Abstract
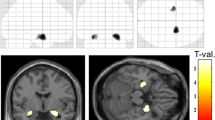
Temporal lobe epilepsy with (TLE-mts) and without (TLE-no) mesial temporal sclerosis display different patterns of cortical neuronal loss, suggesting that the distribution of white matter damage may also differ between the sub-groups. The purpose of this study was to examine patterns of white matter damage in TLE-mts and TLE-no and to determine if identified changes are related to neuronal loss at the presumed seizure focus. The 4 T diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and T1-weighted data were acquired for 22 TLE-mts, 21 TLE-no and 31 healthy controls. Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) was used to compare fractional anisotropy (FA) maps and voxel-based morphometry (VBM) was used to identify grey matter (GM) volume atrophy. Correlation analysis was conducted between the FA maps and neuronal loss at the presumed seizure focus. In TLE-mts, reduced FA was identified in the genu, body and splenium of the corpus callosum, bilateral corona radiata, cingulum, external capsule, ipsilateral internal capsule and uncinate fasciculus. In TLE-no, FA decreases were identified in the genu, the body of the corpus callosum and ipsilateral anterior corona radiata. The FA positively correlated with ipsilateral hippocampal volume. Widespread extra-focal GM atrophy was associated with both sub-groups. Despite widespread and extensive GM atrophy displaying different anatomical patterns in both sub-groups, TLE-mts demonstrated more extensive FA abnormalities than TLE-no. The microstructural organization in the corpus callosum was related to hippocampal volume in both patients and healthy subjects demonstrating the association of these distal regions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scanlon C, Mueller SG, Tosun D, Cheong I, Garcia P, Barakos J, Weiner MW, Laxer KD (2011) Impact of Methodologic choice for automatic detection of different aspects of brain atrophy by using temporal lobe epilepsy as a model. Am J Neuroradiol. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2578
Mueller SG, Laxer KD, Barakos J, Cheong I, Garcia P, Weiner MW (2009) Widespread neocortical abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial sclerosis. NeuroImage 46(2):353–359. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.020
Mueller SG, Laxer KD, Schuff N, Weiner MW (2007) Voxel-based T2 relaxation rate measurements in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia 48(2):220–228. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00916.x
Carne R, Cook M, MacGregor L, Kilpatrick C, Hicks R, O’brien T (2007) “Magnetic resonance imaging negative positron emission tomography positive” Temporal lobe epilepsy: FDG-PET pattern differs from mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Mol Imag Biol 9(1):32–42
Gross DW (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 52(Suppl 4):32–34. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03149.x
Bonilha L, Edwards JC, Kinsman SL, Morgan PS, Fridriksson J, Rorden C, Rumboldt Z, Roberts DR, Eckert MA, Halford JJ (2010) Extrahippocampal gray matter loss and hippocampal deafferentation in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 51(4):519–528. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02506.x
Shon YM, Kim YI, Koo BB, Lee JM, Kim HJ, Kim WJ, Ahn KJ, Yang DW (2010) Group-specific regional white matter abnormality revealed in diffusion tensor imaging of medial temporal lobe epilepsy without hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsia 51(4):529–535. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02327.x
Riley JD, Franklin DL, Choi V, Kim RC, Binder DK, Cramer SC, Lin JJ (2010) Altered white matter integrity in temporal lobe epilepsy: association with cognitive and clinical profiles. Epilepsia 51(4):536–545. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02508.x
Concha L, Beaulieu C, Collins DL, Gross DW (2009) White-matter diffusion abnormalities in temporal-lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80(3):312–319. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.139287
Focke NK, Yogarajah M, Bonelli SB, Bartlett PA, Symms MR, Duncan JS (2008) Voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. NeuroImage 40(2):728–737. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.12.031
Tao R, Fletcher P, Gerber S, Whitaker R (2009) A variational image-based approach to the correction of susceptibility artifacts in the alignment of diffusion weighted and structural MRI. Inf Process Med Imaging 21:664–675
Looi JCL, Lindberg O, Liberg B, Tatham V, Kumar R, Maller J, Millard E, Sachdev P, Högberg G, Pagani M (2008) Volumetrics of the caudate nucleus: reliability and validity of a new manual tracing protocol. Psychiatry Res: NeuroImage 163(3):279–288
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, van der Kouwe A, Killiany R, Kennedy D, Klaveness S (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33(3):341–355
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis I segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9(2):179–194
Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis II: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage 9(2):195–207
Desikan RS, Ségonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31(3):968–980
Van Leemput K, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P (1999) Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 18(10):897–908
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. NeuroImage 26(3):839–851
Ashburner J (2007) A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage 38(1):95–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage 44(1):83–98
Hua K, Zhang J, Wakana S, Jiang H, Li X, Reich DS, Calabresi PA, Pekar JJ, van Zijl PCM, Mori S (2008) Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. NeuroImage 39(1):336–347. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.053
Wakana S, Caprihan A, Panzenboeck MM, Fallon JH, Perry M, Gollub RL, Hua K, Zhang J, Jiang H, Dubey P, Blitz A, van Zijl P, Mori S (2007) Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. NeuroImage 36(3):630–644. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.049
Keller SS, Roberts N (2007) Voxel-based morphometry of temporal lobe epilepsy: an introduction and review of the literature. Epilepsia 49(5):741–757
Lopez PHH, Ahmad AS, Mehta NR, Toner M, Rowland EA, Zhang J, Doré S, Schnaar RL (2011) Myelin-associated glycoprotein protects neurons from excitotoxicity. J Neurochem 116(5):900–908
Thom M, Sisodiya S, Harkness W, Scaravilli F (2001) Microdysgenesis in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 124(11):2299–2309
Eriksson S, Malmgren K, Nordborg C (2005) Microdysgenesis in epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 111(5):279–290
Kasper BS, Stefan H, Paulus W (2003) Microdysgenesis in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: a clinicopathological study. Ann Neurol 54(4):501–506
Vossler DG, Kraemer DL, Haltiner AM, Rostad SW, Kjos BO, Davis BJ, Morgan JD, Caylor LM (2004) Intracranial EEG in temporal lobe epilepsy: location of seizure onset relates to degree of hippocampal pathology. Epilepsia 45(5):497–503
Tournier JD, Mori S, Leemans A (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magn Reson Med 65(6):1532–1556. doi:10.1002/mrm.22924
Jones DK (2004) The effect of gradient sampling schemes on measures derived from diffusion tensor MRI: a Monte Carlo study†. Magn Reson Med 51(4):807–815
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Tom Fletcher, Assistant Professor at the Scientific Computing and Imaging Institute, University of Utah, for his help with the DTI processing and software. This work was supported by a NIH grant R01NS0311966 to K.D.L.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scanlon, C., Mueller, S.G., Cheong, I. et al. Grey and white matter abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J Neurol 260, 2320–2329 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6974-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6974-3