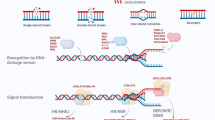
Abstract
Ionizing radiation modulates several signaling pathways resulting in transcription factor activation. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is one of the most important transcription factors that respond to changes in the environment of a mammalian cell. NF-κB plays a key role not only in inflammation and immune regulation but also in cellular radiation response. In response to DNA damage, NF-κB might inhibit apoptosis and promote carcinogenesis. Our previous studies showed that ionizing radiation is very effective in inducing biological damages. Therefore, it is important to understand the radiation-induced NF-κB signaling cascade. The current study aims to improve existing mammalian cell-based reporter assays for NF-κB activation by the use of DD-tdTomato which is a destabilized variant of red fluorescent protein tdTomato. It is demonstrated that exposure of recombinant human embryonic kidney cells (HEK/293 transfected with a reporter constructs containing NF-κB binding sites in its promoter) to ionizing radiation induces NF-κB-dependent DD-tdTomato expression. Using this reporter assays, NF-κB signaling in mammalian cells was monitored by flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy. Activation of NF-κB by the canonical pathway was found to be quicker than by the genotoxin- and stress-induced pathway. X-rays activate NF-κB in HEK cells in a dose-dependent manner, and the extent of NF-κB activation is higher as compared to camptothecin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner BP, Shackelford RE, Baldwin AS, Paules RS (1999) Lack of involvement of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) in regulation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) in human diploid fibroblasts. Cancer Res 59:5456–5460
Baichwal VR, Baeuerle PA (1997) Activate NF-kappa B or die? Curr Biol 7:94–96
Baldwin AS (2001) Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J Clin Invest 107:241–246
Banaszynski LA, Chen L, Maynard-Smith LA, Ooi AGL, Wandless TJ (2006) A rapid, reversible, and tunable method to regulate protein function in living cells using synthetic small molecules. Cell 126:995–1004
Basu S, Rosenzweig KR, Youmell M, Price BD (1998) The DNA-dependent protein kinase participates in the activation of NF kappa B following DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247:79–83
Baumstark-Khan C, Hellweg CE, Palm M, Horneck G (2001) Enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) for space radiation research using mammalian cells in the International Space Station. Phys Med Biol 17(Suppl 1):210–214
Baumstark-Khan C, Hellweg CE, Arenz A, Meier MM (2005) Cellular monitoring of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway for assessment of space environmental radiation. Radiat Res 164:527–530
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Sweeney CJ, Nakshatri H (2002) Identification of signal transduction pathways involved in constitutive NF-kappaB activation in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21:2066–2078
Bora RS, Gupta D, Malik R, Chachra S, Sharma P, Saini KS (2008) Development of a cell-based assay for screening of phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) inhibitors using a stable recombinant HEK-293 cell line expressing high levels of PDE10A. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 49:129–134
Brzoska K, Szumiel I (2008) Signalling loops and linear pathways: NF-κB activation in response to genotoxic stress. Mutagenesis 24:1–8
Cervera L, Gutierrez S, Godia F, Segura MM (2011) Optimization of HEK 293 cell growth by addition of non-animal derived components using design of experiments. BMC Proc 5:126
Chandel NS, Trzyna WC, McClintock DS, Schumacker PT (2000) Role of oxidants in NF-kappa B activation and TNF-alpha gene transcription induced by hypoxia and endotoxin. J Immunol 165:1013–1021
Chen X, Shen B, Xia L, Khaletzkiy A, Chu D, Wong Jeffrey YC, Li J (2002) Activation of nuclear factor kappaB in radioresistance of TP53-inactive human keratinocytes. Cancer Res 62:1213–1221
Fitzgerald DC, Meade KG, McEvoy AN, Lillis L, Murphy EP, MacHugh DE, Baird AW (2007) Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increases nuclear factor κB (NFκB) activity in and interleukin-8 (IL-8) release from bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet Immunol Immunopath 116:59–68
Fuseler JW, Merrill DM, Rogers JA, Grisham MB, Wolf RE (2006) Analysis and quantitation of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) activated vascular endothelial cells. Microsc Microanal 12:269–276
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2008) New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:837–848
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2012) Celebrating 25 years of NF-kappaB research. Immunol Rev 246:5–13
Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB (1998) NF-kappa B and rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 16:225–260
Ghosh S, Jimi E, Dong J, Zhong HH (2004) Regulation of NF-κB transcriptional activity. Shock 21:44
Grandage VL, Gale RE, Linch DC, Khwaja A (2005) PI3-kinase/Akt is constitutively active in primary acute myeloid leukaemia cells and regulates survival and chemoresistance via NF-kappa B, MAPkinase and p53 pathways. Leukemia 19:586–594
Habraken Y, Piette J (2006) NF-kappaB activation by double-strand breaks. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1132–1141
Hadian K, Krappmann D (2011) Signals from the nucleus: activation of NF-kappaB by cytosolic ATM in the DNA damage response. Sci Signal 4:e2
Hargrave BY, Tiangco DA, Lattanzio FA, Beebe SJ (2003) Cocaine, not morphine, causes the generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of NF-kappaB in transiently cotransfected heart cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol 3:141–151
Hayden MS (2004) Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappa B signaling. Cell 132:344–362
Hellweg CE, Baumstark-Khan C, Horneck G (2003) Generation of stably transfected Mammalian cell lines as fluorescent screening assay for NF-kappaB activation-dependent gene expression. J Biomol Screen 8:511–521
Hellweg CE, Arenz A, Meier MM, Baumstark-Khan C (2005) Cellular monitoring systems for the assessment of space environmental factors. Adv Space Res 36:1673–1679
Hellweg CE, Baumstark-Khan C, Schmitz C, Lau P, Meier MM, Testard I, Berger T, Reitz G (2011) Carbon-ion-induced activation of the NF-κB pathway. Radiat Res 175:424–431
Huang TT, Wuerzberger-Davis S, Seufzer BJ, Shumway SD, Kurama T, Boothman DA, Miyamoto S (2000) NF-kappaB activation by camptothecin. A linkage between nuclear DNA damage and cytoplasmic signaling events. J Biol Chem 275:9501–9509
Janssens S, Tinel A, Lippens S, Tschopp J (2005) PIDD mediates NF-kappaB activation in response to DNA damage. Cell 123:1079–1092
Jin S, Lu D, Ye S, Ye H, Zhu L, Feng Z, Liu S, Wang D, Hu Q (2005) A simplified probe preparation for ELISA-based NF-kappaB activity assay. J Biochem Biophys Methods 65:20–29
Jung M, Dritschilo A (2001) NF-kappa B signaling pathway as a target for human tumor radiosensitization. Semin Radiat Oncol 11:346–351
Kawakami K, Scheidereit C, Roeder RG (1988) Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (Nf-κb) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type-1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4700–4704
Kiefer J (1971) Target theory and survival curves. J Theor Biol 30:307–331
Kim MJ, Pal S, Tak YK, Lee K, Yang TK, Lee S, Song JM (2007) Determination of the dose-depth distribution of proton beam using resazurin assay in vitro and diode laser-induced fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 593:214–223
Lai C, Jiang X, Li X (2006) Development of luciferase reporter-based cell assays. Assay Drug Dev Technol 4:307–315
Lam LT, Davis R, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Wright G, Xu W, Zhao H, Yu X, Dang L, Staudt LM (2008) Compensatory IKK alpha activation of classical NF-kappa B signaling during IKK beta inhibition identified by an RNA interference sensitization screen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20798–20803
Lau PN, Chow-Kevin BS, Chan C, Cheng-Christopher HK, Wise H (2009) The constitutive activity of the ghrelin receptor attenuates apoptosis via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 299:232–239
Leonore MLT (1999) Extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2, Jun N-terminal kinase, and c-jun are involved in NF-κB-dependent IL-6 expression in human monocytes. J Immunol 162:4893–4902
Li X, Zhao X, Fang Y, Jiang X, Duong T, Fan C, Huang CC, Kain SR (1998) Generation of destabilized green fluorescent protein as a transcription reporter. J Biol Chem 273:34970–34975
Li N, Banin S, Ouyang H, Li GC, Courtois G, Shiloh Y, Karin M, Rotman G (2001) ATM is required for IkappaB kinase (IKKk) activation in response to DNA double strand breaks. J Biol Chem 276:8898–8903
Lin Y, Ma W, Benchimol S (2000) Pidd, a new death–domain-containing protein, is induced by p53 and promotes apoptosis. Nat Genet 26:122–127
Liu Z, Hazan-Halevy I, Harris DM, Li P, Ferrajoli A, Faderl S, Keating MJ, Estrov Z (2011) STAT-3 activates NF-κB in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Res 9:507–515
Mao W, Ye J, Guan Z, Zhao J, Zhang C, Zhang N, Jiang P, Tian T (2007) Cadmium induces apoptosis in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells by caspase-dependent and -independent pathways acting on mitochondria. Toxicol In Vitro 21:343–354
Matsuda M, Tsukiyama T, Bohgaki M, Nonomura K, Hatakeyama S (2007) Establishment of a newly improved detection system for NF-κB activity. Immunol Lett 109:175–181
Miyamoto S (2010) Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage. Cell Res 21:116–130
Mukogawa T, Koyama F, Tachibana M, Takayanagi A, Shimizu N, Fujii H, Ueno M, Matsumoto H, Takeuchi T, Nakajima Y (2003) Adenovirus-mediated gene transduction of truncated I kappa B alpha enhances radiosensitivity in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci 94:745–750
Muroi M, Tanamoto K (2008) TRAF6 distinctively mediates MyD88- and IRAK-1-induced activation of NF-kappaB. J Leukoc Biol 83:702–707
Pessara U, Koch N (1990) Tumor necrosis factor alpha regulates expression of the major histocompatibility complex class II-associated invariant chain by binding of an NF-kappa B-like factor to a promoter element. Mol Cell Biol 10:4146–4154
Piret B, Piette J (1996) Topoisomerase poisons activate the transcription factor NF-kappaB in ACH-2 and CEM cells. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4242–4248
Puck T, Marcus P (1956) Action of X-rays on mammalian cells. J Exp Med 103:653–666
Raju U, Gumin GJ, Tofilon PJ (2000) Radiation-induced transcription factor activation in the rat cerebral cortex. Int J Radiat Biol 76:1045–1053
Russell JS, Tofilon PJ (2002) Radiation-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB involves selective degradation of plasma membrane-associated I(kappa)B(alpha). Mol Biol Cell 13:3431–3440
Sahijdak WM, Yang CR, Zuckerman JS, Meyers M, Boothman DA (1994) Alterations in transcription factor binding in radioresistant human melanoma cells after ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 138:S47–S51
Sellmyer MA, Chen Lc, Egeler EL, Rakhit R, Wandless TJ (2012) Intracellular context affects levels of a chemically dependent destabilizing domain. Plos One 7
Sen R, Smale ST (2010) Selectivity of the NF-κB response. Perspect Biol 2:a000257
Shaner NC, Campbell RE, Steinbach PA, Giepmans Ben NG, Palmer AE, Tsien RY (2004) Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 22:1567–1572
Shaner NC, Steinbach PA, Tsien RY (2005) A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins. Nat Meth 2:905–909
Solan NJ, Miyoshi H, Carmona EM, Bren GD, Paya CV (2002) RelB cellular regulation and transcriptional activity are regulated by p100. J Biol Chem 277:1405–1418
Strongin DE, Bevis B, Khuong N, Downing ME, Strack RL, Sundaram K, Glick BS, Keenan RJ (2007) Structural rearrangements near the chromophore influence the maturation speed and brightness of DsRed variants. Protein Eng Des Sel 20:525–534
Szumiel I (2008) Intrinsic radiation sensitivity: cellular signaling is the key. Radiat Res 169:249–258
Takemoto Y (1999) Increased JNK, AP-1 and NF-κB DNA binding activities in isoproterenol-induced cardiac remodeling. J Molec Cell Cardiol 31:2017–2030
Tamatani M, Che YH, Matsuzaki H, Ogawa S, Okado H, Miyake S, Mizuno T, Tohyama M (1999) Tumor necrosis factor induces Bcl-2 and Bcl-x expression through NFkappaB activation in primary hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 274:8531–8538
Treede I, Braun A, Jeliaskova P, Giese T, llekrug J, Griffiths G, Stremmel W, Ehehalt R (2009) TNF-α-induced up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines is reduced by phosphatidylcholine in intestinal epithelial cells. BMC Gastroenterol 9:53
Troppmair J, Hartkamp J, Rapp UR (1998) Activation of NF-kappa B by oncogenic Raf in HEK 293 cells occurs through autocrine recruitment of the stress kinase cascade. Oncogene 17:685–690
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S (1995) Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev 9:2723–2735
Volcic M, Karl S, Baumann B, Salles D, Daniel P, Fulda S, Wiesmuller L (2012) NF-kappaB regulates DNA double-strand break repair in conjunction with BRCA1-CtIP complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 40:181–195
Watt PM, Hickson ID (1994) Structure and function of type II DNA topoisomerases. Biochem J 303:681–695
Westbrook AM, Wei B, Hacke K, Xia M, Braun J, Schiestl RH (2012) The role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and tumour necrosis factor receptor signalling in inflammation-associated systemic genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 27:77–86
Wheelhouse NM, Chan YS, Gillies SE, Caldwell H, Ross JA, Harrison DJ, Prost S (2003) TNF-alpha induced DNA damage in primary murine hepatocytes. Int J Mol Med 12:889–894
Yang CR, Wilson-Van PC, Planchon SM, Wuerzberger-Davis SM, Davis TW, Cuthill S, Miyamoto S, Boothman DA (2000) Coordinate modulation of Sp1, NF-kappa B, and p53 in confluent human malignant melanoma cells after ionizing radiation. FASEB J 14:379–390
Yu Q, Rose JH, Zhang H, Pommier Y (2001) Antisense inhibition of Chk2/hCds1 expression attenuates DNA damage-induced S and G2 checkpoints and enhances apoptotic activity in HEK-293 cells. FEBS Lett 505:7–12
Zhou D, Brown SA, Yu T, Chen G, Barve S, Kang BC, Thompson JS (1999) A high dose of ionizing radiation induces tissue-specific activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in vivo. Radiat Res 151:703–709
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-und Raumfahrt e.V. (DLR), Helmholtz SpaceLife program for accomplishment of Ph.D degree at the University of Bonn. The authors would like to thank all the members of Biodiagnostics group for their timely help.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The experiments shown in this manuscript comply with the current laws of Germany where they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chishti, A.A., Baumstark-Khan, C., Hellweg, C.E. et al. Imaging of nuclear factor κB activation induced by ionizing radiation in human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 53, 599–610 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-014-0541-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-014-0541-x