Abstract
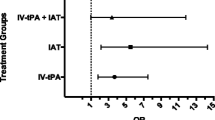
Seizures appear at stroke presentation, during the acute phase or as a late complication of stroke. Thrombolysis has not been investigated as a risk factor despite its potential neurotoxic effect. We try to identify risk factors for seizures during the acute phase of ischemic stroke in a cohort including thrombolysed patients. We undertook a case–control study at a single stroke center using data from Acute Stroke Registry and Analyse of Lausanne (ASTRAL). Patients with seizure occurring during the first 7 days following stroke were retrospectively identified. Bi-variable and multivariable statistical analyses were applied to compare cases and randomly selected controls. We identified 28 patients experiencing from seizures in 2,327 acute ischemic strokes (1.2 %). All seizures occurred during the first 72 h. Cortical involvement, thrombolysis with rt-PA, arterial recanalization, and higher initial NIHSS were statistically associated with seizures in univariated analysis. Backward linear regression identified cortical involvement (OR 7.53, 95 % CI 1.6–35.2, p < 0.01) and thrombolysis (OR 4.6, 95 % CI 1.6–13.4, p = 0.01) as being independently associated with seizure occurrence. Overall, 3-month outcome measured by the modified Rankin scale (mRS) was comparable in both groups. In the subgroup of thrombolysed patients, outcome was significantly worse at 3 months in the seizure group with 9/12 (75 %) patients with mRS ≥3, compared to 6/18 (33.3 %) in the seizure-free group (p = 0.03). Acute seizures in acute ischemic stroke were relatively infrequent. Cortical involvement and thrombolysis with rt-PA are the principal risk factors. Seizures have a potential negative influence on clinical outcome in thrombolysed patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferro JM, Pinto F (2004) Poststroke epilepsy: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. Drugs Aging 21:639–653
Bladin CF, Alexandrov AV, Bellavance A et al (2000) Seizures after stroke: a prospective multicenter study. Arch Neurol 57:1617–1622
Kammersgaard LP, Olsen TS (2005) Poststroke epilepsy in the Copenhagen stroke study: incidence and predictors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Disord 14:210–214
Beghi E, D’Alessandro R, Beretta S et al (2011) Incidence and predictors of acute symptomatic seizures after stroke. Neurology 77:1785–1793
De Herdt V, Dumont F, Hénon H et al (2011) Early seizures in intracerebral hemorrhage: incidence, associated factors, and outcome. Neurology 77:1794–1800
Arboix A, García-Eroles L, Massons JB, Oliveres M, Comes E (1997) Predictive factors of early seizures after acute cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 28:1590–1594
Giroud M, Gras P, Fayolle H et al (1994) Early seizures after acute stroke: a study of 1,640 cases. Epilepsia 35:959–964
Yepes M, Roussel BD, Ali C, Vivien D (2009) Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the ischemic brain: more than a thrombolytic. Trends Neurosci 32:48–55
Qian Z, Gilbert ME, Colicos MA, Kandel ER, Kuhl D (1993) Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature 361:453–457
Iyer AM, Zurolo E, Boer K et al (2010) Tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase plasminogen activator in human epileptogenic pathologies. Neuroscience 167:929–945
Michel P, Odier C, Rutgers M et al (2010) The Acute STroke Registry and Analysis of Lausanne (ASTRAL): design and baseline analysis of an ischemic stroke registry including acute multimodal imaging. Stroke 41:2491–2498
Fisher RS, Boas WVE, Blume W et al (2005) Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46:470–472
Berg A, Berkovic S, Brodie M, Buchhalter J (2010) Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005–2009. Epilepsia 51:676–685
Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ et al (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee, ESO Writing Committee (2008) Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack. Cerebrovasc Dis 25:457–507
Michel P, Arnold M, Hans Jörg H et al (2006) Thrombolyse de l’ attaque cérébrale ischémique: recommandations actualisées. Swiss Medical Forum 6:225–228
Larrue V, von Kummer R, Muller A, Bluhmki E (2001) Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke 32:438–441
Carrera E, Michel P, Despland P-A et al (2006) Continuous assessment of electrical epileptic activity in acute stroke. Neurology 67:99–104
Devuyst G, Karapanayiotides T, Hottinger I (2003) Prodromal and early epileptic seizures in acute stroke: does higher serum cholesterol protect? Neurology 61:249–252
Labovitz DL, Hauser WA, Sacco RL (2001) Prevalence and predictors of early seizure and status epilepticus after first stroke. Neurology 57:200–206
Burn J, Dennis M, Bamford J et al (1997) Epileptic seizures after a first stroke: the Oxfordshire community stroke project. BMJ 315:1582–1587
Mohr JP, Caplan LR, Melski JW et al (1978) The Harvard Cooperative Stroke Registry: a prospective registry. Neurology 28:754–762
Rodan LH, Aviv RI, Sahlas DJ et al (2006) Seizures during stroke thrombolysis heralding dramatic neurologic recovery. Neurology 67:2048–2049
Wunderlich MT, Goertler M, Postert T et al (2007) Recanalization after intravenous thrombolysis: does a recanalization time window exist? Neurology 68:1364–1368
Yepes M, Sandkvist M, Coleman TA et al (2002) Regulation of seizure spreading by neuroserpin and tissue-type plasminogen activator is plasminogen-independent. J Clin Invest 109:1571–1578
Tsirka SE, Gualandris A, Amaral DG, Strickland S (1995) Excitotoxin-induced neuronal degeneration and seizure are mediated by tissue plasminogen activator. Nature 377:340–344
Paciaroni M, Medeiros E, Bogousslavsky J (2009) Desmoteplase. Expert Opin Biol Ther 9:773–778
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 333:1581–1587
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E et al (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke (ECASS-III). N Engl J Med 359:1317–1329
Englander J, Bushnik T, Duong TT et al (2003) Analyzing risk factors for late posttraumatic seizures: a prospective, multicenter investigation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 84:365–373
van Breemen MSM, Wilms EB, Vecht CJ (2007) Epilepsy in patients with brain tumours: epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Neurol 6:421–430
Connors BW (1984) Initiation of synchronized neuronal bursting in neocortex. Nature 310:685–687
Bentes C, Pimentel J, Ferro JM (2001) Epileptic seizures following subcortical infarcts. Cerebrovasc Dis 12:331–334
Biagini G, Panuccio G, Avoli M (2010) Neurosteroids and epilepsy. Curr Opin Neurol 23:170–176
D’Amelio M, Terruso V, Famoso G et al (2011) Cholesterol levels and risk of hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 32:234–238
Jung S, Schindler K, Findling O et al (2012) Adverse effect of early epileptic seizures in patients receiving endovascular therapy for acute stroke. Stroke 43:1584–1590
Conflicts of interest
Vincent Alvarez: nothing to disclose. Andrea O. Rossetti: research support: Pfizer, UCB, Sandoz, EISAI, and GSK. Patrik Michel: research support: Lundbeck Europe, consulting: Lundbeck Europe, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bayer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, V., Rossetti, A.O., Papavasileiou, V. et al. Acute seizures in acute ischemic stroke: does thrombolysis have a role to play?. J Neurol 260, 55–61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6583-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6583-6