Abstract
Introduction
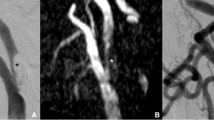
In highgrade stenosis, carotid artery stenting (CAS) may be chosen as an alternative to carotid surgery. Ischemic periprocedural complications may be documented best with diffusion–weighted MRI (DWMRI). In this prospective study serial DW–MRI and color–coded duplex sonography (CCDS) were used to identify carotid stenosis, which is associated with an increased risk of ischemic events due to CAS.
Methods
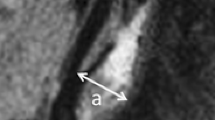
High resolution DW–MRI were performed in 74 out of 77 patients before and after CAS. All MRI scans were analyzed in a blinded manner. With CCDS each carotid stenosis was evaluated according to the grade, length, echo properties and plaque surface.
Results
In 42 out of 74 patients (56.8 %) a total of 188 new procedure– related DWI–lesions could be detected, while in 32 patients MRI–controls remained normal. Of the lesions 79.25 % had a size < 1 cm. In one major and two minor strokes due to CAS (total complication rate 3.9 %) corresponding territorial infarcts could be demonstrated. A highly significant correlation was found between the length of the stenosis and the incidence of new DWI–lesions (p = 0.0141). In contrast, neither the grade of ICA stenosis nor the sonographic plaque morphology or plaque surface correlated with the number of DWI–lesion in postinterventional scans.
Conclusions
The length—and not the degree—of an ICA stenosis seems to be the most decisive sonographic factor for estimating the periprocedural risk of embolism. DWI–lesions are much more frequent than clinical complications and may represent an important surrogate marker for improving the techniques of carotid artery stenting, especially comparing the benefit of different mechanical protection devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phatouros CC, Higashida RT, Malek AM, Meyers PM, Lempert TE, Dowd CF, et al. (2000) Carotid artery stent placement for atherosclerotic disease: rationale, technique and current status. Radiology 217:26–41
Roubin GS, New G, Iyer SS, Vitek JJ, Al Mubarak N, Liu MW, et al. (2001) Immediate and Late Clinical Outcomes of Carotid Artery Stenting in Patients With Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis: A 5–Year Prospective Analysis. Circulation 103(4):532–537
Wholey MH, Wholey M, Mathias K, Roubin GS, Diethrich EB, Henry M, et al. (2000) Global experience in cervical carotid artery stent placement. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 50(2):160–167
Mathur A, Roubin GS, Iyer SS, Piamsonboon C, Liu MW, Gomez CR, et al. (1998) Predictors of Stroke Complicating Carotid Artery Stenting. Circulation 97:1239–1245
Markus HS, Clifton A, Buckenham T, Brown MM (1994) Carotid angioplasty. Detection of embolic signals during and after the procedure. Stroke 25:2403–2406
Crawley F, Stygall J, Lunn S, Harrison M, Brown MM, Newman S (2000) Comparison of microembolism detected by transcranial Doppler and neuropsychological sequelae of carotid surgery and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Stroke 31:1329–1334
Orlandi G, Fanucchi S, Fioretti C, Acerbi G, Puglioli M, Padolecchia R, et al. (2001) Characteristics of cerebral microembolism during carotid stenting and angioplasty alone. Arch Neurol 58:1410–1413
Bendszus M, Koltzenburg M, Burger R, Warmuth–Metz M, Hofmann E, Solymosi L (1999) Silent embolism in diagnostic cerebral angiography and neurointerventional procedures: a prospective study. Lancet 354(9190):1594–1597
Jaeger HJ, Mathias KD, Drescher R, Hauth E, Bockisch G, Demirel E, et al. (2001) Diffusion–weighted MR imaging after angioplasty or angioplasty plus stenting of arteries supplying the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1251–1259
Lövblad KO, Plüschke W, Remonda L, Gruber–Wiest D, Do DD, Barth A, et al. (2000) Diffusion–weighted MRI for monitoring neurovascular interventions. Neuroradiology 42:134–138
Tomczak R, Wunderlich A, Liewald F, Stuber G, Gorich J (2001) Diffusionweighted MRI: detection of cerebral ischemia before and after carotid thromboendarterectomy. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25:247–250
Forbes KP, Shill HA, Britt PM, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF, Heiserman JE (2001) Assessment of silent embolism from carotid endarterectomy by use of diffusion–weighted imaging: work in progress. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:650–653
Feiwell RJ, Besmertis L, Sarkar R, Saloner DA, Rapp JH (2001) Detection of clinically silent infarcts after carotid endarterectomy by use of diffusionweighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:646–649
Muller M, Reiche W, Langenscheidt P, Hassfeld J, Hagen T (2000) Ischemia after carotid endarterectomy: comparison between transcranial Doppler sonography and diffusion–weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:47–54
Carpenter JP, Lexa FJ, Davis JT (1996) Determination of Duplex Doppler Ultrasound Criteria Appropriate to the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial. Stroke 27:695–699
Huston J, Nichols DA, Luetmer PH, Rydberg CH, Lewis BD, Meyer FB, et al. (1998) MR angiographic and sonographic indications for endarterectomy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:309–315
Alexandrov AV, Brodie DS, McLean A, Hamilton P, Murphy J, Burns PN (1997) Correlation of Peak Systolic Velocity and Angiographic Measurement of Carotid Stenosis Revisited. Stroke 28(2):339–342
Goertler M, Widder B, Schuetz U (1996) Quantifying medium– and high–grade carotid artery stenosis by ultrasound. J E M U 17:235–239
Widder B (1999) Doppler– und Duplexsonographie der hirnversorgenden Arterien. 5 ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Rubba P, Mercuri M, Faccenda F, Iannuzzi A, Irace C, Strisciuglio P, et al. (1994) Premature carotid atherosclerosis: does it occur in both familial hypercholesterolemia and homocystinuria? Ultrasound assessment of arterial intima–media thickness and blood flow velocity. Stroke 25:943–950
Friese S, Krapf H, Fetter M, Klose U, Skalej M, Küker W (2001) Ultrasonography and contrast–enhanced MRA in ICA–stenosis: is conventional angiography obsolete? J Neurol 248:506–513
Küker W, Weise J, Krapf H, Schmidt F, Friese S, Bähr M (2002) MRI characteristics of acute and subacute brainstem and thalamic infractions: value of T2– and diffusion–weighted sequences. J Neurol 249:33–42
Hobson RW, Lal BK, Chakhtoura E, Goldstein J, Haser PB, Kubicka R, et al. (2003) Carotid artery stenting: analysis of data for 105 patients at high risk. J Vasc Surg 37:1234–1239
Hahnel S, Bender J, Jansen O, Hartmann M, Knauth M, Busing K, et al. (2001) [Clinically silent cerebral embolisms after cerebral catheter angiography]. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 173:300–305
van Heesewijk HP, Vos JA, Louwerse ES, Van Den Berg JC, Overtoom TT, Ernst SM, et al. (2002) New brain lesions at MR imaging after carotid angioplasty and stent placement. Radiology 224:361–365
Alexandrov AV (2003) Ultrasound and angiography in the selection of patients for carotid endarterectomy. Curr Cardiol Rep 5:141–147
Kastrup A, Gröschel K, Krapf H, Brehm B, Dichgans J, Schultz J (2003) Early outcome of carotid angioplasty and stenting with and without cerebral protection devices. Stroke 34:813–819
Barr JD, Connors JJ, Sacks D, Wojak JC, Becker GJ, Cardella JF, et al. (2003) Quality improvement guidelines for the performance of cervical carotid angioplasty and stent placement. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:2020–2034
Mathiesen EB, Bonaa KH, Joakimsen O (2001) Echolucent plaques are associated with high risk of ischemic cerebrovascular events in carotid stenosis: the Tromso study. Circulation 103:2171–2175
Liapis CD, Kakisis JD, Kostakis AG (2001) Carotid stenosis: factors affecting symptomatology. Stroke 32:2782–2786
Orlandi G, Fanucchi S, Fioretti C, Acerbi G, Puglioli M, Padolecchia R, et al. (2001) Characteristics of cerebral microembolism during carotid stenting and angioplasty alone. Arch Neurol 58:1410–1413
Tegos TJ, Sabetai MM, Nicolaides AN, Elatrozy TS, Dhanjil S, Stevens JM (2001) Patterns of brain computed tomography infarction and carotid plaque echogenicity. J Vasc Surg 33:334–339
Wholey MH, Wholey M (2003) Current status in cervical carotid artery stent placement. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 44:331–339
Castriota F, Cremonesi A, Manetti R, Liso A, Oshola K, Ricci E, et al. (2002) Impact of cerebral protection devices on early outcome of carotid stenting. J Endovasc Ther 9:786–792
Jaeger H, Mathias K, Drescher R, Hauth E, Bockisch G, Demirel E, et al. (2001) Clinical results of cerebral protection with a filter device during stent implantation of the carotid artery. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 24:249–256
Macdonald S, McKevitt F, Venables GS, Cleveland TJ, Gaines PA (2002) Neurological outcomes after carotid stenting protected with the NeuroShield filter compared to unprotected stenting. J Endovasc Ther 9:777–785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krapf, H., Nägele, T., Kastrup, A. et al. Risk factors for periprocedural complications in carotid artery stenting without filter protection. J Neurol 253, 364–371 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0005-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0005-y