Abstract
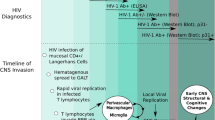
HIV-1-associated en cephalopathy (HIVE) remains an important manifestation of advanced HIV infection despite recent advances in antiretroviral therapy. Special pharmacological and virological conditions predominate in the central nervous system (CNS). HIVE is characterized by "subcortical" dementia which becomes manifest as psychomotor slowing as well as mernory and concentration deficits. Deficits of central motor function are an invariable finding. Enhanced viral replication in immunocompetent CNS cells is believed to be the pathogenic basis of CNS disease. This process leads to neurotoxic effects elicited directly by viral products as well as indirectly by the immune response to the virus. HIV-1 associated myelopathy (HIVM) is the other CNS manifestion of advanced HIV-1 infection. The present consensus paper recommends diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in HIVE and HIVM and outlines the state of current research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Additional information
Received: 16 February 2001 Accepted: 3 December 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eggers, C., for the German Neuro-AIDS Working Group. HIV-1 associated encephalopathy and myelopathy. J Neurol 249, 1132–1136 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0721-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0721-5