Abstract
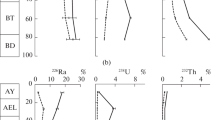
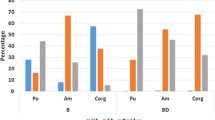
Radiocesium is normally bound only rather weakly and unspecifically by humic substances, in contrast to the actinides Pu and Am. Recently, however, it was observed that fallout 137Cs in the soil solution from an Of-horizon of a podzol forest soil (slightly decomposed plant material) was associated essentially only with one single size fraction of the humic substances. In deeper soil layers with well humified material (AOh-horizon), radiocesium was associated with all size fractions of the dissolved organic matter (DOM). To examine whether this unexpected behaviour is also observable for DOM isolated from other soils, we determined the association of fallout 137Cs,90Sr,238Pu, 239+240Pu and 241Am with various size fractions of DOM from in situ soil solutions isolated from two layers (0–2 cm and 2–5 cm) of two grassland soils (a soddy podzolic soil and a peat soil) within the 10 km zone of the nuclear reactor at Chernobyl (Ukraine). The four size fractions of DOM as obtained by gel filtration of the soil solution were (mean nominal molecular weight in daltons): fraction I: ≥2000, fraction II: 1300; fraction III: 560, fraction IV: inorganic compounds. The results for the well humified DOM (humus accumulation horizon of podzol, deeper layer of peat soil) showed that Pu and Am are essentially associated with the high molecular weight fractions, while Sr is present only in the `inorganic' fraction. Radiocesium is found in all the size fractions separated. A quite similar pattern was also found for Pu, Am, and Sr in the soil solution from only slightly decomposed plant material (0–2 cm of peat soil), but not for radiocesium. This radionuclide was again essentially only observable in one single low molecular weight fraction of DOM. The above results thus support our recent observations in the different horizons of a forest podzol mentioned above, even though no reason for the different binding of radiocesium by well humified soil organic matter and by only slightly decomposed plant material can be given at present. The data demonstrate, however, that information on only the total amount of a radionuclide in the soil solution will not be sufficient to interpret or predict its fate adequately in the soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 February 1998 / Accepted in revised form: 14 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunzl, K., Kracke, W., Agapkina, G. et al. Association of Chernobyl-derived 239+240Pu, 241Am, 90Sr and 137Cs with different molecular size fractions of organic matter in the soil solution of two grassland soils. Radiat Environ Biophys 37, 195–200 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110050117
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110050117