Abstract
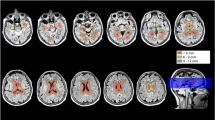
In the current study, we aim to measure T1rho (T 1ρ) in the hippocampus in the brain of control, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and PD patients with dementia (PDD), and to determine efficacy of T 1ρ in differentiating these cohorts. With informed consent, 53 AD patients, 62 PD patients, 11 PDD patients, and 46 age-matched controls underwent a standardized clinical assessment including mini-mental state examination (MMSE) and brain T 1ρ MRI on a 1.5-T clinical-scanner. T1ρ maps were generated by fitting each pixel’s intensity as a function of the spin-lock pulse duration. In control, AD, PD and PDD, mean ± SE T 1ρ values in the right hippocampus (RH) were 92.15 ± 2.00, 99.65 ± 1.98, 85.68 ± 1.87, 102.47 ± 4.66 ms while in the left hippocampus (LH) these values were 90.16 ± 1.82, 99.53 ± 1.91, 84.33 ± 2.03, 95.33 ± 4.64 ms. Significant difference for both RH and LH T 1ρ across the groups (p < 0.001) was observed. Both RH and LH T 1ρ were significantly increased in AD compared to control (p = 0.034, p = 0.001) and PD (p < 0.001, p < 0.001). In control, both RH and LH T 1ρ values were significantly increased compared to PD (p = 0.031, p = 0.027) while compared to PDD only the RH T 1ρ value was significantly decreased (p = 0.043). Both RH and LH T 1ρ values in PD were significantly lower than PDD (p = 0.004, p = 0.032). No significant correlation between the T 1ρ and age as well as between T 1ρ and MMSE scores was observed. The serial measurement of T1ρ in both AD and PD may provide the nature of disease progression and may contribute to their early diagnosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronen HJ, Ramadan UA, Peltonen TK, Markkola AT, Tanttu JI, Jääskeläinen J, Häkkinen AM, Sepponen R (1999) 3D spin-lock imaging of human gliomas. Magn Reson Imaging 17:1001–1010
Borthakur A, Wheaton AJ, Gougoutas AJ, Akella SV, Regatte RR, Charagundla SR, Reddy R (2004) In vivo measurement of T1rho dispersion in the human brain at 1.5 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 19:403–409
Borthakur A, Gur T, Wheaton AJ, Corbo M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Reddy R (2006) In vivo measurement of plaque burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:1011–1017
Borthakur A, Mellon E, Niyogi S, Witschey W, Kneeland JB, Reddy R (2006) Sodium and T1rho MRI for molecular and diagnostic imaging of articular cartilage. NMR Biomed 19:781–821
Borthakur A, Sochor M, Davatzikos C, Trojanowski JQ, Clark CM (2008) T1rho MRI of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 41:1199–1205
Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O’Brien JT (2004) Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain 127:791–800
Davatzikos C, Fan Y, Wu X, Shen D, Resnick SM (2008) Detection of prodromal Alzheimer’s disease via pattern classification of magnetic resonance imaging. Neurobiol Aging 29:514–523
Firbank MJ, Harrison RM, O’Brien JT (2002) A comprehensive review of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 14:64–76
Gibb WRG, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Haris M, McArdle E, Fenty M, Singh A, Davatzikos C, Trojanowski JQ, Melhem ER, Clark CM, Borthakur A (2009) Early marker for Alzheimer’s disease: hippocampus T1rho estimation. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:1008–1012
Ito K, Nagano-Saito A, Kato T, Arahata Y, Nakamura A, Kawasumi Y, Hatano K, Abe Y, Yamada T, Kachi T, Brooks DJ (2002) Striatal and extrastriatal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease with dementia: a 6-[18F]fluoro-l-dopa PET study. Brain 125:1358–1365
Johnson KA, Holman BL, Mueller SP, Rosen TJ, English R, Nagel JS, Growdon JH (1988) Single photon emission computed tomography in Alzheimer’s disease. Abnormal iofetamine I 123 uptake reflects dementia severity. Arch Neurol 45:392–396
Laakso MP, Partanen K, Riekkinen P, Lehtovirta M, Helkala EL, Hallikainen M, Hanninen T, Vainio P, Soininen H (1996) Hippocampal volumes in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, and in vascular dementia: an MRI study. Neurology 46:678–681
Mäkelä HI, De Vita E, Gröhn OH, Kettunen MI, Kavec M, Lythgoe M, Garwood M, Ordidge R, Kauppinen RA (2004) B0 dependence of the on-resonance longitudinal relaxation time in the rotating frame (T1rho) in protein phantoms and rat brain in vivo. Magn Reson Med 51:4–8
Matsui H, Udaka F, Miyoshi T, Hara N, Tamura A, Oda M, Kubori T, Nishinaka K, Kameyama M (2005) N-isopropyl-p-123I iodoamphetamine single photon emission computed tomography study of Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Intern Med 44:1046–1050
Matsui H, Nishinaka K, Oda M, Niikawa H, Kubori T, Udaka F (2007) Dementia in Parkinson’s disease: diffusion tensor imaging. Acta Neurol Scand 116:177–181
McGeer PL, Kamo H, Harrop R, Li DK, Tuokko H, McGeer EG, Adam MJ, Ammann W, Beattie BL, Calne DB et al (1986) Positron emission tomography in patients with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease. CMAJ 134:597–607
McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA et al (1996) Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47:1113–1124
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of health and human services task force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Michaeli S, Liimatainen T, Rydeen CE, Kotz CM, Nixon JP, Hanson T, Tuite PJ (2010) T(1rho) and T(2rho) MRI in the evaluation of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol (Epub ahead of print)
Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 348:1356–1364
O’Brien J, Barber B (2000) Neuroimaging in dementia and depression. Adv Psychiatr Treat 6:109–119
Padovani A, Costanzi C, Gilberti N, Borroni B (2006) Parkinson’s disease and dementia. Neurol Sci 1:S40–S43
Regatte RR, Akella SV, Wheaton AJ, Lech G, Borthakur A, Kneeland JB, Reddy R (2004) 3D-T1rho-relaxation mapping of articular cartilage: in vivo assessment of early degenerative changes in symptomatic osteoarthritic subjects. Acad Radiol 11:741–749
Santyr GE (1994) MR imaging of the breast imaging and tissue characterization without intravenous contrast. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2:673–690
Senjem ML, Gunter JL, Shiung MM, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr (2005) Comparison of different methodological implementations of voxel-based morphometry in neurodegenerative disease. Neuroimage 26:600–608
Stebbins GT, Murphy CM (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Behav Neurol 21:39–49
Summerfield C, Junqué C, Tolosa E, Salgado-Pineda P, Gómez-Ansón B, Martí MJ, Pastor P, Ramírez-Ruíz B, Mercader J (2005) Structural brain changes in Parkinson disease with dementia: a voxel-based morphometry study. Arch Neurol 62:281–285
Tam CW, Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, O’Brien JT (2005) Temporal lobe atrophy on MRI in Parkinson disease with dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 64:861–865
Vymazal J, Righini A, Brooks RA, Canesi M, Mariani C, Leonardi M, Pezzoli G (1999) T1 and T2 in the brain of healthy subjects, patients with Parkinson disease, and patients with multiple system atrophy: relation to iron content. Radiology 211:489–495
Witschey WR, Borthakur A, Elliott MA, Fenty M, Sochor MA, Wang C, Reddy R (2008) T1rho-prepared balanced steady-state free precession for rapid 3D T1rho-weighted MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:744–754
Acknowledgments
This work was performed at a NIH supported resource center (NIH RR02305) and from a grant from the Pennsylvania State Tobacco Settlement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haris, M., Singh, A., Cai, K. et al. T1rho (T1ρ) MR imaging in Alzheimer’ disease and Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. J Neurol 258, 380–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5762-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5762-6