131638
Wieshmann UC, Milinis K, Paniker J, Das K, Jenkinson MD, Brodbelt A, Crooks D, Keller SS (2015) The role of the corpus callosum in seizure spread: MRI lesion mapping in oligodendrogliomas. Epilepsy Res 109:126–133. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.10.023
Peterson BS, Vohr B, Staib LH, Cannistraci CJ, Dolberg A, Schneider KC, Katz KH, Westerveld M, Sparrow S, Anderson AW, Duncan CC, Makuch RW, Gore JC, Ment LR (2000) Regional brain volume abnormalities and long-term cognitive outcome in preterm infants. JAMA 284(15):1939–1947
Nosarti C, Nam KW, Walshe M, Murray RM, Cuddy M, Rifkin L, Allin MP (2014) Preterm birth and structural brain alterations in early adulthood. NeuroImage Clin 6:180–191. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2014.08.005
Rademaker KJ, Lam JN, Van Haastert IC, Uiterwaal CS, Lieftink AF, Groenendaal F, Grobbee DE, de Vries LS (2004) Larger corpus callosum size with better motor performance in prematurely born children. Semin Perinatol 28(4):279–287
Counsell SJ, Edwards AD, Chew AT, Anjari M, Dyet LE, Srinivasan L, Boardman JP, Allsop JM, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA, Cowan FM (2008) Specific relations between neurodevelopmental abilities and white matter microstructure in children born preterm. Brain J Neurol 131(Pt 12):3201–3208. doi:10.1093/brain/awn268
Acknowledgments
We thank the families for their contribution to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Local Ethic Committee of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Policlinico of Bari, all children were recruited after obtaining written informed consent by their parents; in addition, informed consent was also obtained from the patients who could understand the content and aim of study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Funding
No fundings were provided for this study. The authors declare that they have no financial relationship with any sponsoring organization.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Margari, L., Palumbi, R., Campa, M.G. et al. Clinical manifestations in children and adolescents with corpus callosum abnormalities. J Neurol 263, 1939–1945 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8225-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8225-x