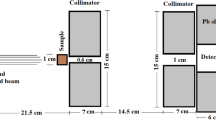
Abstract
Mass attenuation coefficient, \( \mu_{m} \), atomic cross-section, \( \sigma_{i} \), electronic cross-section, \( \sigma_{e} \), effective atomic number, \( Z_{\text{eff}} \) and effective electron density, \( N_{\text{el}} \), were determined experimentally and theoretically for some vitamins (retinol, beta-carotene, thiamine, riboflavin, niacinamide, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, biotin, folic acid, cyanocobalamin, ascorbic acid, cholecalciferol, alpha-tocopherol, ketamine, hesperidin) at 30.82, 59.54, 80.99, 356.61, 661.66 and 1,408.01 keV photon energies using a NaI(Tl) scintillation detector. The theoretical mass attenuation coefficients were estimated using mixture rules. The calculated values were compared with the experimental values for all vitamins.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandal GS, Singh K, Rani R, Kumar V (1994) Energy absorption coefficients for 662 and 1,115 keV gamma rays in some fatty acids. Appl Radiat Isot 45:379–381
Chitralekha B, Kerur R, Lagare MT, Nathuram R, Sharma DN (2005) Mass attenuation coefficients of saccharides for low-energy X-rays. Radiat Phys Chem 72:1–5
Demir D, Keleş G (2006) Radiation transmission of concrete including boron waste for 59.54 and 80.99 keV gamma rays. Nucl Instrum Methods B 245:501–504
Gerward L, Guilbert N, Jensen KB, Levring H (2001) X-ray absorption in matter reengineering XCOM. Radiat Phys Chem 60:23–24
Hine GJ (1952) The effective atomic numbers of materials for various gamma interactions. Phys Rev 85:725–728
Hubbell JH (1999) Review of photon interaction cross section data in the medical and biological context. Phys Med Biol 44:R1–R22
Kerur BR, Thontadarya SR, Hanumaiah B (1991) A novel method for the determination of X-ray mass attenuation coefficients. Appl Radiat Isot 42:571–576
Manjunathaguru V, Umesh TK (2009) Simple parametrization of photon mass energy absorption coefficients of H-, C-, N- and O-based samples of biological interest in the energy range 200–1500 keV. Pramana J Phys 72:375–387
Manohara SR, Hanagodimath SM, Gerward L (2008a) Energy dependence of effective atomic numbers for photon energy absorption and photon interaction: studies of some biological molecules in the energy range 1 keV–20 MeV. Med Phys 35:388–402
Manohara SR, Hanagodimath SM, Thind KS, Gerward L (2008b) On the effective atomic number and electron density: a comprehensive set of formulas for all types of materials and energies above 1 keV. Nucl Instrum Methods B 266:3906–3912
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, D., Turşucu, A. & Öznülüer, T. Studies on mass attenuation coefficient, effective atomic number and electron density of some vitamins. Radiat Environ Biophys 51, 469–475 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-012-0427-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-012-0427-8