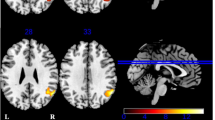
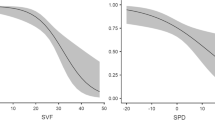
Abstract
Verbal fluency tasks are commonly used to explore semantic memory and executive functions. The aim of this study was to gain a better understanding of the cognitive and neural mechanisms underlying verbal fluency impairment in the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia (fv-FTD) and in semantic dementia (SD). Semantic and phonemic fluency tasks were performed by 36 fv-FTD and SD patients and 18 elderly controls. We also carried out a neuropsychological investigation of semantic memory, working memory and shifting and updating processes. We performed correlative and regression analyses of fluency scores and neuropsychological data. In addition, patients underwent a resting positron emission tomography examination, and statistical parametric mapping was used to establish correlations between resting-state FDG uptake in the whole brain and fluency scores for each patient group. Both patient groups displayed impaired performances on both fluency tasks compared with controls, but with different patterns. While fv-FTD patients scored higher than SD patients on semantic fluency, their performances on the phonemic task did not differ. Correlation and regression analyses clearly demonstrated that the fv-FTD patients’ performances on both fluency tasks depended on their executive abilities, while those of the SD patients were hampered by the impairment of their semantic memory store. Correlations with resting FDG uptake were consistent with the results of the cognitive study. In fv-FTD, both fluency performances were related to the metabolism of the frontal lobes, while we observed significant correlations between performances on both fluency tasks and the left temporal lobe metabolism in SD.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BD-Span:
-
Backward digit span
- BVS-Span:
-
Backward visuospatial span
- FD-Span:
-
Forward digit span
- FVS-Span:
-
Forward visuospatial span
- fv-FTD:
-
Frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia
- MMSE:
-
Mini-mental state examination
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PVE:
-
Partial volume effect
- SD:
-
Semantic dementia
- TMT:
-
Trail making test
References
Alexander MP, Benson DF, Stuss DT (1989) Frontal lobes and language. Brain Lang 37:656–691
Arbuthnott K, Frank J (2000) Trail making test, part B as a measure of executive control: validation using a set-switching paradigm. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 22:518–528
Aron AR, Monsell S, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2004) A componential analysis of task-switching deficits associated with lesions of left and right frontal cortex. Brain 127:1561–1573
Baddeley AD (1996) The fractionation of working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13468–13472
Bamiou DE, Musiek FE, Luxon LM (2003) The insula (Island of Reil) and its role in auditory processing. Literature review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 42:143–154
Behrmann M, Geng JJ, Shomstein S (2004) Parietal cortex and attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:212–217
Boxer AL, Miller BL (2005) Clinical features of frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 19(Suppl 1):S3–S6
Cabeza R, Nyberg L (2000) Neural bases of learning and memory: functional neuroimaging evidence. Curr Opin Neurol 13:415–421
Cardebat D, Demonet JF, Viallard G, Faure S, Puel M, Celsis P (1996) Brain functional profiles in formal and semantic fluency tasks: a SPECT study in normals. Brain Lang 52:305–313
Chételat G, Desgranges B, de la Sayette V, Viader F, Berkouk K, Landeau B, Lalevée C, Le Doze F, Dupuy B, Hannequin D, Baron JC, Eustache F (2003) Dissociating atrophy and hypometabolism impact on episodic memory in mild cognitive impairment. Brain 126:1955–1967
Collette F, Hogge M, Salmon E, Van der Linden M (2006) Exploration of the neural substrates of executive functioning by functional neuroimaging. Neuroscience 139:209–221
D’Esposito M, Detre JA, Aguirre GK, Stallcup M, Alsop DC, Tippet LJ, Farah MJ (1997) A functional MRI study of mental image generation. Neuropsychologia 35:725–730
Davachi L, Maril A, Wagner AD (2001) When keeping in mind supports later bringing to mind: neural markers of phonological rehearsal predict subsequent remembering. J Cogn Neurosci 13:1059–1070
Desgranges B, Baron JC, de la Sayette V, Petit-Taboué MC, Benali K, Landeau B, Lechevalier B, Eustache F (1998) The neural substrates of memory systems impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. A PET study of resting brain glucose utilization. Brain 121:611–631
Desgranges B, Baron JC, Giffard B, Chételat G, Lalevée C, Viader F, de la Sayette V, Eustache F (2002) The neural basis of intrusions in free recall and cued recall: a PET study in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 17:1658–1664
Desgranges B, Matuszewski V, Piolino P, Chételat G, Mézenge F, Landeau B, de la Sayette V, Belliard S, Eustache F (2007) Anatomical and functional alterations in semantic dementia: A voxel-based MRI and PET study. Neurobiol Aging 28:1904–1913
Eustache F, Desgranges B, Aupée AM, Guillery B, Baron JC (2000) Functional neuroanatomy of amnesia: positron emission tomography studies. Microsc Res Tech 51:94–100
Eustache F, Piolino P, Giffard B, Viader F, de la Sayette V, Baron JC, Desgranges B (2004) ‘In the course of time’: a PET study of the cerebral substrates of autobiographical amnesia in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 127:1549–1560
Foster NL, Heidebrink JL, Clark CM, Jagust WJ, Arnold SE, Barbas NR, DeCarli CS, Turner RS, Koeppe RA, Higdon R, Minoshima S (2007) FDG-PET improves accuracy in distinguishing frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 130:2616–2635
Galton CJ, Patterson K, Graham KS, Lambon-Ralph MA, Williams G, Antoun N, Sahakian BJ, Hodges JR (2001) Differing patterns of temporal atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and semantic dementia. Neurology 57:216–225
Giffard B, Desgranges B, Nore-Mary F, Lalevée C, de la Sayette V, Pasquier F, Eustache F (2001) The nature of semantic memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease: new insights from hyperpriming effects. Brain 124:1522–1532
Giffard B, Laisney M, Mézenge F, de la Sayette V, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2008) The neural substrates of semantic memory deficits in early Alzheimer’s disease: clues from semantic priming effects and FDG-PET. Neuropsychologia 46:1657–1666
Grasby PM, Frith CD, Friston KJ, Bench C, Frackowiak RS, Dolan RJ (1993) Functional mapping of brain areas implicated in auditory–verbal memory function. Brain 116:1–20
Gurd JM, Amunts K, Weiss PH, Zafiris O, Zilles K, Marshall JC, Fink GR (2002) Posterior parietal cortex is implicated in continuous switching between verbal fluency tasks: an fMRI study with clinical implications. Brain 125:1024–1038
Henry JD, Crawford JR (2004) A meta-analytic review of verbal fluency performance following focal cortical lesions. Neuropsychology 18:284–295
Hirono N, Mori E, Ishii K, Imamura T, Tanimukai S, Kazui H, Hashimoto M, Takatsuki Y, Kitagaki H, Sasaki M (2001) Neuronal substrates for semantic memory: a positron emission tomography study in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 12:15–21
Hodges JR, Patterson K, Oxbury S, Funnell E (1992) Semantic dementia. Progressive fluent aphasia with temporal lobe atrophy. Brain 115:1783–1806
Hodges JR, Patterson K, Tyler LK (1994) Loss of semantic memory: implications for the modularity of of mind. Cogn Neuropsychol 11:505–542
Hodges JR, Patterson K, Ward R, Garrard P, Bak T, Perry RJ, Gregory CA (1999) The differentiation of semantic dementia and frontal lobe dementia (temporal and frontal variants of frontotemporal dementia) from early Alzheimer’s disease: a comparative neuropsychological study. Neuropsychology 13:31–40
Jonides J, Schumacher EH, Smith EE, Koeppe RA, Awh E, Reuter-Lorenz PA, Marshuetz C, Willis CR (1998) The role of parietal cortex in verbal working memory. J Neurosci 18:5026–5034
Kalpouzos G, Chételat G, Baron JC, Landeau B, Mevel K, Godeau C, Barre L, Constans JM, Viader F, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2009) Voxel-based mapping of brain gray matter volume and glucose metabolism profiles in normal aging. Neurobiol Aging 30:112–124
Klein D, Milner B, Zatorre RJ, Meyer E, Evans AC (1995) The neural substrates underlying word generation: a bilingual functional-imaging study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2899–2903
Kramer JH, Quitania L, Dean D, Neuhaus J, Rosen HJ, Halabi C, Weiner MW, Magnotta VA, Delis DC, Miller BL (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging correlates of set shifting. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 13:386–392
Lekeu F, Van der Linden M, Chicherio C, Collette F, Degueldre C, Franck G, Moonen G, Salmon E (2003) Brain correlates of performance in a free/cued recall task with semantic encoding in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 17:35–45
Majerus S, Laureys S, Collette F, Del Fiore G, Degueldre C, Luxen A, Van der Linden M, Maquet P, Metz-Lutz MN (2003) Phonological short-term memory networks following recovery from Landau and Kleffner syndrome. Hum Brain Mapp 19:133–144
Marczinski CA, Kertesz A (2006) Category and letter fluency in semantic dementia, primary progressive aphasia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Lang 97:258–265
Martin A (2001) Functional neuroimaging of semantic memory. In: Cabeza R, Kingstone A (eds) Handbook of functional neuroimaging cognition. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 153–186
Martin A, Chao LL (2001) Semantic memory and the brain: structure and processes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:194–201
Martin A, Wiggs CL, Lalonde F, Mack C (1994) Word retrieval to letter and semantic cues: a double dissociation in normal subjects using interference tasks. Neuropsychologia 32:1487–1494
Matuszewski V, Piolino P, de la Sayette V, Lalevée C, Pélerin A, Dupuy B, Viader F, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2006) Retrieval mechanisms for autobiographical memories: insights from the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia 44:2386–2397
Moll J, de Oliveira-Souza R, Moll FT, Bramati IE, Andreiuolo PA (2002) The cerebral correlates of set-shifting: an fMRI study of the trail making test. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 60:900–905
Mummery CJ, Patterson K, Wise RJ, Vandenbergh R, Price CJ, Hodges JR (1999) Disrupted temporal lobe connections in semantic dementia. Brain 122:61–73
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss DT, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A, Robert PH, Albert M, Boone K, Miller BL, Cummings J, Benson DF (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
Pasquier F, Lebert F, Grymonprez L, Petit H (1995) Verbal fluency in dementia of frontal lobe type and dementia of Alzheimer type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:81–84
Paulesu E, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS (1993) The neural correlates of the verbal component of working memory. Nature 362:342–345
Paulesu E, Goldacre B, Scifo P, Cappa SF, Gilardi MC, Castiglioni I, Perani D, Fazio F (1997) Functional heterogeneity of left inferior frontal cortex as revealed by fMRI. Neuroreport 8:2011–2017
Perret E (1974) The left frontal lobe of man and the suppression of habitual responses in verbal categorical behaviour. Neuropsychologia 12:323–330
Perry RJ, Hodges JR (2000) Differentiating frontal and temporal variant frontotemporal dementia from Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 54:2277–2284
Petersen SE, Fox PT, Posner MI, Mintun M, Raichle ME (1988) Positron emission tomographic studies of the cortical anatomy of single-word processing. Nature 331:585–589
Petrides M, Alivisatos B, Meyer E, Evans AC (1993) Functional activation of the human frontal cortex during the performance of verbal working memory tasks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:878–882
Piolino P, Chételat G, Matuszewski V, Landeau B, Mézenge F, Viader F, de la Sayette V, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2007) In search of autobiographical memories: A PET study in the frontal variant of frontotemporal dementia. Neuropsychologia 45:2730–2743
Price CJ, Mummery CJ, Moore CJ, Frakowiak RS, Friston KJ (1999) Delineating necessary and sufficient neural systems with functional imaging studies of neuropsychological patients. J Cogn Neurosci 11:371–382
Quarantelli M, Berkouk K, Prinster A, Landeau B, Svarer C, Balkay L, Alfano B, Brunetti A, Baron JC, Salvatore M (2004) Integrated software for the analysis of brain PET/SPECT studies with partial-volume-effect correction. J Nucl Med 45:192–201
Quinette P, Guillery B, Desgranges B, de la Sayette V, Viader F, Eustache F (2003) Working memory and executive functions in transient global amnesia. Brain 126:1917–1934
Rahman S, Sahakian BJ, Hodges JR, Rogers RD, Robbins TW (1999) Specific cognitive deficits in mild frontal variant frontotemporal dementia. Brain 122:1469–1493
Rascovsky K, Salmon DP, Hansen LA, Thal LJ, Galasko D (2007) Disparate letter and semantic category fluency deficits in autopsy-confirmed frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology 21:20–30
Rauchs G, Piolino P, Mézenge F, Landeau B, Lalevée C, Pélerin A, Viader F, de la Sayette V, Eustache F, Desgranges B (2007) Autonoetic consciousness in Alzheimer’s disease: neuropsychological and PET findings using an episodic learning and recognition task. Neurobiol Aging 28:1410–1420
Reitan RM (1958) Validity of the Trail Making test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 8:271–276
Rogers TT, Ivanoiu A, Patterson K, Hodges JR (2006) Semantic memory in Alzheimer’s disease and the frontotemporal dementias: a longitudinal study of 236 patients. Neuropsychology 20:319–335
Rogers TT, Lambon Ralph MA, Garrard P, Bozeat S, McClelland JL, Hodges JR, Patterson K (2004) Structure and deterioration of semantic memory: a neuropsychological and computational investigation. Psychol Rev 111:205–235
Rosser AE, Hodges JR (1994) The Dementia Rating Scale in Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol 241:531–536
Ruff RM, Light RH, Parker SB, Levin HS (1997) The psychological construct of word fluency. Brain Lang 57:394–405
Salmon E, Garraux G, Delbeuck X, Collette F, Kalbe E, Zuendorf G, Perani D, Fazio F, Herholz K (2003) Predominant ventromedial frontopolar metabolic impairment in frontotemporal dementia. NeuroImage 20:435–440
Snowden JS, Bathgate D, Varma AR, Blackshaw A, Gibbons ZC, Neary D (2001) Distinct behavioural profiles in frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:323–332
Snowden JS, Goulding PJ, Neary D (1989) Semantic dementia: a form of circumscribed cerebral atrophy. Behav Neurol 2:167–182
Tomaszewski-Farias S, Jagust W (2004) Neuroimaging in non-Alzheimer’s dementias. Clin Neurosci Res 3:383–395
Troyer AK, Moscovitch M, Winocur G, Alexander MP, Stuss DT (1998) Clustering and switching on verbal fluency: the effects of focal frontal- and temporal-lobe lesions. Neuropsychologia 36:499–504
Tulving E, Habib R, Nyberg L, Lepage M, McIntosh AR (1999) Positron emission tomography correlations in and beyond medial temporal lobes. Hippocampus 9:71–82
Tyler LK, Bright P, Dick E, Tavares P, Pilgrim L, Fletcher P, Greer MJ, Moss HE (2003) Do semantic categories activate distinct cortical regions? Evidence for a distributed neural semantic system. Cogn Neuropsychol 20:541–559
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15:273–289
Wager TD, Jonides J, Reading S (2004) Neuroimaging studies of shifting attention: a meta-analysis. NeuroImage 22:1679–1693
Williams GB, Nestor PJ, Hodges JR (2005) Neural correlates of semantic and behavioural deficits in frontotemporal dementia. NeuroImage 24:1042–1051
Zakzanis KK, Mraz R, Graham SJ (2005) An fMRI study of the Trail making test. Neuropsychologia 43:1878–1886
Zurowski B, Gostomzyk J, Gron G, Weller R, Schirrmeister H, Neumeier B, Spitzer M, Reske SN, Walter H (2002) Dissociating a common working memory network from different neural substrates of phonological and spatial stimulus processing. NeuroImage 15:45–57
Acknowledgments
First, we are indebted to the patients, their families and to the control subjects for their willingness to devote such time and effort to this experiment. We also wish to thank Prof. F. Viader, Prof. D. Hannequin, Dr F. Ledoze, L. Bon, E. Bliaux, C. Descat, C. Giry, C. Lalevée, J. Lambert, N. Loisel, and A. Pélerin for their contributions to this study. M.L.’s research was funded by the Conseil Régional de Basse-Normandie, Eisai, Lundbeck, Novartis and Pfizer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laisney, M., Matuszewski, V., Mézenge, F. et al. The underlying mechanisms of verbal fluency deficit in frontotemporal dementia and semantic dementia. J Neurol 256, 1083–1094 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5073-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5073-y