Abstract
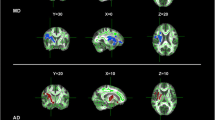
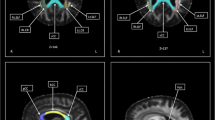
Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) can present with varying degrees of upper motor neuron (UMN) and lower motor neuron dysfunction. Previous diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies, in which ALS patients were not separated by the degree of UMN dysfunction, have resulted in conflicting or inconclusive results. We hypothesized that (1) categorizing ALS patients by their clinical phenotype can reveal differences in DTI abnormalities along the corticospinal tract (CST), and (2) data obtained from routine clinical DTI scans can provide this type of information. Clinical DTI scans were obtained at 1.5T in 87 ALS patients (categorized into four subgroups based on clinical phenotype) and in 12 neurologic controls. Fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD) and radial diffusivity values from the CST were compared between ALS subgroups and controls. Significantly reduced FA and elevated MD values were observed in ALS patients compared to controls at the subcortical motor cortex level. Significant differences in AD values were not only seen between control and ALS patients but also between the ALS subgroups, suggesting divergent pathologies in these ALS patients. Classifying ALS patients by phenotype reveals differences in CST abnormalities between subgroups and may provide novel insights into disease mechanisms. The close similarity of our results from routine clinical scans with published research studies suggests wider accessibility to useful DTI metrics.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Axial diffusivity
- ALS:
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CP:
-
Cerebral peduncle
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CSoLV:
-
Centrum semiovale at top of lateral ventricle
- CST:
-
Corticospinal tract
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DW:
-
Diffusion weighted
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
- EPI:
-
Echo planar imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FTD:
-
Frontotemporal dementia
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery
- FWE:
-
Family wise error
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- IC:
-
Posterior limb of internal capsule
- LMN:
-
Lower motor neuron
- MD:
-
Mean diffusivity
- MoCA:
-
Montreal cognitive assessment
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- RD:
-
Radial diffusivity
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SS-EPI:
-
Single shot echo planar imaging
- SubPMC:
-
Subjacent to primary motor cortex
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- UMN:
-
Upper motor neuron
References
Ellis CM, Simmons A, Jones DK, Bland J, Dawson JM, Horsfield MA, Williams SC, Leigh PN (1999) Diffusion tensor MRI assesses corticospinal tract damage in ALS. Neurology 53(5):1051–1058
Filippi M, Cercignani M, Inglese M, Horsfield MA, Comi G (2001) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 56(3):304–311
Lowe MJ, Horenstein C, Hirsch JG, Marrie RA, Stone L, Bhattacharyya PK, Gass A, Phillips MD (2006) Functional pathway-defined MRI diffusion measures reveal increased transverse diffusivity of water in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 32(3):1127–1133
Medina DA, Gaviria M (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging investigations in Alzheimer’s disease: the resurgence of white matter compromise in the cortical dysfunction of the aging brain. Neuropsychiatr dis treat 4(4):737–742
Cosottini M, Giannelli M, Siciliano G, Lazzarotti G, Michelassi MC, Del Corona A, Bartolozzi C, Murri L (2005) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of corticospinal tract in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and progressive muscular atrophy. Radiology 237(1):258–264
Ulug AM, Grunewald T, Lin MT, Kamal AK, Filippi CG, Zimmerman RD, Beal MF (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging in the diagnosis of primary lateral sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 19(1):34–39
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(5):293–299
Mitusmoto H, Chad DA, Pioro EP (1998) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis contemporary neurology series. Oxford University Press, Philadelphia
Kaufmann P, Pullman SL, Shungu DC, Chan S, Hays AP, Del Bene ML, Dover MA, Vukic M, Rowland LP, Mitsumoto H (2004) Objective tests for upper motor neuron involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Neurology 62(10):1753–1757
Hong YH, Sung JJ, Kim SM, Park KS, Lee KW, Chang KH, Song IC (2008) Diffusion tensor tractography-based analysis of the pyramidal tract in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 18(3):282–287
Senda J, Ito M, Watanabe H, Atsuta N, Kawai Y, Katsuno M, Tanaka F, Naganawa S, Fukatsu H, Sobue G (2009) Correlation between pyramidal tract degeneration and widespread white matter involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a study with tractography and diffusion-tensor imaging. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10(5–6):288–294
Toosy AT, Werring DJ, Orrell RW, Howard RS, King MD, Barker GJ, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging detects corticospinal tract involvement at multiple levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(9):1250–1257
Wang S, Poptani H, Bilello M, Wu X, Woo JH, Elman LB, McCluskey LF, Krejza J, Melhem ER (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: volumetric analysis of the corticospinal tract. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(6):1234–1238
Jones DK (2004) The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study. Magn Reson Med 51(4):807–815
Jaermann T, Crelier G, Pruessmann KP, Golay X, Netsch T, van Muiswinkel AM, Mori S, van Zijl PC, Valavanis A, Kollias S, Boesiger P (2004) SENSE-DTI at 3 T. Magn Reson Med 51(2):230–236
Beaulieu C (ed) (2009) Diffusion MRI: From quantitative measurement to in vivo neuroanatomy, 1st edn. Elsevier, San Diego
Matte GP, Pioro EP (2010) Clinical features and natural history in ALS patients with upper motor neuron abnormalities on conventional brain MRI. Neurology 75:673
Jenkinson M (2003) Fast, automated, N-dimensional phase-unwrapping algorithm. Magn Reson Med 49(1):193–197
Jenkinson M (2004) Improving the registration of B0-disorted EPI images using calculated cost function weights. Paper presented at the Tenth IntConf on Functional Mapping of the Human Brain
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219
Leemans A, Jones DK (2009) The B-matrix must be rotated when correcting for subject motion in DTI data. Magn Reson Med 61(6):1336–1349
Sage CA, Van Hecke W, Peeters R, Sijbers J, Robberecht W, Parizel P, Marchal G, Leemans A, Sunaert S (2009) Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: revisited. Hum Brain Mapp 30(11):3657–3675
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81(2):106–116
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PC (1999) Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 45(2):265–269
Wakana S, Caprihan A, Panzenboeck MM, Fallon JH, Perry M, Gollub RL, Hua K, Zhang J, Jiang H, Dubey P, Blitz A, van Zijl P, Mori S (2007) Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. Neuroimage 36(3):630–644
Heidi Johansen-Berg TEJB (ed) (2009) Diffusion MRI: From quantitative measurement to in vivo neuroanatomy, 1st edn. Elsevier, San Diego
Klawiter EC, Schmidt RE, Trinkaus K, Liang HF, Budde MD, Naismith RT, Song SK, Cross AH, Benzinger TL (2011) Radial diffusivity predicts demyelination in ex vivo multiple sclerosis spinal cords. Neuroimage 55(4):1454–1460
Wong JC, Concha L, Beaulieu C, Johnston W, Allen PS, Kalra S (2007) Spatial profiling of the corticospinal tract in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using diffusion tensor imaging. J Neuroimaging 17(3):234–240
Blain CR, Williams VC, Johnston C, Stanton BR, Ganesalingam J, Jarosz JM, Jones DK, Barker GJ, Williams SC, Leigh NP, Simmons A (2007) A longitudinal study of diffusion tensor MRI in ALS. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8(6):348–355
Yin H, Lim CC, Ma L, Gao Y, Cai Y, Li D, Liang Y, Guo X (2004) Combined MR spectroscopic imaging and diffusion tensor MRI visualizes corticospinal tract degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 251(10):1249–1254
Abe O, Yamada H, Masutani Y, Aoki S, Kunimatsu A, Yamasue H, Fukuda R, Kasai K, Hayashi N, Masumoto T, Mori H, Soma T, Ohtomo K (2004) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: diffusion tensor tractography and voxel-based analysis. NMR Biomed 17(6):411–416
Graham JM, Papadakis N, Evans J, Widjaja E, Romanowski CA, Paley MN, Wallis LI, Wilkinson ID, Shaw PJ, Griffiths PD (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging for the assessment of upper motor neuron integrity in ALS. Neurology 63(11):2111–2119
Jacob S, Finsterbusch J, Weishaupt JH, Khorram-Sefat D, Frahm J, Ehrenreich H (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging for long-term follow-up of corticospinal tract degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroradiology 45(9):598–600
Sach M, Winkler G, Glauche V, Liepert J, Heimbach B, Koch MA, Buchel C, Weiller C (2004) Diffusion tensor MRI of early upper motor neuron involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 127(Pt 2):340–350
Schimrigk SK, Bellenberg B, Schluter M, Stieltjes B, Drescher R, Rexilius J, Lukas C, Hahn HK, Przuntek H, Koster O (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic mixture model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(4):724–730
Sage CA, Peeters RR, Gorner A, Robberecht W, Sunaert S (2007) Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroimage 34(2):486–499
Roccatagliata L, Bonzano L, Mancardi G, Canepa C, Caponnetto C (2009) Detection of motor cortex thinning and corticospinal tract involvement by quantitative MRI in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 10(1):47–52
The Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale. Assessment of activities of daily living in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The ALS CNTF treatment study (ACTS) phase I–II Study Group (1996). Arch Neurol 53 (2):141–147
Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A (1999) The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J Neurol Sci 169(1–2):13–21
Ni H, Kavcic V, Zhu T, Ekholm S, Zhong J (2006) Effects of number of diffusion gradient directions on derived diffusion tensor imaging indices in human brain. Am J Neuroradiol 27(8):1776–1781
Mori SS (2007) Introduction to diffusion tensor imaging, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amesterdam/Boston
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the patients who participated in this study, Dr. Didier Allexandre for helpful discussions on statistics, and Dr. Ken Sakaie for helpful discussions on DTI image processing. Funding was provided by the Bright Side of the Road Foundation and the Fight ALS Fund.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajagopalan, V., Yue, G.H. & Pioro, E.P. Brain white matter diffusion tensor metrics from clinical 1.5T MRI distinguish between ALS phenotypes. J Neurol 260, 2532–2540 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7012-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7012-1