Abstract
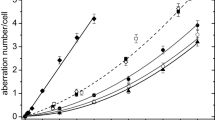
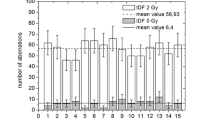
Irradiation of human lymphocytes by x-rays has been seen, in past studies, to produce increasing frequencies of chromosome aberrations at lower x-ray energies. However, in one earlier irradiation experiment with chromium x-rays, the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) did not appear to be larger than that of hard x-rays, especially at higher doses. A possible reason for this unexpected result may have been the irradiation and culture conditions. We have, therefore, in the present study used a technique that has been developed in our laboratory to ensure uniformity of irradiation within lymphocytes and to avoid artefacts due to the cell cycle kinetics. Monolayers of 3-h-stimulated lymphocytes were exposed to 5.4 keV x-rays. A linear-quadratic dose-response was found for dicentrics. The comparison to an earlier finding with 220 kV x-rays shows the expected result of the RBE of the 5.4 keV x-rays to be above that of 220 kV x-rays. The intercellular distribution of dicentrics did not differ significantly from a Poisson distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 January 1997 / Accepted in revised form: 17 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roos, H., Schmid, E. Analysis of chromosome aberrations in human peripheral lymphocytes induced by 5.4 keV x-rays. Radiat Environ Biophys 36, 251–254 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110050079
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110050079