Abstract.
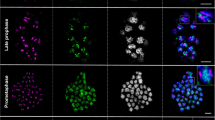
We have used fluorescence in situ hybridization to examine homolog pairing during the synchronous meiosis of the basidiomycete Coprinus cinereus. Using spread preparations of meiotic nuclei, we confirmed previous studies that showed that at 6 h post-karyogamy essentially all meiotic nuclei are in pachytene. We found that homolog pairing occurs rapidly after karyogamy, that a 1 Mb chromosome does not associate more quickly than a 2.5 Mb chromosome, and that interstitial, single-copy sites can associate stably prior to nucleolar fusion. Analysis of two probes for the same pair of homologs revealed that by 4 h after karyogamy each chromosome examined was at least partially paired in all meiotic cells. In addition, these studies showed that chromatin condensation increases after pairing and that chromatin shows stable compaction at pachytene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 January 1999; in revised form: 22 June 1999 / Accepted: 20 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Gerecke, E. & Zolan, M. Homolog pairing and meiotic progression in Coprinus cinereus . Chromosoma 108, 384–392 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050390
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050390