Abstract
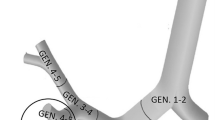
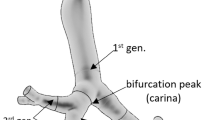
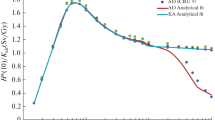
A model for bifurcation regions of the human tracheo-bronchial tree was developed. Equations for the surfaces are given to enable calculations of doses from alpha-particles emitted in these regions. It has been found that a bifurcation region is well approximated by a quasiellipsoid. The absorbed fractions of alpha-particles emitted in bifurcation regions were calculated by the Monte Carlo method. The average absorbed fraction under the bifurcation geometry is close to that found under the cylindrical geometry in the bronchial region. In the bronchiolar region, the absorbed fractions under the bifurcation geometry are up to 20% larger than those under the cylindrical geometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofmann W, Balashazy I, Koblinger L (1995) The effect of gravity on particle deposition patterns in bronchial airway bifurcations. J Aerosol Sci 26:1161–1168
Hofmann W, Balashazy I, Heistracher T (2001) The relationship between secondary flows and particle deposition patterns in airway bifurcations. Aerosol Sci Technol 35:958–968
Martonen TB, Guan X, Schreck RM (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations. I. Primary flows. Inhal Toxicol 13:261–279
Martonen TB, Guan X, Schreck RM (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations. II. Secondary currents. Inhal Toxicol 13:281–289
Martonen TB, Guan X, Schreck RM (2001) Fluid dynamics in airway bifurcations. III. Localized flow conditions. Inhal Toxicol 13:291–305
Balashazy I, Hofmann W (2000) Quantification of local deposition patterns of inhaled radon decay products in human bronchial airway bifurcations. Health Phys 78:147–158
ICRP (1994) ICRP Publication 66. Human respiratory tract model for radiological protection. A report of a Task Group of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Pergamon Press, New York
Spencer RM, Schroeter JD, Martonen TB (2001) Computer simulations of lung airway structures using data-driven surface modeling techniques. Comput Biol Med 31:499–511
Chakravarty S, Mandal PK (1997) An analysis of pulsatile flow in a model aortic bifurcation. Int J Eng Sci 35:409–422
Nikezic D, Yu KN (2002) Distributions of specific energy in sensitive layers of the human respiratory tract. Radiat Res 157:92–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online: 8 April 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikezic, D., Yu, K.N. Absorbed fraction of alpha-particles emitted in bifurcation regions of the human tracheo-bronchial tree. Radiat Environ Biophys 42, 49–53 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-003-0185-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-003-0185-8