Abstract
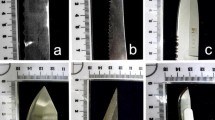
Skeletal cut mark analysis provides relevant information on the general class characteristics of suspect knife. However, there is a lack of research on the influence of blade damage on cut mark analysis. This study aimed to thoroughly investigate the effects of damaged knife blades on cut marks’ morphological and morphometrical characteristics. Fifteen undamaged, non-serrated knives were used to cut human ribs to make control cut marks. The knife blades were then damaged by a series of cuts on the bones. A comparison was made between the control cuts and 3 groups of cut marks inflicted by blades that had been damaged to different degrees. The results showed that the damaged blades created wider cut marks than undamaged one. Kerf morphology was likely to imitate the cuts made by the serrated blades such as an elliptical shape, a V-shaped cross-section and the presence of coarse striations. Wear-related features can affect cut mark analysis as the marks left behind by blades damaged to different degrees showed dissimilar dimensions and morphologies. The findings of this study can be applied to a forensic investigation when cut marks were caused by a knife with a damaged blade.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panichabhongse V, Smativat V, Watanakajorn T, Kasantikul V (1999) Homicide: a report of 4,122 cases from Bangkok and provinces. J Med Assoc Thai 82(9):849–854
Ambade VN, Gobble HV (2006) Comparison of wound patterns in homicide by sharp and blunt force. Forensic Sci Int 156:166–170
Banasr A, de la Grandmaison GL, Durigon M (2003) Frequency of bone/ cartilage lesions in stab and incised wounds fatalities. Forensic Sci Int 131:131–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0379-0738(02)00429-2
Scientific Working Group for Forensic Anthropology (SWGANTH). 2011, Trauma analysis https://www.nist.gov/system/files/documents/2018/03/13/swganth_trauma.pdf (accessed 01/12/2021)
Christensen AM, Passalacqua NV, Bartelink EJ (2019) Analysis of skeletal trauma. Forensic anthropology: current methods and practice, 1st edn. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 341–377
Love JC (2019) Sharp force trauma analysis in bone and cartilage: a literature review. Forensic Sci Int 299:199–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.03.035
Pounder DJ, Reeder FD (2010) Striation patterns in serrated blade stabs to cartilage. Forensic Sci Int 208:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.11.015
Tegtmeyer CE (2012) A comparative analysis of serrated and non-serrated sharp force trauma to bone. MA dissertation, Texas State University-San Marcos, USA
Kooi RJ, Fairgrieve SI (2013) SEM and stereomicroscopic analysis of cut marks in flesh and burned bone. J Forensic Sci 58(2):452–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12050
Crowder C, Rainwater CW, Fridie JS (2013) Microscopic analysis of sharp force trauma in bone and cartilage: a validation study. J Forensic Sci 58(5):1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12180
Vachirawongsakorn V, Painter J, Marquez-Grant N (2022) Knife cut marks inflicted by different blade types and the changes induced by heat: a dimensional and morphological study. Int J Leg Med 136(1):329–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-021-02726-5
Ferllini R (2012) Macroscopic and microscopic analysis of knife stab wounds on fleshed and clothed ribs. J Forensic Sci 57(3):683–690. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2012.02087.x
Komo L, Grassberger M (2018) Experimental sharp force injuries to ribs: multimodal morphological and geometric morphometric analyses using micro-CT, macro photography and SEM. Forensic Sci Int 288:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.04.048
Cerutti E, Magli F, Porta D, Gibelli D, Cattaneo C (2014) Metrical assessment of cut marks on bone: is size important? Leg Med 16(4):208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2014.03.010
Lewis JE (2008) Identifying sword marks on bone: criteria for distinguishing between cut marks made by different classes of blade weapons. J Archaeo Sci 35:2001–2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2008.01.016
Lynn KS, Fairgrieve SI (2009) Macroscopic analyses of axe and hatchet trauma in fleshed and defleshed mammalian long bones. J Forensic Sci 54(4):786–792. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01061.x
Sandras A, Guilbeau-Frugier C, Savall F, Telmon N, Capuani C (2018) Sharp bone trauma diagnosis: a validation study using epifluorescence microscopy. Int J Leg Med 133(2):521–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1944-z
Tennick CJ (2012) The identification and classification of sharp force trauma on bone using low power microscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Central Lancashire, UK. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1944-z
Norman DG, Watson DG, Burnett B, Fenne PM, Williams MA (2018) The cutting edge: micro-CT for quantitative toolmark analysis of sharp force trauma to bone. Forensic Sci Int 283:156–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.12.039
Menschel M, Pokines JT, Reinecke G (2021) Correlation between saw blade width and kerf width. J Forensic Sci 66(1):25–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.14556
Sánchez-Molina D, Galtés I, García-Vilana S, Velázquez-Ameijide J (2023) A probabilistic model for murder weapon identification using stab-marks in human ribs. Int J Legal Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-022-02933-8
Bello SM, Parfitt SA, Stringer C (2009) Quantitative micromorphological analyses of cut marks produced by ancient and modern handaxes. J Archaeol Sci 36(9):1869–1880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2009.04.014
Capuani C, Telmon N, Moscovici J, Molinier F, Aymeric A, Delisle M et al (2014) Modeling and determination of directionality of the kerf in epifluorescence sharp bone trauma analysis. Int J Leg Med 128(6):1059–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-014-1022-0
Ofele AS, Eliopoulos C, Borrini M (2018) Sharp force trauma: the effects of blade damage on cut mark characteristics. SF J Forensics 1:2
Freas LE (2012) Assessment of wear-related features of the kerf wall from saw marks in bone. J Forensic Sci 55(6):1561–1569. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2010.01468.x
Henderson JP, Morgan SE, Patel M, Tiplady ME (2005) Patterns of non-firearm homicide. J Clin Forensic Med 12(3):128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcfm.2004.10.011
Hunt AC, Cowling RJ (1991) Murder by stabbing. Forensic Sci Int 52(1):107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-0738(91)90102-O
Vachirawongsakorn V, Marquez-Grant N, Painter J (2023) Survival of sharp force trauma in burnt bones: effects of environmental factors. Int J Legal Med 137:809–823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-022-02916-9
Boschin F, Crezzini J (2012) Morphometrical analysis on cut marks using a 3D digital microscope. Int J Osteoarchaeol 22(5):549–562. https://doi.org/10.1002/oa.1272
Cerutti E, Spagnoli L, Araujo N, Gibelli D, Mazzarelli D, Cattaneo C (2016) Analysis of cutmarks on bone: can light microscopy be of any help? Am J Forensic Med Pathol 37(4):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAF.0000000000000260
Humphrey C, Kumaratilake J, Henneberg M (2017) Characteristics of bone injuries resulting from knife wounds incised with different forces. J Forensic Sci 62(6):1445–1451. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13467
Bello SM, Soligo C (2008) A new method for the quantitative analysis of cutmark micromorphology. J Archaeol Sci 35:1542–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2007.10.018
Bartelink EJ, Wiersema JM, Demaree RS (2001) Quantitative analysis of sharp-force trauma: an application of scanning electron microscopy in forensic anthropology. J Forensic Sci 46(6):1288–1293
Thompson TJU, Inglis J (2009) Differentiation of serrated and non-serrated blades from stab marks in bone. Int J Legal Med 123:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-008-0275-x
Acknowledgements
We give special thanks to Assist. Prof. Chulaluk Komoltri for her assistance with the statistical analyses. We also thank Ms. Maneerat Saithong for her help with the graphic design preparation. We are also indebted to Mr. David Park for the English-language editing of this manuscript. Finally, we thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was fully approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanyavises, K., Vachirawongsakorn, V. Stereomicroscopic analysis of cut marks inflicted by a knife with blade damage. Int J Legal Med 138, 15–23 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-023-03102-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-023-03102-1