Abstract
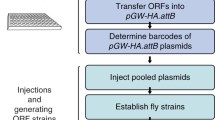
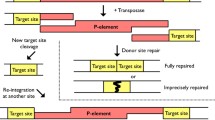
The genome of the model organism Drosophila melanogaster has been sequenced and annotated. Based on this groundwork, we performed a systematic genetic screen of the D. melanogaster X chromosome, which carries about one sixth of the genes of the organism. We generated a collection of single P-element insertions to provide genetic and molecular access to virtually all X-chromosomal genes. The study complements earlier work designed to systematically identify vital genes on the X chromosome by targeting transcription units which are phenotypically silent. We describe single UAS sequence-bearing P-element insertions throughout the X chromosome, which allows one to express the tagged genes under control of tissue/organ-directed GAL4 activity. In addition, the present collection of single insertion lines provides a tool to generate chromosomal deletions which are on average less than 33 kb in size.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, et al (2000) The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287:2185–2195
Akieda Y, Merriam JR (2001) Genes with ectopic expression phenotypes are common, not rare. Drosoph Inf Serv 84:130–132
Altschul SF, Madden TF, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ashburner M, et al (1999) An exploration of the sequence of a 2.9-Mb region of the genome of Drosophila melanogaster: the Adh region. Genetics 153:179–219
Bellen HJ (1999) Ten years of enhancer detection: lessons from the fly. Plant Cell 11:2271–2281
Bellen HJ, O’Kane CJ, Wilson C, Grossniklaus U, Pearson RK, Gehring WJ (1989) P element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev 3:1288–1300
Bellen HJ, Levis RW, Liao G, He Y, Carlson JW, Tsang G, Evans-Holm M, Hiesinger PR, Schulze KL, Rubin GM, Hoskins RA, Spradling AC (2004) The BDGP gene disruption project: single transposon insertions associated with 40% of Drosophila genes. Genetics 167:761–781
Bender W, Spierer P, Hogness DS (1983) Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 168:17–33
Bier E, Vaessin H, Shepherd S, Lee K, McCall K, Barbel S, Ackerman L, Carretto R, Uemura T, Grell E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1989) Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev 3:1273–1287
Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415
Bridges CB (1935) Salivary chromosome maps with a key to the banding of the chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. J Hered 26:60–64
Celniker SE, et al (2002) Finishing a whole-genome shotgun: release 3 of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatic genome sequence. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0079.1–0079.14
Crisp J, Merriam J (1997) Efficiency of an F1 selection screen in a pilot two-component mutagenesis involving Drosophila melanogaster misexpression phenotypes. Drosoph Inf Serv 80:90–92
FlyBase (2003) The FlyBase database of the Drosophila genome projects and community literature. Nucleic Acids Res 31:172–175
Hild M, Beckmann B, Haas SA, Koch B, Solovyev V, Busold C, Fellenberg K, Boutros M, Vingron M, Sauer F, Hoheisel JD, Paro R (2003) An integrated gene annotation and transcriptional profiling approach towards the full gene content of the Drosophila genome. Genome Biol 90–92:R3
Ito K, Awano W, Suzuki K, Hiromi Y, Yamamoto D (1997) The Drosophila mushroom body is a quadruple structure of clonal units each of which contains a virtually identical set of neurones and glial cells. Development 124:761–771
Kimmerly W, Stultz K, Lewis S, Lewis K, Lustre V, Romero R, Benke J, Sun D, Shirley G, Martin C, Palazzolo M (1996) A P1-based physical map of the Drosophila euchromatic genome. Genome Res 6:414–430
Lindsley DL, Zimm GG (1992) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Academic, San Diego
Miklos GL, Rubin GM (1996) The role of the genome project in determining gene function: insights from model organisms. Cell 86:521–529
Parks AL, et al (2004) Systematic generation of high-resolution deletion coverage of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Nat Genet 36:288–292
Peter A, et al (2002) Mapping and identification of essential gene functions on the X chromosome of Drosophila. EMBO Rep 3:34–38
Reiter LT, Potocki L, Chien S, Gribskov M, Bier E (2001) A systematic analysis of human disease-associated gene sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res 11:1114–1125
Robertson HM, Preston CR, Phillis RW, Johnson-Schlitz DM, Benz WK, Engels WR (1988) A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 118:461–470
Rørth P (1996) A modular misexpression screen in Drosophila detecting tissue-specific phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12418–12422
Rørth P, Szabo K, Bailey A, Laverty T, Rehm J, Rubin GM, Weigmann K, Milan M, Benes V, Ansorge W, Cohen SM (1998) Systematic gain-of-function genetics in Drosophila. Development 125:1049–1057
Rubin GM, Hong L, Brokstein P, Evans-Holm M, Frise E, Stapleton M, Harvey DA (2000a) A Drosophila complementary DNA resource. Science 287:2222–2224
Rubin GM, et al (2000b) Comparative genomics of the eukaryotes. Science 287:2204–2215
Ryder E, et al (2004) The DrosDel collection: a set of P-element insertions for generating custom chromosomal aberrations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 167:797–813
Silver J (1991) Inverse polymerase chain reaction. In: McPherson MJ, Quirke P, Taylor GR (eds) PCR, a practical approach. IRL, Oxford, pp 137–146
Spradling AC, Stern DM, Kiss I, Roote J, Laverty T, Rubin GM (1995) Gene disruptions using P transposable elements: an integral component of the Drosophila genome project. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10824–10830
Spradling AC, Stern D, Beaton A, Rhem EJ, Laverty T, Mozden N, Misra S, Rubin GM (1999) The Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project gene disruption project: single P element insertions mutating 25% of vital Drosophila genes. Genetics 153:135–177
Stark A, Brennecke J, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2003) Identification of Drosophila microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 1:397–409
Sturtevant AH (1913) The linear arrangement of six X-linked factors in Drosophila, as shown by their mode of association. J Exp Zool 14:43–59
Thibault ST, et al (2004) A complementary transposon tool kit for Drosophila melanogaster using P and piggyBac. Nat Genet 3:283–287
Voigt A, Pflanz R, Schäfer U, Jäckle H (2002) Perlecan participates in proliferation activation of quiescent Drosophila neuroblasts. Dev Dyn 224:403–412
Wensink PC, Finnegan DJ, Donelson JE, Hogness DS (1974) A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 3:315–325
Acknowledgements
We thank many colleagues for their help, John Merriam and the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center for fly strains. Supported by the German Human Genome Project (grant 01 KW 9632/9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E.A. Nigg
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beinert, N., Werner, M., Dowe, G. et al. Systematic gene targeting on the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 113, 271–275 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0313-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0313-5