Abstract
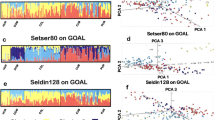
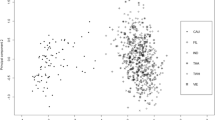
DNA can provide forensic intelligence regarding a donor’s biogeographical ancestry (BGA) and other externally visible characteristics (EVCs). A number of algorithms have been proposed to assign individual human genotypes to a BGA using ancestry informative marker (AIM) panels. This study compares the BGA assignment accuracy of the population clustering program STRUCTURE and three generic classification approaches including a Bayesian algorithm, genetic distance, and multinomial logistic regression (MLR). A selection of 142 ancestry informative single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were chosen from existing marker panels (SNPforID 34-plex, Eurasiaplex, Seldin, and Kidd’s AIM panels) to assess BGA classification at the continental level for Africans, Europeans, East Asians, and Amerindians. A training set of 1093 individuals with self-declared BGA from the 1000 Genomes phase 1 database was used by each classifier to predict BGA in a test set of 516 individuals from the HGDP-CEPH (Stanford) cell line panel. Tests were repeated with 0, 10, 50, 70, and 90% of the genotypes missing. Comparison of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUROCs) showed high accuracy in STRUCTURE and the generic Bayesian approach. The latter algorithm offers a computationally simpler alternative to STRUCTURE with little loss in accuracy and is suitable for phenotype prediction while STRUCTURE is not.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V, Thein SL (1985) Individual-specific ‘fingerprints’ of human DNA. Nature 316(4):76–79. doi:10.1038/316076a0
Phillips C, Aradas AF, Kriegel AK, Fondevila M, Bulbul O, Santos C, Serrulla Rech F, Perez Carceles MD, Carracedo Á, Schneider PM, Lareu MV (2013) Eurasiaplex: a forensic SNP assay for differentiating European and South Asian ancestries. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 7(3):359–366. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2013.02.010
Phillips C, Salas A, Sanchez JJ, Fondevila M, Gómez-Tato A, Alvarez-Dios J, Calaza M, de Cal Casares M, Ballard D, Lareu MV, Carracedo Á, The SNPforID Consortium (2007) Inferring ancestral origin using a single multiplex assay of ancestry-informative marker SNPs. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 1(3):273–280. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2007.06.008
Kidd KK, Speed WC, Pakstis AJ, Furtado MR, Fang R, Madbouly A, Maiers M, Middha M, Friedlaender FR, Kidd JR (2014) Progress toward an efficient panel of SNPs for ancestry inference. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 10:23–32. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2014.01.002
Kosoy R, Nassir R, Tian C, White PA, Butler LM, Silva G, Kittles R, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Gregersen PK, Belmont JW, De La Vega FM, Seldin MF (2009) Ancestry informative marker sets for determining continental origin and admixture proportions in common populations in America. Hum Mutat 30(1):69–78. doi:10.1002/humu.20822
Fondevila M, Phillips C, Santos C, Aradas AF, Vallone PM, Butler JM, Lareu MV, Carracedo A (2013) Revision of the SNPforID 34-plex forensic ancestry test: assay enhancements, standard reference sample genotypes and extended population studies. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 7(1):63–74. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.06.007
Dang M-TN, Hambleton J, Kayser SR (2005) The influence of ethnicity on warfarin dosage requirement. Ann Pharmacother 39(6):1008–1012. doi:10.1345/aph.1E566
Gan GG, Teh A, Goh KY, Chong HT, Pang KW (2003) Racial background is a determinant factor in the maintenance dosage of warfarin. Int J Hematol 78(1):84–86. doi:10.1007/BF02983247
Min DI, Lee M, Ku Y-M, Flanigan M (2000) Gender-dependent racial difference in disposition of cyclosporine among healthy African American and white volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 68(5):478–486. doi:10.1067/mcp.2000.111255
Deffenbacher KA (1980) Eyewitness accuracy and confidence. Law Human Behav 4(4):243–260. doi:10.1007/BF01040617
Steblay NK, Tix RW, Benson SL (2013) Double exposure: the effects of repeated identification lineups on eyewitness accuracy. Appl Cognitive Psych 27(5):644–654. doi:10.1002/acp.2944
Wells GL, Lindsay RC, Tousignant J (1980) Effects of expert psychological advice on human performance in judging the validity of eyewitness testimony. Law Human Behav 4(4):275. doi:10.1007/BF01040619
Wells GL, Olson EA (2003) Eyewitness testimony. Annu Rev Psychol 54(1):277–295. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145028
IGSR: The International Genome Sample Resource (2015) The 1000 Genomes Project Phase 1. http://www.1000genomes.org/
Fondation Jean-Dausset HGDP-CEPH Human Genome Diversity Cell Line Panel. http://www.cephb.fr/en/hgdp_panel.php. Accessed 21 Sept 2016
Amigo J, Salas A, Phillips C, Carracedo A (2008) SPSmart: adapting population based SNP genotype databases for fast and comprehensive web access. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1):428. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-428
1000 Genomes Project Consortium (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491(7422):56–65. doi:10.1038/nature11632
1000 Genomes Project Consortium (2015) A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526(7571):68–74. doi:10.1038/nature15393
Sudmant PH, Rausch T, Gardner EJ, Handsaker RE, Abyzov A, Huddleston J, Zhang Y, Ye K, Jun G, Fritz MH-Y, Konkel MK, Malhotra A, Stütz AM, Shi X, Casale FP, Chen J, Hormozdiari F, Dayama G, Chen K, Malig M, Chaisson MJP, Walter K, Meiers S, Kashin S, Garrison E, Auton A, Lam HYK, Mu XJ, Alkan C, Antaki D, Bae T, Cerveira E, Chines P, Chong Z, Clarke L, Dal E, Ding L, Emery S, Fan X, Gujral M, Kahveci F, Kidd JM, Kong Y, Lameijer E-W, McCarthy S, Flicek P, Gibbs RA, Marth G, Mason CE, Menelaou A, Muzny DM, Nelson BJ, Noor A, Parrish NF, Pendleton M, Quitadamo A, Raeder B, Schadt EE, Romanovitch M, Schlattl A, Sebra R, Shabalin AA, Untergasser A, Walker JA, Wang M, Yu F, Zhang C, Zhang J, Zheng-Bradley X, Zhou W, Zichner T, Sebat J, Batzer MA, McCarroll SA, The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium, Mills RE, Gerstein MB, Bashir A, Stegle O, Devine SE, Lee C, Eichler EE, Korbel JO (2015) An integrated map of structural variation in 2,504 human genomes. Nature 526(7571):75–81. doi:10.1038/nature15394
Cann HM, De Toma C, Cazes L, Legrand M-F, Morel V, Piouffre L, Bodmer J, Bodmer WF, Bonne-Tamir B, Cambon-Thomsen A (2002) A human genome diversity cell line panel. Science 296(5566):261. doi:10.1126/science.296.5566.261b
Rosenberg NA (2006) Standardized subsets of the HGDP-CEPH human genome diversity cell line panel, accounting for atypical and duplicated samples and pairs of close relatives. Ann Hum Genet 70(6):841–847. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2006.00285.x
Li JZ, Absher DM, Tang H, Southwick AM, Casto AM, Ramachandran S, Cann HM, Barsh GS, Feldman M, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Myers RM (2008) Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation. Science 319(5866):1100–1104. doi:10.1126/science.1153717
Tishkoff SA, Kidd KK (2004) Implications of biogeography of human populations for ‘race’ and medicine. Nat Genet 36:S21–S27. doi:10.1038/ng1438
Collins-Schramm HE, Chima B, Morii T, Wah K, Figueroa Y, Criswell LA, Hanson RL, Knowler WC, Silva G, Belmont JW, Seldin MF (2004) Mexican American ancestry-informative markers: examination of population structure and marker characteristics in European Americans, Mexican Americans, Amerindians and Asians. Hum Genet 114(3):263–271. doi:10.1007/s00439-003-1058-6
Halder I, Shriver M, Thomas M, Fernandez JR, Frudakis T (2008) A panel of ancestry informative markers for estimating individual biogeographical ancestry and admixture from four continents: utility and applications. Hum Mutat 29(5):648–658. doi:10.1002/humu.20695
Frudakis T, Venkateswarlu K, Thomas MJ, Gaskin Z, Ginjupalli S, Gunturi S, Ponnuswamy V, Natarajan S, Nachimuthu PK (2003) A classifier for the SNP-based inference of ancestry. J Forensic Sci 48(4):771–782
Santos C, Phillips C, Fondevila M, Daniel R, van Oorschot RA, Burchard EG, Schanfield MS, Souto L, Uacyisrael J, Via M (2016) Pacifiplex: an ancestry-informative SNP panel centred on Australia and the Pacific region. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 20:71–80. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.10.003
Kidd JR, Friedlaender FR, Speed WC, Pakstis AJ, De La Vega FM, Kidd KK (2011) Analyses of a set of 128 ancestry informative single-nucleotide polymorphisms in a global set of 119 population samples. Investig Genet 2(1):1. doi:10.1186/2041-2223-2-1
Nassir R, Kosoy R, Tian C, White PA, Butler LM, Silva G, Kittles R, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Gregersen PK, Belmont JW, De La Vega FM, Seldin MF (2009) An ancestry informative marker set for determining continental origin: validation and extension using human genome diversity panels. BMC Genet 10(1):39. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-10-39
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959
McNevin D, Santos C, Gómez-Tato A, Álvarez-Dios J, Casares de Cal M, Daniel R, Phillips C, Lareu MV (2013) An assessment of Bayesian and multinomial logistic regression classification systems to analyse admixed individuals. Forensic Sci Int-Gen-Supp 4(1):e63–e64. doi:10.1016/j.fsigss.2013.10.032
Liu F, van Duijn K, Vingerling JR, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Janssens ACJW, Kayser M (2009) Eye color and the prediction of complex phenotypes from genotypes. Curr Biol 19(5):192–193. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.01.027
Walsh S, Liu F, Ballantyne KN, van Oven M, Lao O, Kayser M (2011) IrisPlex: a sensitive DNA tool for accurate prediction of blue and brown eye colour in the absence of ancestry information. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 5(3):170–180. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2010.02.004
Walsh S, Liu F, Wollstein A, Kovatsi L, Ralf A, Kosiniak-Kamysz A, Branicki W, Kayser M (2013) The HIrisPlex system for simultaneous prediction of hair and eye colour from DNA. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 7(1):98–115. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2012.07.005
Lao O, Vallone PM, Coble MD, Diegoli TM, van Oven M, van der Gaag KJ, Pijpe J, de Knijff P, Kayser M (2010) Evaluating self-declared ancestry of U.S. Americans with autosomal, Y-chromosomal and mitochondrial DNA. Hum Mutat 31(12):E1875–E1893. doi:10.1002/humu.21366
Llamas B, Fehren-Schmitz L, Valverde G, Soubrier J, Mallick S, Rohland N, Nordenfelt S, Valdiosera C, Richards SM, Rohrlach A (2016) Ancient mitochondrial DNA provides high-resolution time scale of the peopling of the Americas. Sci Adv 2(4):e1501385. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1501385
Lao O, van Duijn K, Kersbergen P, de Knijff P, Kayser M (2006) Proportioning whole-genome single-nucleotide-polymorphism diversity for the identification of geographic population structure and genetic ancestry. Am J Hum Genet 78(4):680–690. doi:10.1086/501531
Weiner J (2015) Three dimensional PCA plots, version 0.8. R CRAN Repository
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour 9(5):1322–1332. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02591.x
Kaeuffer R, Reale D, Coltman DW, Pontier D (2007) Detecting population structure using STRUCTURE software: effect of background linkage disequilibrium. Heredity 99(4):374–380. doi:10.1038/sj.hdy.6801010
Phillips C, Prieto L, Fondevila M, Salas A, Gómez-Tato A, Álvarez-Dios J, Alonso A, Blanco-Verea A, Brión M, Montesino M, Carracedo Á, Lareu MV (2009) Ancestry analysis in the 11-M Madrid bomb attack investigation. PLoS One 4(8):e6583. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006583
Kalinowski ST (2011) The computer program STRUCTURE does not reliably identify the main genetic clusters within species: simulations and implications for human population structure. Heredity 106(4):625–632. doi:10.1038/hdy.2010.95
Lee AB, Luca D, Klei L, Devlin B, Roeder K (2010) Discovering genetic ancestry using spectral graph theory. Genet Epidemiol 34(1):51–59. doi:10.1002/gepi.20434
McVean G (2009) A genealogical interpretation of principal components analysis. PLoS Genet 5(10):e1000686. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000686
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Cox DR (1958) The regression analysis of binary sequences. J Roy Stat Soc B Met 20(2):215–242
Metz CE (1978) Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin Nucl Med 8(4):283–298. doi:10.1016/S0001-2998(78)80014-2
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez J-C, Müller M (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12(1):77. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Marzban C (2004) The ROC curve and the area under it as performance measures. Weather Forecast 19(6):1106–1114. doi:10.1175/825.1
Hall M (2007) A decision tree-based attribute weighting filter for naive Bayes. Knowl-Based Syst 20(2):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2006.11.008
Phillips C (2015) Forensic genetic analysis of bio-geographical ancestry. Forensic Sci Int-Gen 18:49–65. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.05.012
Carvajal-Carmona LG, Soto ID, Pineda N, Ortíz-Barrientos D, Duque C, Ospina-Duque J, McCarthy M, Montoya P, Alvarez VM, Bedoya G, Ruiz-Linares A (2000) Strong Amerind/white sex bias and a possible Sephardic contribution among the founders of a population in Northwest Colombia. Am J Hum Genet 67(5):1287–1295. doi:10.1016/S0002-9297(07)62956-5
Salas A, Richards M, Lareu M-V, Scozzari R, Coppa A, Torroni A, Macaulay V, Carracedo Á (2004) The African diaspora: mitochondrial DNA and the Atlantic slave trade. Am J Hum Genet 74(3):454–465. doi:10.1086/382194
Wang S, Lewis CM Jr, Jakobsson M, Ramachandran S, Ray N, Bedoya G, Rojas W, Parra MV, Molina JA, Gallo C, Mazzotti G, Poletti G, Hill K, Hurtado AM, Labuda D, Klitz W, Barrantes R, Bortolini MC, Salzano FM, Petzl-Erler ML, Tsuneto LT, Llop E, Rothhammer F, Excoffier L, Feldman MW, Rosenberg NA, Ruiz-Linares A (2007) Genetic variation and population structure in Native Americans. PLoS Genet 3(11):e185. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030185
Schroeder KB, Jakobsson M, Crawford MH, Schurr TG, Boca SM, Conrad DF, Tito RY, Osipova LP, Tarskaia LA, Zhadanov SI, Wall JD, Pritchard JK, Malhi RS, Smith DG, Rosenberg NA (2009) Haplotypic background of a private allele at high frequency in the Americas. Mol Biol Evol 26(5):995–1016. doi:10.1093/molbev/msp024
Verdu P, Pemberton TJ, Laurent R, Kemp BM, Gonzalez-Oliver A, Gorodezky C, Hughes CE, Shattuck MR, Petzelt B, Mitchell J, Harry H, William T, Worl R, Cybulski JS, Rosenberg NA, Malhi RS (2014) Patterns of admixture and population structure in native populations of Northwest North America. PLoS Genet 10(8). doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004530
Nievergelt CM, Maihofer AX, Shekhtman T, Libiger O, Wang X, Kidd KK, Kidd JR (2013) Inference of human continental origin and admixture proportions using a highly discriminative ancestry informative 41-SNP panel. Investig Genet 4:13. doi:10.1186/2041-2223-4-13
Paschou P, Ziv E, Burchard EG, Choudhry S, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Mahoney MW, Drineas P (2007) PCA-correlated SNPs for structure identification in worldwide human populations. PLoS Genet 3(9):e160. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030160
Bryc K, Auton A, Nelson MR, Oksenberg JR, Hauser SL, Williams S, Froment A, Bodo J-M, Wambebe C, Tishkoff SA (2010) Genome-wide patterns of population structure and admixture in West Africans and African Americans. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107(2):786–791. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909559107
Price AL, Patterson N, Yu F, Cox DR, Waliszewska A, McDonald GJ, Tandon A, Schirmer C, Neubauer J, Bedoya G (2007) A genomewide admixture map for Latino populations. Am J Hum Genet 80(6):1024–1036. doi:10.1086/518313
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheung, E.Y.Y., Gahan, M.E. & McNevin, D. Prediction of biogeographical ancestry from genotype: a comparison of classifiers. Int J Legal Med 131, 901–912 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-016-1504-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-016-1504-3