Abstract
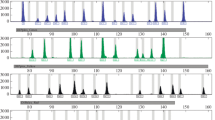
Living in the heart of Eurasia, the Kyrgyz ethnic minority have a complex human evolutionary and migration history. However, the genetic architecture of the Kyrgyz population has not been fully explored. We studied 526 Kyrgyz samples from Kizilsu Kirghiz Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang using the Investigator® DIPplex kit. All loci followed Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE). The combined power of discrimination (CPD) and combined power of paternity exclusion (CPE) was 0.9999999999988 and 0.9936, respectively. Compared with 90 reference populations, five InDels (HLD99, HLD81, HLD64, HLD118, and HLD111) have the potential to distinguish the Kyrgyz/Uyghur/Kazak population from other East Asian populations. Our results suggested a close genetic relationship between the Kyrgyz population and the Uyghur/Kazak populations, followed by South Asian populations. This was in accordance with the inland migration hypothesis or modern human migration influenced by warfare. Overall, this system can be used as a powerful tool in forensic individual identification and as a complementary tool in paternity cases and biogeographic ancestry analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng QD, Lu Y, Ni XM, Yuan K, Yang YJ, Yang X, Liu C, Lou HY, Ning ZL, Wang YC, Lu DS, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Shi M, Tian L, Wang XJ, Zhang X, Li J, Khan A, Guan YQ, Tang K, Wang SJ, Xu SH (2017) Genetic history of Xinjiang's Uyghurs suggests bronze age multiple-way contacts in Eurasia. Mol Biol Evol 34(10):2572–2582. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx177
Xie M, Song F, Li J, Lang M, Luo H, Wang Z, Wu J, Li C, Tian C, Wang W, Ma H, Song Z, Fan Y, Hou Y (2019) Genetic substructure and forensic characteristics of Chinese Hui populations using 157 Y-SNPs and 27 Y-STRs. Forensic Sci Int Genet 41:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.03.022
Guo Y, Chen C, Xie T, Cui W, Meng H, Jin X, Zhu B (2018) Forensic efficiency estimate and phylogenetic analysis for Chinese Kyrgyz ethnic group revealed by a panel of 21 short tandem repeats. R Soc Open Sci 5(6):172089. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.172089
Peng MS, Xu WF, Song JJ, Chen X, Sulaiman X, Cai LH, Liu HQ, Wu SF, Gao Y, Abdulloevich NT, Afanasevna ME, Ibrohimovich KB, Chen X, Yang WK, Wu M, Li GM, Yang XY, Rakha A, Yao YG, Upur H, Zhang YP (2018) Mitochondrial genomes uncover the maternal history of the Pamir populations. Eur J Hum Genet 26(1):124–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-017-0028-8
Zhan XN, Adnan A, Zhou YZ, Khan A, Kasim K, McNevin D (2018) Forensic characterization of 15 autosomal STRs in four populations from Xinjiang, China, and genetic relationships with neighboring populations. Sci Rep 8:4673. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22975-6
Guo YX, Chen C, Jin XY, Cui W, Wei YY, Wang HD, Kong TT, Mu YL, Zhu BF (2018) Autosomal DIPs for population genetic structure and differentiation analyses of Chinese Xinjiang Kyrgyz ethnic group. Sci Rep 8:11054. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29010-8
Guo YX, Chen C, Xie T, Cui W, Meng HT, Jin XY, Zhu BF (2018) Forensic efficiency estimate and phylogenetic analysis for Chinese Kyrgyz ethnic group revealed by a panel of 21 short tandem repeats. Roy Soc Open Sci 5(6):172089. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.172089
Li Y, Li X, Chen WY, Fan YJ, Xie MK, Wu J (2019) Allele and haplotype frequencies of 19 X-STRs in the Kyrgyz and Han populations from Kizilsu prefecture. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 40:E259–E261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.02.007
Li Y, Li X, Chen W, Fan Y, Xie M, Wu J (2019) Allele and haplotype frequencies of 19 X-STRs in the Kyrgyz and Han populations from Kizilsu prefecture. Forensic Sci Int Genet 40:e259–e261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.02.007
Excoffier L, Lischer HE (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10(3):564–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02847.x
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2007) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles. Mol Ecol Notes 7(4):574–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x
He G, Wang Z, Wang M, Luo T, Liu J, Zhou Y, Gao B, Hou Y (2018) Forensic ancestry analysis in two Chinese minority populations using massively parallel sequencing of 165 ancestry-informative SNPs. Electrophoresis 39(21):2732–2742. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800019
Underhill PA, Passarino G, Lin AA, Shen P, Mirazon Lahr M, Foley RA, Oefner PJ, Cavalli-Sforza LL (2001) The phylogeography of Y chromosome binary haplotypes and the origins of modern human populations. Ann Hum Genet 65(Pt 1):43–62. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-1809.2001.6510043.x
Lou H, Li S, Jin W, Fu R, Lu D, Pan X, Zhou H, Ping Y, Jin L, Xu S (2015) Copy number variations and genetic admixtures in three Xinjiang ethnic minority groups. Eur J Hum Genet 23(4):536–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.134
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 81701866) and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Central South University (No. 229795).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sichuan University, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, M., Li, Y., Wu, J. et al. Genetic structure and forensic characteristics of the Kyrgyz population from Kizilsu Kirghiz autonomous prefecture based on autosomal DIPs. Int J Legal Med 136, 539–541 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-020-02277-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-020-02277-1