Abstract
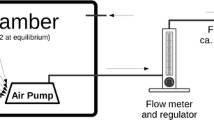
The purpose of this study is to investigate the biokinetics of inhaled radon, radon activity concentrations in mouse tissues and organs were determined after mice had been exposed to about 1 MBq/m3 of radon in air. Radon activity concentrations in mouse blood and in other tissues and organs were measured with a liquid scintillation counter and with a well-type HP Ge detector, respectively. Radon activity concentration in mouse blood was 0.410 ± 0.016 Bq/g when saturated with 1 MBq/m3 of radon activity concentration in air. In addition, average partition coefficients obtained were 0.74 ± 0.19 for liver, 0.46 ± 0.13 for muscle, 9.09 ± 0.49 for adipose tissue, and 0.22 ± 0.04 for other organs. With these results, a value of 0.414 for the blood-to-air partition coefficient was calculated by means of our physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. The time variation of radon activity concentration in mouse blood during exposure to radon was also calculated. All results are compared in detail with those found in the literature.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross FT (1988) Radon inhalation studies in animals. Radiat Prot Dosim 24:463–466
Deetjen P (1997) Epidemiology and biological effects of radon. In: Pratzel HG, Deetjen P (eds) Radon in der kurortmedizin, ISMH, Verlag Geretsried, pp 32–38
Falkenbach A, Kovacs J, Franke A, Jörgens K, Ammer K (2005) Radon therapy for the treatment of rheumatic diseases – review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Rheumatol Int 25:205–210
Franke A, Reiner L, Resch K-L (2007) Long-term benefit of radon spa therapy in the rehabilitation of rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blinded trial. Rheumatol Int 27:703–713
ICRP (2009) Adult reference computational phantoms. ICRP publication 110. Ann ICRP 39 (2)
Ishimori Y (2014) Current status of the projects of JAEA Ningyo-toge and investigation of properties of radon hot springs in Misasa. J Hot Spring Sci 64:289–295 (Japanese)
Khursheed A (2000) Doses to systemic tissues from radon gas. Radiat Prot Dosim 88:171–181
Leggett R, Marsh J, Gregoratto D, Blanchardon E (2013) A generic biokinetic model for noble gases with application to radon. J Radiol Prot 33:413–432
Mitsunobu F, Yamaoka K, Hanamoto K, Kojima S, Hosaki Y, Ashida K, Sugita K, Tanizaki Y (2003) Elevation of antioxidant enzymes in the clinical effects of radon and thermal therapy for bronchial asthma. J Radiat Res 44:95–99
Monchaux G, Morlier JP (2002) Influence of exposure rate on radon-induced lung cancer in rats. J Radiol Prot 22:A81–A87
Monchaux G, Morlier JP, Morin M, Chameaud J, Lafuma J, Masse R (1994) Crcinogenic and cocarcinogenic effects of radon and radon daughters in rat. Environ Health Persp 102:64–73
National Research Council (NRC) (1999) Risk assessment of radon in drinking water. National Academy Press, Washington
Nussbaum E, Hursh JB (1957) Radon solubility in rat tissues. Science 125:552–553
Sakoda A, Ishimori Y, Kawabe A, Kataoka T, Hanamoto K, Yamaoka K (2010) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of inhaled radon to calculate absorbed doses in mice, rats and humans. J Nucl Sci Technol 47:731–738
Strong JC, Morlier JP, Monchaux G, Bartstra RW, Groen JS, Baker T (1996) Intercomparison of measurement techniques used in radon exposure facilities for animals in Europe. Appl Radiat Isot 47:355–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishimori, Y., Tanaka, H., Sakoda, A. et al. Measurements of radon activity concentration in mouse tissues and organs. Radiat Environ Biophys 56, 161–165 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-017-0682-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-017-0682-9