Abstract
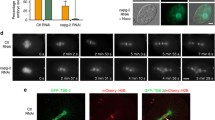
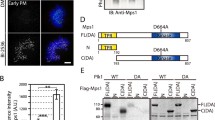
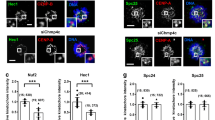
Members of the Mps1 protein kinase family have been implicated in the regulation of the kinetochore-mediated spindle assembly checkpoint in species ranging from yeast to man. However, conflicting data have been reported on the subcellular localization of vertebrate Mps1 kinases and their possible roles in centrosome duplication. Moreover, little is presently known about the regulation of Mps1 kinases during the cell cycle. Here, we have used immunofluorescence microscopy, immunoblotting and siRNA-mediated depletion of hMps1 to re-investigate the subcellular localization of this kinase. Our data confirm the kinetochore association of hMps1 but suggest that the centrosome staining produced by some anti-hMps1 antibodies could be due to cross-reactivity with other proteins. We also show that the kinetochore association of hMps1 is mediated by the amino-terminal, non-catalytic domain and specifically requires the presence of the Hec1/Ndc80-Nuf2 complex at the kinetochore. Finally, we have combined in vitro binding studies and kinase assays to explore the influence of microtubules on hMps1 activity. Our data indicate that the catalytic domain of hMps1 displays affinity for microtubules and that microtubule binding could contribute to the regulation of kinase activity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
- Mab:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- MBP:
-
Myelin basic protein
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RT:
-
Room temperature
References
Abrieu A, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Kahana JA, Peter M, Castro A, Vigneron S, Lorca T, Cleveland DW, Labbe JC (2001) Mps1 is a kinetochore-associated kinase essential for the vertebrate mitotic checkpoint. Cell 106:83–93
Bharadwaj R, Qi W, Yu H (2004) Identification of two novel components of the human Ndc80 kinetochore complex. J Biol Chem 279:13076–13085
Campbell MS, Gorbsky GJ (1995) Microinjection of mitotic cells with the 3F3/2 anti-phosphoepitope antibody delays the onset of anaphase. J Cell Biol 129:1195–1204
Chan GK, Jablonski SA, Sudakin V, Hittle JC, Yen TJ (1999) Human BUBR1 is a mitotic checkpoint kinase that monitors CENP-E functions at kinetochores and binds the Cyclosome/APC. J Cell Biol 146:941–954
Cleveland DW, Mao Y, Sullivan KF (2003) Centromeres and kinetochores: from epigenetics to mitotic checkpoint signaling. Cell 112:407–421
Connolly JA, Kalnins VI (1978) Visualization of centrioles and basal bodies by fluorescent staining with nonimmune rabbit sera. J Cell Biol 79:526–532
De Brabander M, Geuens G, Nuydens R, Willebrords R, Aerts F, De Mey J (1986) Microtubule dynamics during the cell cycle: the effects of taxol and nocodazole on the microtubule system of Pt K2 cells at different stages of the mitotic cycle. Int Rev Cytol 101:215–274
DeLuca JG, Howell BJ, Canman JC, Hickey JM, Fang G, Salmon ED (2003) Nuf2 and Hec1 are required for retention of the checkpoint proteins Mad1 and Mad2 to kinetochores. Curr Biol 13:2103–2109
Ditchfield C, Johnson VL, Tighe A, Ellston R, Haworth C, Johnson T, Mortlock A, Keen N, Taylor SS (2003) Aurora B couples chromosome alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to kinetochores. J Cell Biol 161:267–280
Douville EM, Afar DE, Howell BW, Letwin K, Tannock L, Ben David Y, Pawson T, Bell JC (1992) Multiple cDNAs encoding the esk kinase predict transmembrane and intracellular enzyme isoforms. Mol Cell Biol 12:2681–2689
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T (2001) Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411:494–498
Evan GI, Lewis GK, Ramsay G, Bishop JM (1985) Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol 5:3610–3616
Fisk HA, Winey M (2001) The mouse Mps1p-like kinase regulates centrosome duplication. Cell 106:95–104
Fisk HA, Mattison CP, Winey M (2003) Human Mps1 protein kinase is required for centrosome duplication and normal mitotic progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14875–14880
Fisk HA, Mattison CP, Winey M (2004) A field guide to the Mps1 family of protein kinases. Cell Cycle 3:439–442
Fry AM, Meraldi P, Nigg EA (1998) A centrosomal function for the human Nek2 protein kinase, a member of the NIMA family of cell cycle regulators. EMBO J 17:470–481
Gorbsky GJ (2001) The mitotic spindle checkpoint. Curr Biol 11:R1001–R1004
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM (2003) The small molecule hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 161:281–294
He X, Jones MH, Winey M, Sazer S (1998) mph1, a member of the Mps1-like family of dual specificity protein kinases, is required for the spindle checkpoint in S. pombe. J Cell Sci 111:1635–1647
Hori T, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Kimura H, Fukagawa T (2003) Dynamic behavior of Nuf2-Hec1 complex that localizes to the centrosome and centromere and is essential for mitotic progression in vertebrate cells. J Cell Sci 116:3347–3362
Hoyt MA, Totis L, Roberts BT (1991) S. cerevisiae genes required for cell cycle arrest in response to loss of microtubule function. Cell 66:507–517
Kallio MJ, McCleland ML, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2002) Inhibition of aurora B kinase blocks chromosome segregation, overrides the spindle checkpoint, and perturbs microtubule dynamics in mitosis. Curr Biol 12:900–905
van Kreeveld S, Winey M (2004) The budding yeast spindle pole body: a centrosome analog. In: Nigg EA (ed) Centrosomes in development and disease. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (in press)
Li R, Murray AW (1991) Feedback control of mitosis in budding yeast. Cell 66:519–531
Lindberg RA, Fischer WH, Hunter T (1993) Characterization of a human protein threonine kinase isolated by screening an expression library with antibodies to phosphotyrosine. Oncogene 8:351–359
Liu ST, Chan GK, Hittle JC, Fujii G, Lees E, Yen TJ (2003) Human MPS1 kinase is required for mitotic arrest induced by the loss of CENP-E from kinetochores. Mol Biol Cell 14:1638–1651
Mao Y, Abrieu A, Cleveland DW (2003) Activating and silencing the mitotic checkpoint through CENP-E-dependent activation/inactivation of BubR1. Cell 114:87–98
Martin-Lluesma S, Stucke VM, Nigg EA (2002) Role of Hec1 in spindle checkpoint signaling and kinetochore recruitment of Mad1/Mad2. Science 297:2267–2270
McCleland ML, Kallio MJ, Barrett-Wilt GA, Kestner CA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Gorbsky GJ, Stukenberg PT (2004) The vertebrate Ndc80 complex contains Spc24 and Spc25 homologs, which are required to establish and maintain kinetochore-microtubule attachment. Curr Biol 14:131–137
Meraldi P, Lukas J, Fry AM, Bartek J, Nigg EA (1999) Centrosome duplication in mammalian somatic cells requires E2F and Cdk2-cyclin A. Nat Cell Biol 1:88–93
Mills GB, Schmandt R, McGill M, Amendola A, Hill M, Jacobs K, May C, Rodricks AM, Campbell S, Hogg D (1992) Expression of TTK, a novel human protein kinase, is associated with cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 267:16000–16006
Musacchio A, Hardwick KG (2002) The spindle checkpoint: structural insights into dynamic signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:731–741
Neef R, Preisinger C, Sutcliffe J, Kopajtich R, Nigg EA, Mayer TU, Barr FA (2003) Phosphorylation of mitotic kinesin-like protein 2 by polo-like kinase 1 is required for cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 162:863–875
Nicklas RB, Ward SC, Gorbsky GJ (1995) Kinetochore chemistry is sensitive to tension and may link mitotic forces to a cell cycle checkpoint. J Cell Biol 130:929–939
Nigg EA (2002) Centrosome aberrations: cause or consequence of cancer progression? Nat Rev Cancer 2:815–825
Poss KD, Nechiporuk A, Hillam AM, Johnson SL, Keating MT (2002) Mps1 defines a proximal blastemal proliferative compartment essential for zebrafish fin regeneration. Development 129:5141–5149
Stucke VM, Sillje HH, Arnaud L, Nigg EA (2002) Human Mps1 kinase is required for the spindle assembly checkpoint but not for centrosome duplication. EMBO J 21:1723–1732
Tao W, Zhang S, Turenchalk GS, Stewart RA, St John MA, Chen W, Xu T (1999) Human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster lats tumour suppressor modulates CDC2 activity. Nat Genet 21:177–181
Weiss E, Winey M (1996) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae spindle pole body duplication gene MPS1 is part of a mitotic checkpoint. J Cell Biol 132:111–123
Wilkinson CJ, Andersen JS, Mann M, Nigg EA (2004) A proteomic approach to the inventory of the human centrosome. In: Nigg EA (ed) Centrosomes in development and disease. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (in press)
Winey M, Huneycutt BJ (2002) Centrosomes and checkpoints: the MPS1 family of kinases. Oncogene 21:6161–6169
Winey M, Goetsch L, Baum P, Byers B (1991) MPS1 and MPS2: novel yeast genes defining distinct steps of spindle pole body duplication. J Cell Biol 114:745–754
Yu H (2002) Regulation of APC-Cdc20 by the spindle checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:706–714
Acknowledgements
We are particularly grateful to Drs. Emma Lees and Mark Winey for kindly providing the Ag3 antibody and the bacterial hMps1 expression plasmids, respectively. We also thank Drs. Martin-Lluesma, H.H.W. Silljé, and S. Taylor for providing additional antibodies and plasmids, and Dr. T.U. Mayer for a generous gift of polymerized microtubules. Finally, we thank Dr. R. Neef and T.A. Kufer for helpful discussions and advice. This work was supported by the Max Planck Society and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stucke, V.M., Baumann, C. & Nigg, E.A. Kinetochore localization and microtubule interaction of the human spindle checkpoint kinase Mps1. Chromosoma 113, 1–15 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0288-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0288-2