Abstract
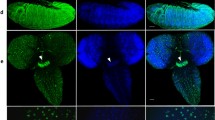
In Drosophila melanogaster, the two chromosomal proteins HP1 and HP2 colocalize on heterochromatic and euchromatic sites in polytene chromosomes. Mutations in the HP2 gene act as dominant suppressors of position effect variegation, demonstrating a role for HP2 in the formation or maintenance of heterochromatin. In this paper, we investigated whether a putative homolog of the D. melanogaster HP2 is involved in the facultative heterochromatinization process in mealybugs. Using an antibody raised against the Drosophila HP2, we identified in the mealybug Planococcus citri a cross-reactive epitope, which we refer to as HP2-like. We investigated the HP2-like pattern during the male embryo development where the entire paternal haploid chromosome set becomes heterochromatic. The HP2 antibody heavily decorates the chromocenters, where it localizes with HP1, and marks the chromatin before it acquires the full cytological characteristics of the male-specific heterochromatin. In euchromatic chromosomes, HP2-like is mainly concentrated at telomeric sites. The interplay between HP2-like and HP1-like was studied by dsRNA interference experiments. Extinguishing HP1-like expression by RNAi does not prevent the association of HP2-like with facultative heterochromatin, implying that HP2-like binds to chromatin in a HP1-independent manner. Our results confirm and extend the structural and functional conservation of proteins involved in heterochromatin assembly.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120–124
Bongiorni S, Prantera G (2003) Imprinted facultative heterochromatization in mealybugs. Genetica 117:271–279
Bongiorni S, Cintio O, Prantera G (1999) The relationship between DNA methylation and chromosome imprinting in the coccid Planococcus citri. Genetics 151:1471–1478
Bongiorni S, Mazzuoli M, Masci S, Prantera G (2001) Facultative heterochromatization in parahaploid male mealybugs: involvement of a heterochromatin-associated protein. Development 128:3809–3817
Bongiorni S, Fiorenzo P, Pippoletti D, Prantera G (2004) Inverted meiosis and meiotic drive in mealybugs. Chromosoma 112:331–341
Bongiorni S, Pasqualini B, Taranta M, Singh PB, Prantera G (2007) Epigenetic regulation of facultative heterochromatinisation in the mealybug. Planococcus citri via the Me(3)K9H3/HP1/Me(3)K20H4 pathway. J Cell Sci (in press)
Brown SW, Nur U (1964) Heterochromatic chromosomes in the coccids. Science 145:130–136
Cenci G, Siriaco G, Raffa GD, Kellum R, Gatti M (2003) The Drosophila HOAP protein is required for telomere capping. Nat Cell Biol 5:82–84
Cowell IG, Aucott R, Mahadevaiah SK, Burgoyne PS, Huskisson N, Bongiorni S, Prantera G, Fanti L, Pimpinelli S, Wu R, Gilbert DM, Shi W, Fundele R, Morrison H, Jeppesen P, Singh PB (2002) Heterochromatin, HP1 and methylation at lysine 9 of histone H3 in animals. Chromosoma 111:22–36
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SC (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:204–210
Eissenberg JC, Morris GD, Reuter G, Hartnett T (1992) The heterochromatin-associated protein HP-1 is an essential protein in Drosophila with dosage-dependent effects on position-effect variegation. Genetics 13:345–352
Epstein H, James TC, Singh PB (1992) Cloning and expression of Drosophila HP1 homologs from a mealybug, Planococcus citri. J Cell Sci 101:463–474
Fanti L, Giovinazzo G, Berloco M, Pimpinelli S (1998) The heterochromatin protein 1 prevents telomere fusions in Drosophila. Mol Cell 2:527–538
James TC, Elgin SC (1986) Identification of nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila and its gene. Mol Cell Biol 6:3862–3872
Kourmouli N, Jeppesen P, Mahadevhaiah S, Burgoyne P, Wu R, Gilbert DM, Bongiorni S, Prantera G, Fanti L, Pimpinelli S, Shi W, Fundele R, Singh PB (2004) Heterochromatin and tri-methylated lysine 20 of histone H4 in animals. J Cell Sci 117:2491–2501
Lachner M, O’Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001) Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410:116–120
Lyon MF (1992) Some milestones in the history of X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet 26:16–28
Maeda I, Kohara Y, Yamamoto M, Sugimoto A (2001) Large-scale analysis of gene function in Caenorhabditis elegans by high-throughput RNAi. Curr Biol 11:171–176
Nur U (1967) Reversal of heterochromatization and the activity of the paternal chromosome set in the male mealy bug. Genetics 56: 375–389
Nur U (1990) Heterochromatization and euchromatization of whole genomes in scale insects (Coccoidea: Homoptera). Development [Suppl]:29–34
Piacentini L, Fanti L, Berloco M, Perrini B, Pimpinelli S (2003) Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is associated with induced gene expression in Drosophila euchromatin. J Cell Biol 161:707–714
Shaffer CD, Stephens GE, Thompson BA, Funches L, Bernat JA, Craig, CA, Elgin SC (2002) Heterochromatin protein 2 (HP2), a partner of HP1 in Drosophila heterochromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14332–14337
Shaffer CD, Cenci G, Thompson B, Stephens GE, Slawson EE, Adu-Wusu K, Gatti M, Elgin SCR (2006) The large isoform of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin protein 2 plays a critical role in gene silencing and chromosome structure. Genetics 174:1189–1204
Singh PB, Georgatos SD (2002) HP1: facts, open questions, and speculation. J Struct Biol 140:10–16
Singh PB, Miller JR, Pearce J, Kothary R, Burton RD, Paro R, James TC, Gaunt SJ (1991) A sequence motif found in a Drosophila heterochromatin protein is conserved in animals and plants. Nucleic Acids Res 19:789–794
Somma MP, Fasulo B, Cenci G, Cundari E, Gatti M (2002) Molecular dissection of cytokinesis by RNA interference in Drosophila cultured cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:2448–2460
Stephens GE, Slawson EE, Craig CA, Elgin SC (2005) Interaction of heterochromatin protein 2 with HP1 defines a novel HP1-binding domain. Biochemistry 44:13394–13403
Vakoc CR, Mandat SA, Olenchock BA, Blobel GA (2005) Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and HP1 gamma are associated with transcription elongation through mammalian chromatin. Mol Cell 19:381–391
Wakimoto BT (1998) Beyond the nucleosome: Epigenetic aspects of position effect variegation in Drosophila. Cell 93:321–324
Acknowledgments
We thank Sarah Elgin for supplying us with the HP2 antibody and for an insightful discussion. We greatly appreciated Gena Stephens for helpful suggestions. We are grateful to Barbara Wakimoto for the critical reading of the manuscript and the C1A9 antibody. This work was supported by a grant from the University of Tuscia to GP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Pimpinelli
Silvia Volpi and Silvia Bongiorni contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volpi, S., Bongiorni, S. & Prantera, G. HP2-like protein: a new piece of the facultative heterochromatin puzzle. Chromosoma 116, 249–258 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0095-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-007-0095-7