Abstract
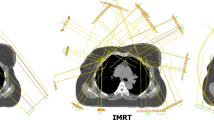
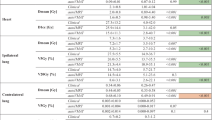
The clinical information on the relationship between the cardiac contact distance (CCD), the maximum dose (Dmax) delivered to the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery and the mean heart dose has mostly focused on patients with breast-conserving surgery (BCS), being scarce in postmastectomy patients. The aim of this study is to determine the association between the CCD and the Dmax delivered to the LAD. The secondary objective was to evaluate the dosimetric results of comparing three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) to intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) techniques for post mastectomized breast cancer patients with irradiation to the left chest wall. 53 cases of women who received adjuvant standard fractionated postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) were used. Three types of plans were created for each patient: 3D-CRT, seven equidistant IMRT fields, and four partial VMAT arcs. Correlations were evaluated using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Plans made with IMRT and VMAT showed improved homogeneity and conformity. Associations between CCD and Dmax to LAD were positive for all three plan types. Compared to 3D-CRT, the modulated intensity plans obtained better dose homogeneity and conformity to the target volume. The LAD and heart doses were significantly lower for IMRT and VMAT plans. The CCD can be used as a predictor of the maximum and mean doses of the LAD. Modulated intensity techniques allow for better dose distribution and dose reduction to the heart and LAD.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author E.A Martín-Tovar, upon reasonable request.
References
Atkins KM, Bitterman DS, Chaunzwa TL et al (2021) Mean heart dose is an inadequate surrogate for left anterior descending coronary artery dose and the risk of major adverse cardiac events in lung cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.03.005
Aznar M, Korreman SS, Pedersen AN et al (2011) Evaluation of dose to cardiac structures during breast irradiation. Br J Radiol 84:743–746. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/12497075
Beaton L, Bergman A, Nichol A et al (2019) Clinical and Translational Radiation Oncology Cardiac death after breast radiotherapy and the QUANTEC cardiac guidelines. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 19:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctro.2019.08.001
Borger JH, Clinic M, Hooning MJ et al (2007) Cardiotoxic effects of tangential breast irradiation in early breast cancer patients: the role of irradiated heart volume breast cancer patients: the role of irradiated heart volume. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.04.042
Bramkamp M, Rock T, Schneemann M et al (2007) Case report radiotherapy and the heart. Lancet 369:2007
Braunstein LZ, Gillespie EF, Hong L et al (2020) Breast radiation therapy under COVID-19 pandemic resource constraints d approaches to defer or shorten treatment from a comprehensive cancer center in the United States. Advancesradonc 5:582–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2020.03.013
Chaikh A, Giraud JY, Perrin E et al (2014) The choice of statistical methods for comparisons of dosimetric data in radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-9-205
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2011.01.025
Coon AB, Dickler A, Kirk MC et al (2010) Tomotherapy and multifield intensity-modulated radiotherapy planning reduce cardiac doses in left-sided breast cancer patients with unfavorable cardiac anatomy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1705
Cooper BT, Li X, Shin SM et al (2016) Corresponding author: SC. Adv Radiat Oncol 1:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2016.08.001
Darby SC, McGale P, Taylor CW, Peto R (2005) Long-term mortality from heart disease and lung cancer after radiotherapy for early breast cancer: prospective cohort study of about 300 000 women in US SEER cancer registries. Lancet Oncol 6:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70251-5
Darby SC, Cutter DJ, Boerma M et al (2010) Radiation-related heart disease: current knowledge and future prospects. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:656–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.064
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P et al (2013) Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 368:987–998. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1209825
Dodge JT, Brown BG, Bolson EL, Dodge HT (1992) Lumen diameter of normal human coronary arteries. Influence of age, sex, anatomic variation, and Left ventricular hypertrophy or dilation. Circulation 86:232–246
Duane F, Aznar MC, Bartlett F et al (2017) Original article A cardiac contouring atlas for radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 122:416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2017.01.008
Duma MN (2017) Tangential field radiotherapy for breast cancer—the dose to the heart and heart subvolumes: what structures must be contoured in future clinical trials? Front Oncol 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2017.00130
Evans SB, Sioshansi S, Moran MS et al (2012) Prevalence of poor cardiac anatomy in carcinoma of the breast treated with whole-breast radiotherapy: reconciling modern cardiac dosimetry with cardiac mortality data. Am J Clin Oncol Cancer Clin Trials 35:587–592. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e31822d9cf6
Evans SB, Panigrahi B, Northrup V et al (2013) Analysis of coronary artery dosimetry in the 3-dimensional era: implications for organ-at-risk segmentation and dose tolerances in left-sided tangential breast radiation. Pract Radiat Oncol 3:e55–e60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2012.06.007
Fan L, Luo Y, Xu J et al (2014) A dosimetry study precisely outlining the heart substructure of left breast cancer patients using intensity-modulated radiation therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 15:265–274
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39:175–191. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193146
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang A-G (2009) Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 41:1149–1160. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149
Feng M, Moran J, Koelling T et al (2011) Development and validation of a heart atlas to study cardiac exposure to radiation following treatment for breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.10.058
Fiorentino A, Ruggieri R, Giaj-Levra N et al (2017) Three-dimensional conformal versus intensity modulated radiotherapy in breast cancer treatment: is necessary a medical reversal? Radiol Medica 122:146–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-016-0700-z
Fogliata A, Clivio A, Nicolini G et al (2007) A treatment planning study using non-coplanar static fields and coplanar arcs for whole breast radiotherapy of patients with concave geometry. Radiother Oncol 85:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2007.10.006
Gagliardi G, Constine L, Moiseenko V et al (2010) Radiation dose–volume effects in the heart. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.04.093
Giraud P, Houle A (2013) Respiratory gating for radiotherapy: main technical aspects and clinical benefits. Int Sch Res Not 2013:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/519602
Harris E, Port M, Sardaro A et al (2006) Late cardiac mortality and morbidity in early-stage breast cancer patients a er breast-conservation treatment. J Clin Oncol 24:4100–4106. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.05.1037
Hector SS, Trott KR (2007) Radiation-induced cardiovascular diseases: is the epidemiologic evidence compatible with the radiobiologic data? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.071
Hiatt JR, Evans SB, Price LL et al (2006) Dose-modeling study to compare external beam techniques from protocol NSABP B-39/RTOG 0413 for patients with highly unfavorable cardiac anatomy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1368–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.03.060
Hong L, Hunt M, Chui C et al (1999) Intensity-modulated tangential beam irradiation of the intact breast. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 44:1155–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00132-7
Huang B, Fang Z, Huang Y et al (2014) A dosimetric analysis of volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy with jaw width restriction vs 7 field intensity-modulated radiotherapy for definitive treatment of cervical cancer. Br J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20140183
Jacob S, Camilleri J, Derreumaux S et al (2019) Is mean heart dose a relevant surrogate parameter of left ventricle and coronary arteries exposure during breast cancer radiotherapy: a dosimetric evaluation based on individually-determined radiation dose (BACCARAT study ). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14:1–10
Kaderka R, Gillespie EF, Mundt RC et al (2019) Geometric and dosimetric evaluation of atlas based auto-segmentation of cardiac structures in breast cancer patients. Radiother Oncol 131:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.07.013
Kang S-H, Chung J-B, Kim K-H et al (2019) Comparison of dosimetrical and radiobiological parameters on three VMAT techniques for left-sided breast cancer. Prog Med Phys 30:7. https://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2019.30.1.7
Kirby AM, Evans PM, Donovan EM et al (2010) Prone versus supine positioning for whole and partial-breast radiotherapy: a comparison of non-target tissue dosimetry. Radiother Oncol 96:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.05.014
Lakens D (2022) Sample size justification collabra: psychology. Collabra Psychol 8:1–28
Lee G, Rosewall T, Fyles A et al (2015) Anatomic features of interest in women at risk of cardiac exposure from whole breast radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 115:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2015.05.002
Lee J, Hua K, Hsu S et al (2017) Development of delineation for the left anterior descending coronary artery region in left breast cancer radiotherapy: an optimized organ at risk. Radiother Oncol 122:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.12.029
Lin JF, Yeh DC, Yeh HL et al (2015) Dosimetric comparison of hybrid volumetric-modulated arc therapy, volumetric-modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for left-sided early breast cancer. Med Dosim 40:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2015.05.003
Lohr F, El-Haddad M, Dobler B et al (2009) Potential effect of robust and simple IMRT approach for left-sided breast cancer on cardiac mortality. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.07.018
Lorenzen EL, Taylor CW, Maraldo M et al (2013) Inter-observer variation in delineation of the heart and left anterior descending coronary artery in radiotherapy for breast cancer: a multi-centre study from Denmark and the UK. Radiother Oncol 108:254–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.06.025
Mast ME, Van Kempen-Harteveld L, Heijenbrok MW et al (2013) Left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy with and without breath-hold: does IMRT reduce the cardiac dose even further? Radiother Oncol 108:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.07.017
Mège A, Ziouèche A, Pourel N, Chauvet B (2011) Toxicité cardiaque de la radiothérapie. Cancer/Radiotherapie 15:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2011.06.003
Mendez LC, Louie AV, Moreno C et al (2018) Evaluation of a new predictor of heart and left anterior descending artery dose in patients treated with adjuvant radiotherapy to the left breast. Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1069-z
Miller S, Zagar T, Marks LB (2012) Distribution of coronary artery stenosis after radiation for breast cancer. Breast Dis A Year B Q 23:280–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breastdis.2012.06.035
Nilsson G, Holmberg L, Garmo H et al (2012) Distribution of coronary artery stenosis after radiation for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.34.5900
Overgaard M, Hansen P, Overgaard J et al (1997) Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 337:949–955
Overgaard M, Jensen M, Overgaard J et al (1999) Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast- cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet 353:1641–1648
Poitevin-Chacón A, Chávez-nogueda J, Prudencio RR et al (2018) Dosimetry of the left anterior descending coronary artery in left breast cancer patients treated with postoperative external radiotherapy. Reports Pract Oncol Radiother 23:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2018.01.003
Poortmans P, Aznar M, Bartelink H (2012) Quality indicators for breast cancer: revisiting historical evidence in the context of technology changes. Semin Radiat Oncol 22:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2011.09.007
Popescu CC, Olivotto I, Patenaude V et al (2006) Inverse-planned, dynamic, multi-beam, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): a promising technique when target volume is the left breast and internal mamary lymph nodes. Med Dosim 31:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2006.05.003
Qiu JJ, Chang Z, Horton JK et al (2014) Dosimetric comparison of 3D conformal, IMRT, and V-MAT techniques for accelerated partial-breast irradiation (APBI). Med Dosim 39:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2013.12.001
Quirk S, Grendarova P, Phan T et al (2020) A retrospective analysis to demonstrate achievable dosimetry for the left anterior descending artery in left-sided breast cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 148:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.04.022
Ramasubramanian V, Balaji K, Subramanian SB et al (2019) Hybrid volumetric modulated arc therapy for whole breast irradiation: a dosimetric comparison of different arc designs. Radiol Med 124:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-00994-1
Rastogi K, Sharma S, Gupta S et al (2018) Dosimetric comparison of IMRT versus 3DCRT for post-mastectomy chest wall irradiation. Radiat Oncol J 36:71–78. https://doi.org/10.3857/roj.2017.00381
Remouchamps V, Vicini F, Sharpe M et al (2003) Significant reductions in heart and lung doses using deep inspiration breath hold with active breathing control and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for patients treated with locoregional breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 55:392–406
Rochet N, Drake JI, Harrington K et al (2015) Deep inspiration breath-hold technique in left-sided breast cancer radiation therapy: Evaluating cardiac contact distance as a predictor of cardiac exposure for patient selection. Pract Radiat Oncol 5:e127–e134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2014.08.003
Rudat V, Alaradi AA, Mohamed A et al (2011) Tangential beam IMRT versus tangential beam 3D-CRT of the chest wall in postmastectomy breast cancer patients: a dosimetric comparison. Radiat Oncol 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.28.15_suppl.e11087
Sanjoy C, Santam C, Arunsingh M et al (2018) Resource requirements and reduction in cardiac mortality from deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) radiotherapy for left sided breast cancer patients: a prospective service development analysis. Pract Radiat Oncol 8:382–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2018.03.007
Sardaro A, Fonte M, Patrizia M et al (2012) Radiation-induced cardiac damage in early left breast cancer patients: risk factors, biological mechanisms, radiobiology, and dosimetric constraints. Radiother Oncol 103:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2012.02.008
Senkus-Konefka E, Jassem J (2007) Cardiovascular effects of breast cancer radiotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev 33:578–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.07.011
Shekel E, Levin D, Epstein D et al (2014) Is contouring the left anterior descending (lad) artery necessary for left-breast patients? A retrospective comparison between treated and revised plans. Radiat Oncol Biol 90:S265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.05.916
Tan W, Liu D, Xue C et al (2012) Anterior myocardial territory may replace the heart as organ at risk in intensity-modulated radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1689–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.03.009
Ugurlu BT, Temelli O (2020) The impact of the field width on VMAT plan quality and the assessment of half field method. J Appl Clin Med Phys 21:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12834
Van Den BVAB, Ta BDP, Van Der SA et al (2017) Validation and modification of a prediction model for acute cardiac events in patients with breast cancer treated with radiotherapy based on three-dimensional dose distributions to cardiac substructures. J Clin Oncol 35:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.71.4113
Vayntraub A, Quinn TJ, Thompson AB et al (2021) Left anterior descending artery avoidance in patients receiving breast irradiation. Med Dosim 46:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2020.07.006
Vikström J, Hjelstuen MH, Wasbø E et al (2018) A comparison of conventional and dynamic radiotherapy planning techniques for early-stage breast cancer utilizing deep inspiration breath-hold. Acta Oncol (Madr) 57:1325–1330. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2018.1497294
Virén T, Heikkilä J, Myllyoja K et al (2015) Tangential volumetric modulated arc therapy technique for left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-015-0392-x
Wang X, Pan T, Pinnix C et al (2012) Cardiac motion during deep-inspiration breath-hold: implications for breast cancer radiotherapy. Int Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:708–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.01.035
Wennstig A, Garmo H, Hållström P et al (2016) Inter-observer variation in delineating the coronary arteries as organs at risk. Radiother Oncol 122:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.11.007
Wennstig A, Garmo H, Isacsson U et al (2019) The relationship between radiation doses to coronary arteries and location of coronary stenosis requiring intervention in breast cancer survivors. Radiat Oncol 14:1–11
White BM, Vennarini S, Lin L et al (2015) Accuracy of routine treatment planning 4-dimensional and deep-inspiration breath-hold computed tomography delineation of the left anterior descending artery in radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol Biol 91:825–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.11.036
White J, Tai A, Arthur D et al (2018) Breast cancer atlas for radiation therapy planning: consensus definitions collaborators. Radiat Ther Oncol Group 73:1–71
Zhou GX, Xu SP, Dai X et al (2011) Clinical dosimetric study of three radiotherapy techniques for postoperative breast cancer: helical tomotherapy, IMRT, and 3D-CRT. Technol Cancer Res Treat 10:15–23. https://doi.org/10.7785/tcrt.2012.500174
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Radiotherapy Department (radiation oncologists, medical physicists, dosimetrists, radiation therapists, nurses and administrative personnel) of IMSS-UMAE Mérida for their work and invaluable collaboration.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to participate
In this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badillo-Alvarado, A.H., Martín-Tovar, E.A., Molina-Salinas, G.M. et al. Association between the cardiac contact distance and the maximum dose at the left anterior descending coronary artery in post mastectomized patients. Radiat Environ Biophys 61, 407–423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-022-00983-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-022-00983-5