Abstract
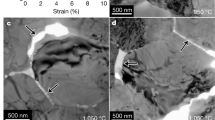
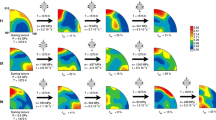
Deformation experiments on olivine aggregates were performed under hydrous conditions using a deformation-DIA apparatus combined with synchrotron in situ X-ray observations at pressures of 1.5–9.8 GPa, temperatures of 1223–1800 K, and strain rates ranging from 0.8 × 10−5 to 7.5 × 10−5 s−1. The pressure and strain rate dependencies of the plasticity of hydrous olivine may be described by an activation volume of 17 ± 6 cm3 mol−1 and a stress exponent of 3.2 ± 0.6 at temperatures of 1323–1423 K. A comparison between previous data sets and our results at a normalized temperature and a strain rate showed that the creep strength of hydrous olivine deformed at 1323–1423 K is much weaker than that for the dislocation creep of water-saturated olivine and is similar to that for diffusional creep and dislocation-accommodated grain boundary sliding, while dislocation microstructures showing the [001] slip or the [001](100) slip system were developed. At temperatures of 1633–1800 K, a much stronger pressure effect on creep strength was observed for olivine with an activation volume of 27 ± 7 cm3 mol−1 assuming a stress exponent of 3.5, water fugacity exponent of 1.2, and activation energy of 520 kJ mol−1 (i.e., power-law dislocation creep of hydrous olivine). Because of the weak pressure dependence of the rheology of hydrous olivine at lower temperatures, water weakening of olivine could be effective in the deeper and colder part of Earth’s upper mantle.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson EH, Browon JM, Slutsky LJ, Zaug J (1997) The elastic constants of San Carlos olivine up to 17 GPa. J Geophys Res 105:7893–7908
Beran A, Libowitzky E (2006) Water in natural mantle minerals II: olivine, garnet and accessory minerals. Rev Miner Geochem 62:169–191
Bollinger C, Raterron P, Cordier P, Merkel S (2014) Polycrystaline olivine rheology in dislocation creep: revisiting experimental data to 8.1 GPa. Phys Earth Planet Inter 228:211–219
Bollinger C, Merkel S, Cordier P, Raterron P (2015) Deformation of forsterite polycrystals at mantle pressure: comparison with Fe-bearing olivine and the effect of iron on its plasticity. Phys Earth Planet Inter 240:95–104
Boneh Y, Skemer P (2014) The effect of deformation history on the evolution of olivine CPO. Earth Planet Sci Lett 406:213–222
Borch RS, Green HW (1987) Dependence of creep in olivine on homologous temperature and its implications for flow in the mantle. Nature 330:345–348
Borch RS, Green HW (1989) Deformation of peridotite at highpressure in a new molten salt cell: comparison of traditional and homologous temperature treatments. Phys Earth Planet Inter 55:269–276
Bunge HJ (1982) Texture analysis in materials science. Butterworths, London
Chopra PN, Paterson MS (1984) The role of water in the deformation of dunite. J Geophys Res 89:7861–7876
Couvy H, Frost DJ, Heidelbach F, Nyilas K, Ungár T, Mackwell S, Cordier P (2004) Shear deformation experiments of forsterite at 11 GPa–1400 °C in the multianvil apparatus. Eur J Miner 16:877–889
Demouchy S, Tommasi A, Barou F, Mainprice D, Cordier P (2012) Deformation of olivine in torsion under hydrous conditions. Phys Earth Planet Inter 202–203:56–70
Demouchy S, Mussi A, Barou F, Tommasi A, Cordier P (2014) Viscoplasticity of polycrystalline olivine experimentally deformed at high pressure and 900 °C. Techtonophys 623:123–135
Dresen G, Wang Z, Bai Q (1996) Kinetics of grain growth in anorthite. Techtonophys 258:251–262
Durham WB, Mei S, Kohlstedt DL, Wang L, Dixon N (2009) New measurements of activation volume in olivine under anhydrous conditions. Phys Earth Planet Inter 172:67–73
Faul UH, Cline CJ, David EC, Berry AJ, Jackson I (2016) Titanium-hydroxyl defect-controlled rheology of the Earth’s upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 452:227–237
Férot A, Bolfan-Casanova N (2012) Water storage capacity in olivine and pyroxene to 14 GPa: implications for the water content of the earth’s upper mantle and nature of seismic discontinuities. Earth Planet Sci Lett 349–350:218–230
Girard J, Chen J, Raterron P III, Holyoke C (2013) Hydrolytic weakening of olivine at mantle pressure: evidence of [100](010) slip system softening from single-crystal deformation experiments. Phys Earth Planet Inter 216:12–20
Grant KJ, Brooker RA, Kohn SC, Wood BJ (2007) The effect of oxygen fugacity on hydroxyl concentrations and speciation in olivine: implications for water solubility in the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 261:217–229
Green HW, Borch RS (1987) The pressure dependence of creep. Acta Metall 35:1301–1305
Hansen LN, Zimmerman ME, Kohlstedt DL (2011) Grain boundary sliding in San Carlos olivine: flow law parameters and crystallographic-preferred orientation. J Geophys Res 116:B08201. doi:10.1029/2011JB008220
Hansen LN, Zimmerman ME, Dillman A, Kohlstedt D (2012) Strain localization in olivine aggregates at high temperature: a laboratory comparison of constant-strain-rate and constant-stress boundary conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 333–334:134–145
Hirschmann MM (2006) Water, melting, and the deep Earth H2O cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 34:629–653
Hirth G, Kohlstedt DL (1996) Water in the oceanic upper mantle: implications for rheology, melt extraction and the evolution of the lithosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144:93–108
Hirth G, Kohlstedt DL (2003) Rheology of the upper mantle and the mantle wedge: a view from the experimentalists. In: Eiler J (ed) Inside the subduction factory, Geophys. Monogr. Ser. American Geophysical Union, pp 83–105
Huang Y, Humphreys FJ (2000) Subgrain growth and low angle boundary mobility in aluminium crystals of orientation {110}<001>. Acta Mater 48:2017–2030
Isaak DG (1992) High-temperature elasticity of iron-bearing olivines. J Geophys Res 97:1871–1885
Jung H, Karato S (2001a) Effects of water on dynamically recrystallized grain-size of olivine. J Struct Geol 23:1337–1344
Jung H, Karato S (2001b) Water-induced fabric transitions in olivine. Science 293:1460–1463
Jung H, Katayama I, Jiang Z, Hiraga T, Karato S (2006) Effect of water and stress on the lattice-preferred orientation of olivine. Tectonophysics 421:1–22
Kaminski É (2002) The influence of water on the development of lattice preferred orientation in olivine aggregates. Geophys Res Lett 29:17-1. doi:10.1029/2002GL014710
Karato S (1989a) Defects and plastic deformation in olivine. In: Karato S, Toriumi M (eds) Rheology of solids and of the earth. Oxford University Press, London, pp 176–208
Karato S (1989b) Grain growth kinetics in olivine aggregates. Tectonophysics 168:255–273
Karato S, Jung H (2003) Effects of pressure on high-temperature dislocation creep in olivine. Philos Mag 83:401–414
Karato S, Rubie DC (1997) Toward an experimental study of deep mantle rheology: a new multianvil sample assembly for deformation studies under high pressures and temperatures. J Geophys Res 102:20111–20122
Karato S, Paterson MS, FitzGerald JD (1986) Rheology of synthetic olivine aggregates: influence of grain size and water. J Geophys Res 91:8151–8176
Karato S, Zhang S, Wenk H-R (1995) Superplasticity in Earth’s lower mantle: evidence from seismic anisotropy and rock physics. Science 270:458–461
Katayama I, Karato S (2008) Low-temperature, high-stress deformation of olivine under water-saturated conditions. Phys Earth Planet Inter 168:125–133
Katayama I, Jung H, Karato S (2004) New type of olivine fabric from deformation experiments at modest water content and low stress. Geology 32:1045–1048
Kawazoe T, Karato S, Otsuka K, Jing Z, Mookherjee M (2009) Shear deformation of dry polycrystalline olivine under deep upper mantle conditions using a rotational Drickamer apparatus (RDA). Phys Earth Planet Inter 174:128–137
Kawazoe T, Nishihara Y, Ohuchi T, Nishiyama N, Higo Y, Funakoshi K, Irifune T (2011) In situ stress–strain measurements in a deformation-DIA apparatus at P-T conditions of the upper part of the mantle transition zone. Am Miner 96:1665–1672
Keefner JW, Mackwell SJ, Kohlstedt DL, Heidelbach F (2011) Dependence of dislocation creep of dunite on oxygen fugacity: implications for viscosity variations in Earth’s mantle. J Geophys Res 116:B05201. doi:10.1029/2010JB007748
Keppler H, Bolfan-Casanova N (2006) Thermodynamics of water solubility and partitioning. Rev Miner Geochem 62:193–230
Kohlstedt DL, Goetze C, Durham WB (1976a) Experimental deformation of single crystal olivine with application to flow in the mantle. In: Strens RGJ (ed) The physics and chemistry of minerals and rocks. Wiley, New York, pp 35–49
Kohlstedt DL, Goetze C, Durham WB (1976b) New technique for decorating dislocations in olivine. Science 191:1045–1046
Kohlstedt DL, Keppler H, Rubie DC (1996) Solubility of water in the α, β and γ phases of (Mg, Fe)2SiO4. Contrib Miner Petrol 123:345–357
Korenaga J, Karato S (2008) A new analysis of experimental data on olivine rheology. J Geophys Res 113:B02403. doi:10.1029/2007JB005100
Langdon T (2006) Grain boundary sliding revisited: developments in sliding over four decades. J Mater Sci 41:597–609
Li L, Weidner D, Raterron P, Chen J, Vaughan M, Me SH, Durham B (2006) Deformation of olivine at mantle pressure using the D-DIA. Eur J Miner 18:7–19
Liu M, Kerschhofei L, Mosenfelder JL, Rubie DC (1998) The effect of strain energy on growth rates during the olivine-spinel transformation and implications for olivine metastability in subducting slabs. J Geophys Res 103:23897–23909
Liu W, Kung J, Li B (2005) Elasticity of San Carlos olivine to 8 GPa and 1073 K. Geophys Res Lett 32:L16301. doi:10.1029/2005GL023453
Lizarralde D, Chave A, Hirth G, Schultz A (1995) Northeastern Pacific mantle conductivity profile from long-period magnetotelluric sounding using Hawaii to California submarine cable data. J Geophys Res 100:17837–17854
Mainprice D, Silver PG (1993) Interpretation of SKS-waves using samples from the subcontinental lithosphere. Phys Earth Planet Inter 78:257–280
McDonnell RD, Peach CJ, Spiers CJ (1999) Flow behavior of fine-grained synthetic dunite in the presence of 0.5 wt% H2O. J Geophys Res 104:17823–17845
McDonnell RD, Peach CJ, van Roermund HLM, Spiers CJ (2000) Effect of varying enstatite content on the deformation behavior of fine-grained synthetic peridotite under wet conditions. J Geophys Res 105:13535–13553
Mei S, Kohlstedt DL (2000a) Influence of water on plastic deformation of olivine aggregates 1. Diffusion creep regime. J Geophys Res 105:21457–21469
Mei S, Kohlstedt DL (2000b) Influence of water on plastic deformation of olivine aggregates 2. Dislocation creep regime. J Geophys Res 105:21471–21481
Mercier J-C (1980) Magnitude of the continental lithospheric stresses inferred from rheomorphic petrology. J Geophys Res 85:6293–6303
Merkel S (2006) X-ray diffraction evaluation of stress in high pressure deformation experiments. J Phys Condens Matter 18:S949–S962
Miyazaki T, Sueyoshi K, Hiraga T (2014) Olivine crystals align during diffusion creep of Earth’s upper mantle. Nature 502:321–327
Nishihara Y, Shinmei T, Karato S (2006) Grain-growth kinetics in wadsleyite: effects of chemical environment. Phys Earth Planet Inter 154:30–43
Nishihara Y, Ohuchi T, Kawazoe T, Spengler D, Tasaka M, Kikegawa T, Suzuki A, Ohtani E (2014) Rheology of fine-grained forsterite aggregate at deep upper mantle conditions. J Geophys Res 119:253–273. doi:10.1002/2013JB010473
Ohuchi T, Irifune T (2013) Development of A-type olivine fabric in water-rich deep upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 362:20–30
Ohuchi T, Irifune T (2014) Crystallographic preferred orientation of olivine in the Earth’s deep upper mantle. Phys Earth Planet Inter 228:220–231
Ohuchi T, Kawazoe T, Nishiyama N, Nishihara Y, Irifune T (2010) Technical development of simple shear deformation experiments using a deformation-DIA apparatus. J Earth Sci 21:523–531
Ohuchi T, Karato S, Fujino K (2011) Strength of single crystal of orthopyroxene under lithospheric conditions. Contrib Miner Petrol 161:961–975
Ohuchi T, Kawazoe T, Nishihara Y, Irifune T (2012a) Change of olivine a-axis alignment induced by water: origin of seismic anisotropy in subduction zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 317–318:111–119
Ohuchi T, Nishihara Y, Kawazoe T, Spengler D, Shiraishi R, Suzuki A, Kikegawa T, Ohtani E (2012b) Superplasticity in hydrous melt-bearing dunite: implications for shear localization in Earth’s upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 335–336:59–71
Ohuchi T, Kawazoe T, Higo Y, Funakoshi K, Suzuki A, Kikegawa T, Irifune T (2015) Dislocation-accommodated grain boundary sliding of water-rich olivine in the Earth’s deep upper mantle. Sci Adv 1:e1500360. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1500360
Paterson MS (1982) The determination of hydroxyl by infrared absorption in quartz, silicate glasses and similar materials. Bull Minér 105:20–29
Ross JV, Ave’Lallemant HG, Carter N (1979) Activation volume for creep in the upper mantle 203:261–263
Seto Y (2012) Whole pattern fitting for two-dimensional diffraction patterns from polycrystalline materials. Rev High Press Sci Technol 22:144–152
Shiraishi R, Ohtani E, Kubo T, Doi N, Suzuki A, Shimojuku A, Kato T, Kikegawa T (2011) Deformation cubic anvil press and stress and strain measurements using monochromatic X-rays at high pressure and high temperature. High Press Res 31:399–406
Singh AK, Balasingh C, Mao H-K, Hemley RJ, Shu J (1998) Analysis of lattice strains measured under nonhydrostatic pressure. J Appl Phys 83:7567–7575
Tasaka M, Hiraga T (2013) Influence of mineral fraction on the rheological properties of forsterite + enstatite during grain-size-sensitive creep: 1 grain size and grain growth. J Geophys Res 118:3970–3990. doi:10.1002/jgrb.50285
Tasaka M, Zimmerman ME, Kohlstedt DL (2015) Creep behavior of Fe-bearing olivine under hydrous conditions. J Geophys Res 120:6039–6057. doi:10.1002/2015JB012096
van der Meijde M, Marone F, Giardini D, van der Lee S (2003) Seismic evidence for water deep in Earth’s upper mantle. Science 300:1556–1558
Van der Wal D, Chopra P, Drury M, FitzGerald J (1993) Relationships between dynamically recrystallized grain size and deformation conditions in experimentally deformed olivine rocks. Geophys Res Lett 20:1479–1482
Vissers RLM, Drury MR, Stranting EHH, Spiers CJ, Dvd Wal (1995) Mantle shear zones and their effect on lithosphere strength during continental breakup. Tectonophysics 249:155–171
Wang Z (2002) Effects of pressure and water on the kinetic properties of olivine (PhD Thesis). University of Minnesota, p 134
Wang D, Mookherjee M, Xu Y, Karato S (2006) The effect of water on the electrical conductivity of olivine. Nature 443:977–980
Wenk H-R, Bennett K (1991) Modelling plastic deformation of peridotite with the self-consistent theory. J Geophys Res 96:8337–8349
Withers AC, Hirschmann MM (2008) Influence of temperature, composition, silica activity and oxygen fugacity on the H2O storage capacity of olivine at 8 GPa. Contrib Miner Petrol 156:595–605
Yoshino T, Matsuzaki T, Yamashita S, Katsura T (2006) Hydrous olivine unable to account for conductivity anomaly at the top of the asthenosphere. Nature 443:973–976
Zhao YD, Ginsberg SB, Kohlstedt DL (2004) Solubility of hydrogen in olivine: dependence on temperature and iron content. Contrib Miner Petrol 147:155–161
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Y. Nishihara, K. Funakoshi, T. Kikegawa, and T. Irifune for their technical support for the synchrotron experiments, T. Sakai for preparation of a TEM foil using the FIB system, and K. Fujino for his help with TEM observations. Official review by three anonymous reviewers improved the manuscript. This research was conducted with the approvals of the Photon Factory Program Advisory Committee (Proposal Nos. 2010G136 and 2012G133) and SPring-8 (No. 2013B0082), supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Nos. 22340161 and 25707040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Hans Keppler.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohuchi, T., Kawazoe, T., Higo, Y. et al. Flow behavior and microstructures of hydrous olivine aggregates at upper mantle pressures and temperatures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 172, 65 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1375-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1375-8