Abstract
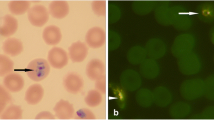
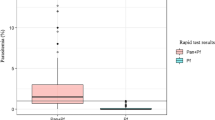
To test the diagnostic value of a rapid and simple immunochromatographic test (ICT) based on the detection of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP2) for post-mortem examination, blood samples from 30 consecutive corpses were analysed by ICT and Giemsa-stained blood films. Compared to microscopy, ICT had 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity even after a considerable time had passed between the presumed time of death and testing or after prolonged storage of whole blood samples. The ICT yielded positive results for four travellers who had returned from Kenya and died from Pl. falciparum malaria. The ICT might therefore serve as an additional tool for rapid malaria diagnosis, especially in non-endemic countries where experience with microscopic malaria detection is limited.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 August 1999 / Received in revised form: 7 October 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sing, A., Rauch, E., Roggenkamp, A. et al. Evaluation of the ICT Malaria Pf test for rapid post-mortem diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in corpses examined for forensic reasons. Int J Leg Med 113, 251–252 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004149900123
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004149900123