Abstract
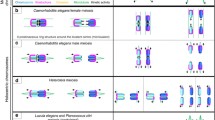
Sister chromatid cohesion is a prerequisite for correct segregation and possibly other functions of replicated chromosomes. Except for yeast, no details are known about arrangement of cohesion sites along interphase chromosomes. Within nuclei of several higher plants, sister chromatids are frequently not aligned at various positions along chromosome arms. Therefore, we tested whether preferential alignment positions (“cohesion hot spots”) and constant extension of and distances between aligned sites occur in plants. Along a ~1.2-Mb contig from the bottom arm of chromosome 1, the sister chromatid positions of 13 individual BAC inserts were found to be aligned for ~67–77% of homologues in 4C Arabidopsis thaliana nuclei. The differences between the 13 BAC positions were not significant at the P < 0.01 level. This suggests variability of alignment positions between cells and indicates the absence of cohesion “hot spots”. Similar as for single BACs, FISH with the entire contig indicated complete alignment for ~69% and complete separation of sister chromatids for ~31% of homologues in 4C nuclei. Partial alignment or separation was barely detectable. When three BAC inserts from a 760-kb region were tested simultaneously, alignment or separation of only the central BAC occurred in 3.3% and 3.5% of replicated chromosomes, respectively. Thus, we assume that sister chromatids can be separated or aligned within a Mb range in differentiated cells. However, the minimum extension of aligned sites or distances between them may (in rare cases) fall below ~500 kb.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berr A, Pecinka A, Meister A, Kreth G, Fuchs J, Blattner FR, Lysak MA, Schubert I (2006) Chromosome arrangement and nuclear architecture but not centromeric sequences are conserved between Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. Plant J 48:771–783
D'Amours D, Stegmeier F, Amon A (2004) Cdc14 and condensin control the dissolution of cohesin-independent chromosome linkages at repeated DNA. Cell 117:455–469
Dynek JN, Smith S (2004) Resolution of sister telomere association is required for progression through mitosis. Science 304:97–100
Glynn EF, Megee PC, Yu H-G, Mistrot C, Ünal E, Koshland DE, DeRisi JL, Gerton JL (2004) Genome-wide mapping of the cohesin complex in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Biol 2:1325–1339
Guacci V, Hogan E, Koshland D (1994) Chromosome condensation and sister chromatid pairing in budding yeast. J Cell Biol 125:517–530
Hirano T (2006) At the heart of the chromosome: SMC proteins in action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:311–322
Hosouchi T, Kumekawa N, Tsuruoka H, Kotani H (2002) Physical map-based sizes of the centromeric regions of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosomes 1, 2, and 3. DNA Res 9:117–121
Kim J-S, Krasieva TB, LaMorte V, Taylor AMR, Yokomori K (2002) Specific recruitment of human cohesin to laser-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem 277:45149–45153
Laloraya S, Guacci V, Koshland D (2000) Chromosomal addresses of the cohesin component Mcd1p. J Cell Biol 151:1047–1056
Lengronne A, Katou Y, Mori S, Yokobayashi S, Kelly GP, Itoh T, Watanabe Y, Shirahige K, Uhlmann F (2004) Cohesin relocation from sites of chromosomal loading to places of convergent transcription. Nature 430:573–578
Melaragno JE, Mehrotra B, Coleman AW (1993) Relationship between endopolyploidy and cell size in epidermal tissue of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 5:1661–1668
Nasmyth K, Haering CH (2005) The structure and function of SMC and kleisin complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 74:595–648
Pecinka A, Schubert V, Meister A, Kreth G, Klatte M, Lysak MA, Fuchs J, Schubert I (2004) Chromosome territory arrangement and homologous pairing in nuclei of Arabidopsis thaliana are predominantly random except for NOR-bearing chromosomes. Chromosoma 113:258–269
Rieder CL, Cole R (1999) Chromatid cohesion during mitosis: lessons from meiosis. J Cell Sci 112:2607–2613
Schubert I, Fransz PF, Fuchs J, de Jong JH (2001) Chromosome painting in plants. Methods Cell Sci 23:57–69
Schubert V, Kim Y-M, Berr A, Fuchs J, Meister A, Marschner S, Schubert I (2007) Random homologous pairing and incomplete sister chromatid alignment are common in angiosperm interphase nuclei. Mol Genet Genomics 278:167–176
Schubert V, Klatte M, Pecinka A, Meister A, Jasencakova Z, Schubert I (2006) Sister chromatids are often incompletely aligned in meristematic and endopolyploid interphase nuclei of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 172:467–475
Shimada K, Gasser SM (2007) The origin recognition complex functions in sister-chromatid cohesion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell 128:85–99
Ström L, Karlsson C, Lindroos HB, Wedahl S, Katou Y, Shirahige K, Sjögren C (2007) Postreplicative formation of cohesion is required for repair and induced by a single DNA break. Science 317:242–245
Sullivan M, Higuchi T, Katis VL, Uhlmann F (2004) Cdc14 phosphatase induces rDNA condensation and resolves cohesin-independent cohesion during budding yeast anaphase. Cell 117:471–482
Tang Z, Sun Y, Harley SE, Zou H, Yu H (2004) Human Bub1 protects centromeric sister-chromatid cohesion through Shugoshin during mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:18012–18017
Ünal E, Heidinger-Pauli JM, Koshland D (2007) DNA double-strand breaks trigger genome-wide sister-chromatid cohesion through Eco1 (Ctf7). Science 317:245–248
Volpi EV, Sheer D, Uhlmann F (2001) Cohesion, but not too close. Curr Biol 11:R378
Ward PB (2002) FISH probes and labelling techniques. In: Beatty B, Mai S, Squire J (eds) FISH: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp 5–28
Warren WD, Steffensen S, Lin E, Coelho P, Loupart M, Cobbe N, Lee JY, McKay MJ, Orr-Weaver T, Heck MM, Sunkel CE (2000) The Drosophila RAD21 cohesin persists at the centromere region in mitosis. Curr Biol 10:1463–1466
Weber SA, Gerton JL, Polancic JE, DeRisi JL, Koshland D, Megee PC (2004) The kinetochore is an enhancer of pericentric cohesin binding. PLoS Biol 2:1340–1353
Yalon M, Gal S, Segev Y, Selig S, Skorecki KL (2004) Sister chromatid separation at human telomeric regions. J Cell Sci 117:1961–1970
Acknowledgements
We thank Armin Meister for help with statistics, Jörg Fuchs for sorting of nuclei, Andreas Houben and Rigomar Rieger for the critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E.A. Nigg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schubert, V., Kim, YM. & Schubert, I. Arabidopsis sister chromatids often show complete alignment or separation along a 1.2-Mb euchromatic region but no cohesion “hot spots”. Chromosoma 117, 261–266 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0141-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0141-5