Abstract
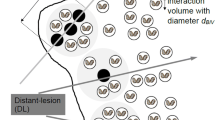
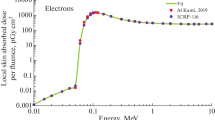
For radiation exposures employing targeted sources such as particle microbeams, the deposition of energy and dose will depend on the spatial heterogeneity of the sample. Although cell structural variations are relatively minor for two-dimensional cell cultures, they can vary significantly for fully differentiated tissues. Employing high-resolution confocal microscopy, we have determined the spatial distribution, size, and shape of epidermal keratinocyte nuclei for the full-thickness EpiDerm™ skin model (MatTek, Ashland, VA). Application of these data to calculate the microdosimetry and microdistribution of energy deposition by an electron microbeam is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belyakov OV, Mitchell SA, Parikh D, Randers-Pehrson G, Marino SA, Amundson SA, Geard CR, Brenner DJ (2005) Biological effects in unirradiated human tissue induced by radiation damage up to 1 mm away. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(40):14203–14208
Gangatirkar P, Paquet-Fifield S, Li A, Rossi R, Kaur P (2007) Establishment of 3D organotypic cultures using human neonatal epidermal cells. Nat Protoc 2(1):178–186
Griffith LG, Swartz MA (2006) Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(3):211–224
Hei TK, Ballas LK, Brenner DJ, Geard CR (2009) Advances in radiobiological studies using a microbeam. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 50(Suppl A):A7–A12
Kellerer AM (1985) Fundamentals of microdosimetry. In: Kase KR, Bjarngard BE, Attix FH (eds) The dosimetry of ionizing radiation, vol 1. Academic Press Inc., London, pp 77–162
Khavari PA (2006) Modelling cancer in human skin tissue. Nat Rev 6(4):270–280
Luna LG (ed) (1968) Manual of histologic staining methods of the armed forces institute of pathology, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Miller JH, Suleiman A, Chrisler WB, Sowa MB (2011) Simulation of electron beam irradiation of skin tissue model. Radiat Res 175(1):113–118
Prise KM, Schettino G, Vojnovic B, Belyakov O, Shao C (2009) Microbeam studies of the bystander response. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 50(Suppl A):A1–A6
Sedelnikova OA, Nakamura A, Kovalchuk O, Koturbash I, Mitchell SA, Marion SA, Brenner DJ, Bonner WM (2007) DNA double-strand breaks form in bystander cells after microbeam irradiation of three-dimensional human tissue models. Cancer Res 67(9):4295–4302
Sowa MB, Murphy MK, Miller JH, McDonald JC, Strom DJ, Kimmel GA (2005) A variable-energy electron microbeam: a unique modality for targeted low-LET radiation. Radiat Res 164(5):695–700
Sowa MB, Chrisler WB, Zens KD, Ashjian EJ, Opresko LK (2010a) Three-dimensional culture conditions lead to decreased radiation induced cytotoxicity in human mammary epithelial cells. Mutat Res 687(1–2):78–83
Sowa MB, Goetz W, Baulch JE, Pyles DN, Dziegielewski J, Yovino S, Snyder AR, de Toledo SM, Azzam EI, Morgan WF (2010b) Lack of evidence for low-LET radiation induced bystander response in normal human fibroblasts and colon carcinoma cells. Int J Radiat Biol 86(2):102–113
Vaughan MB, Ramirez RD, Brown SA, Yang JC, Wright WE, Shay JW (2004) A reproducible laser-wounded skin equivalent model to study the effects of aging in vitro. Rejuvenation Res 7(2):99–110
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Biological and Environmental Research Program (BER), US Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-76RLO1830.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is based on a presentation made at the 9th International Microbeam Workshop, July 15–17, 2010, in Darmstadt, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, J.H., Chrisler, W.B., Wang, X. et al. Confocal microscopy for modeling electron microbeam irradiation of skin. Radiat Environ Biophys 50, 365–369 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-011-0371-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-011-0371-z