Abstract
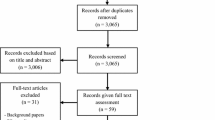
Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy (CIAP) is a term describing neuropathies with both sensory and motor involvement in a length dependant distribution where neurophysiology reveals axonal damage, neuropathy onset is insidious and shows slow or no progression of the disease over at least 6 months with no aetiology being identified despite appropriate investigations. This entity merits further consideration given how common it is, the absence of clarity regarding aetiopathogenesis, natural history and therapies. A systematic computer-based literature search was conducted on PubMed database. We used two Medical Subject Headings terms in title. Term A was “axonal”, “cryptogenic”, “idiopathic” or “unknown” and Term B was “neuropathy” or “polyneuropathy”. This search strategy resulted in the identification of 658 articles. After eligibility assessment, 48 papers were used for this review. CIAP is usually diagnosed in the sixth decade of life and it is more prevalent in males (ratio 3:2). It is usually slowly progressive. Some data support a potential role of autoimmunity in CIAP and further larger prospective studies are required to address such potential link and any treatment implications. CIAP is a common type of polyneuropathy but the least studied. Increasing awareness and research into this entity may result in better understanding and in the development of treatment strategies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martyn CN, Hughes RA (1997) Epidemiology of peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 62(4):310–318
Hughes RA (2002) Peripheral neuropathy. BMJ (Clini Res ed) 324(7335):466–469
Sveen KA, Karime B, Jorum E, Mellgren SI, Fagerland MW, Monnier VM et al (2013) Small- and large-fiber neuropathy after 40 years of type 1 diabetes: associations with glycemic control and advanced protein glycation: the Oslo Study. Diabetes Care 36(11):3712–3717
Lacomis D (2002) Small-fiber neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 26(2):173–188
Marquez-Infante C, Murphy SM, Mathew L, Alsanousi A, Lunn MP, Brandner S et al (2013) Asymmetric sensory ganglionopathy: a case series. Muscle Nerve 48(1):145–150
Visser NA, Notermans NC, Degen LA, de Kruijk JR, van den Berg LH, Vrancken AF (2014) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy and vitamin B6: a controlled population-based study. J Periph Nerv Syst JPNS 19(2):136–144
Lindh J, Tondel M, Osterberg A, Vrethem M (2005) Cryptogenic polyneuropathy: clinical and neurophysiological findings. J Periph Nerv Syst JPNS 10(1):31–37
Vrancken AF, Franssen H, Wokke JH, Teunissen LL, Notermans NC (2002) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy and successful aging of the peripheral nervous system in elderly people. Arch Neurol 59(4):533–540
Teunissen LL, Notermans NC, Franssen H, van der Graaf Y, Oey PL, Linssen WH et al (1997) Differences between hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 2 and chronic idiopathic axonal neuropathy. A clinical and electrophysiological study. Brain J Neurol 120(Pt 6):955–962
Wolfe GI, Baker NS, Amato AA, Jackson CE, Nations SP, Saperstein DS et al (1999) Chronic cryptogenic sensory polyneuropathy: clinical and laboratory characteristics. Arch Neurol 56(5):540–547
Erdmann PG, van Genderen FR, Teunissen LL, Notermans NC, Lindeman E, van Wijck AJ et al (2010) Pain in patients with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Eur Neurol 64(1):58–64
Dalakas MC (1986) Chronic idiopathic ataxic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 19(6):545–554
Notermans NC, Wokke JH, van den Berg LH, van der Graaf Y, Franssen H, Teunissen LL et al (1996) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Comparison of patients with and without monoclonal gammopathy. Brain J Neurol 119(Pt 2):421–427
Notermans NC, Wokke JH, van der Graaf Y, Franssen H, van Dijk GW, Jennekens FG (1994) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy: a five year follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57(12):1525–1527
Notermans NC, Wokke JH, Franssen H, van der Graaf Y, Vermeulen M, van den Berg LH et al (1993) Chronic idiopathic polyneuropathy presenting in middle or old age: a clinical and electrophysiological study of 75 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56(10):1066–1071
Bharucha NE, Bharucha AE, Bharucha EP (1991) Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in the Parsi community of Bombay. Neurology 41(8):1315–1317
Italian General Practitioner Study Group (IGPSG) (1995) Chronic symmetric symptomatic polyneuropathy in the elderly: a field screening investigation in two Italian regions. I. Prevalence and general characteristics of the sample. Neurology 45(10):1832–1836
Rosenberg NR, Vermeulen M (2004) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy revisited. J Neurol 251(9):1128–1132
Smith AG, Singleton JR (2004) The diagnostic yield of a standardized approach to idiopathic sensory-predominant neuropathy. Arch Intern Med 164(9):1021–1025
Singer MA, Vernino SA, Wolfe GI (2012) Idiopathic neuropathy: new paradigms, new promise. J Periph Nerv Syst JPNS 17(Suppl 2):43–49
Vilming ST, Stave R (1987) Idiopathic polyneuropathy. A prospective study including gastrointestinal investigation. J Oslo City Hosp 37(11–12):129–134
Rajabally YA, Shah RS (2011) Dyslipidaemia in chronic acquired distal axonal polyneuropathy. J Neurol 258(8):1431–1436
Sachedina S, Toth C (2013) Progression in idiopathic, diabetic, paraproteinemic, alcoholic, and B12 deficiency neuropathy. J Periph Nerv Syst JPNS 18(3):247–255
Latov N, Kumar G, Vo ML, Chin RL, Carey BT, Langsdorf JA et al (2015) Elevated blood mercury levels in idiopathic axonal neuropathy. JAMA Neurol 72(4):474–475
Tondel M, Lindh J, Jonsson P, Vrethem M, Persson B (2006) Occupational determinants of cryptogenic polyneuropathy. Neuroepidemiology 26(4):187–194
Smith AG (2012) Impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome in idiopathic neuropathy. J Periph Nerv Syst JPNS 17(Suppl 2):15–21
Novella SP, Inzucchi SE, Goldstein JM (2001) The frequency of undiagnosed diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in patients with idiopathic sensory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 24(9):1229–1231
Singleton JR, Smith AG, Bromberg MB (2001) Increased prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance in patients with painful sensory neuropathy. Diabetes Care 24(8):1448–1453
Sumner CJ, Sheth S, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Polydefkis M (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60(1):108–111
Hoffman-Snyder C, Smith BE, Ross MA, Hernandez J, Bosch EP (2006) Value of the oral glucose tolerance test in the evaluation of chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Arch Neurol 63(8):1075–1079
Nebuchennykh M, Loseth S, Jorde R, Mellgren SI (2008) Idiopathic polyneuropathy and impaired glucose metabolism in a Norwegian patient series. Euro J Neurol Off J Euro Feder Neurol Soc 15(8):810–816
Smith AG, Rose K, Singleton JR (2008) Idiopathic neuropathy patients are at high risk for metabolic syndrome. J Neurol Sci 273(1–2):25–28
Singleton JR, Smith AG, Bromberg MB (2001) Painful sensory polyneuropathy associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Muscle Nerve 24(9):1225–1228
American Diabetes Association (2010) Standards of medical care in diabetes–2010. Diabetes Care 33(Suppl 1):S11–S61
Hughes RA, Umapathi T, Gray IA, Gregson NA, Noori M, Pannala AS et al (2004) A controlled investigation of the cause of chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Brain J Neurol 127(Pt 8):1723–1730
Gaist D, Jeppesen U, Andersen M, Garcia Rodriguez LA, Hallas J, Sindrup SH (2002) Statins and risk of polyneuropathy: a case-control study. Neurology 58(9):1333–1337
Anderson JL, Muhlestein JB, Bair TL, Morris S, Weaver AN, Lappe DL et al (2005) Do statins increase the risk of idiopathic polyneuropathy? Am J Cardiol 95(9):1097–1099
Fitchett D (2015) The metabolic syndrome is an important concept in therapeutic decision-making. Canadian J Cardiol 31(5):596–600
Visser NA, Vrancken AF, van der Schouw YT, van den Berg LH, Notermans NC (2013) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy is associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 36(4):817–822
Rezania K, Soliven B, Rezai KA, Roos RP (2011) Impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome in idiopathic polyneuropathy: the role of pain and depression. Med Hypotheses 76(4):538–542
Teunissen LL, Franssen H, Wokke JH, van der Graaf Y, Linssen WH, Banga JD et al (2002) Is cardiovascular disease a risk factor in the development of axonal polyneuropathy? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(5):590–595
Merlini G, Palladini G (2012) Differential diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Hematol Edu Prog Am Soc Hematol Am Soc Hematol Edu Prog 2012:595–603
Gorson KC, Ropper AH (1997) Axonal neuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63(2):163–168
Eurelings M, van den Berg LH, Wokke JH, Franssen H, Vrancken AF, Notermans NC (2003) Increase of sural nerve T cells in progressive axonal polyneuropathy and monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 61(5):707–709
Gherardi RK, Farcet JP, Creange A, Claudepierre P, Malapert D, Authier FJ et al (1998) Dominant T-cell clones of unknown significance in patients with idiopathic sensory neuropathies. Neurology 51(2):384–389
Wolfe GI, El-Feky WH, Katz JS, Bryan WW, Wians FH Jr, Barohn RJ (1997) Antibody panels in idiopathic polyneuropathy and motor neuron disease. Muscle Nerve 20(10):1275–1283
Kelkar P, McDermott WR, Parry GJ (2002) Sensory-predominant, painful, idiopathic neuropathy: inflammatory changes in sural nerves. Muscle Nerve 26(3):413–416
Sobue G, Yasuda T, Kachi T, Sakakibara T, Mitsuma T (1993) Chronic progressive sensory ataxic neuropathy: clinicopathological features of idiopathic and Sjogren’s syndrome-associated cases. J Neurol 240(1):1–7
Teunissen LL, Notermans NC, Jansen GH, Banga JD, Veldman H, Wokke JH (2000) Thickness of endoneurial vessel basal lamina area in chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 100(4):445–450
Vrancken AF, Notermans NC, Jansen GH, Wokke JH, Said G (2004) Progressive idiopathic axonal neuropathy–a comparative clinical and histopathological study with vasculitic neuropathy. J Neurol 251(3):269–278
Erdmann PG, Teunissen LL, van Genderen FR, Notermans NC, Lindeman E, Helders PJ et al (2007) Functioning of patients with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy (CIAP). J Neurol 254(9):1204–1211
Teunissen LL, Eurelings M, Notermans NC, Hop JW, van Gijn J (2000) Quality of life in patients with axonal polyneuropathy. J Neurol 247(3):195–199
Lindh J, Tondel M, Persson B, Vrethem M (2011) Health-related quality of life in patients with cryptogenic polyneuropathy compared with the general population. Disabil Rehabil 33(7):617–623
Rudolph T, Larsen JP, Farbu E (2009) Is there a need for long-term follow-up in chronic idiopathic polyneuropathy? Acta Neurol Scand 120(5):347–352
Takeuchi H, Misu K, Hattori N, Nagamatsu M, Sobue G (2000) Immunoglobulin therapy for idiopathic chronic sensory ataxic neuropathy. Neurology 54(4):1008–1010
Deleplanque P, Pourrat O, Alcalay D, Robert R, Neau JP, Gil R (1990) Treatment of idiopathic chronic polyneuropathy with plasma exchange alone. Prog Clin Biol Res 337:293–296
Coyle PK, Schutzer SE, Sterman AB, Peress N, Miller F (1985) Humoral abnormalities in three patients with idiopathic chronic polyneuropathy. New York State J Med 85(6):248–250
Uncini A, Sabatelli M, Mignogna T, Lugaresi A, Liguori R, Montagna P (1996) Chronic progressive steroid responsive axonal polyneuropathy: a CIDP vaariant or a primary axonal disorder? Muscle Nerve 19(3):365–371
Vrancken AF, van Schaik IN, Hughes RA, Notermans NC (2004) Drug therapy for chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004(2):Cd003456
Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS et al (2010) EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Euro J Neurol Off J Euro Feder Neurol Soc 17(9):1113-e88
Herrmann DN, Barbano RL, Hart-Gouleau S, Pennella-Vaughan J, Dworkin RH (2005) An open-label study of the lidocaine patch 5% in painful idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. Pain Med (Malden, Mass) 6(5):379–384
Schroder C, Johnston M, Teunissen L, Notermans N, Helders P, van Meeteren N (2007) Perceived control is a concurrent predictor of activity limitations in patients with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88(1):63–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Nothing to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zis, P., Sarrigiannis, P.G., Rao, D.G. et al. Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy: a systematic review. J Neurol 263, 1903–1910 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8082-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8082-7