Abstract
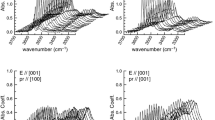
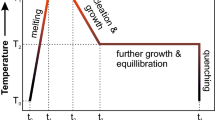
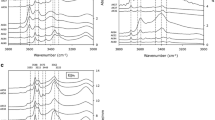
Hydrogen can be stored in the structure of nominally anhydrous minerals as point defects, and these impurities substantially modify many physical properties of Earth’s mantle minerals. However, mantle rocks are composed of mineral grains separated by grain boundaries and interphase grains boundaries. Therefore, as a potential hydrogen reservoir, grain boundaries should be given proper attention. Here, I report an experimental investigation into hydrogen diffusion through grain boundaries in polycrystalline aggregates. Sintering and diffusion experiments were performed using a gas-medium high-pressure vessel at under pressure of 300 MPa and over a temperature range of 900–1,250°C. The diffusion assembly consisted of a polycrystalline cylinder of aluminous spinel + olivine crystals with a talc cylinder as the main hydrogen source. A Ni capsule was used to buffer the oxygen fugacity at Ni–NiO. Experimental durations varied from 5 min to 5 h. The presence of hydrogen in the crystals was measured by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. The calculation of the diffusion coefficients was based on the estimation of the characteristic distance. The absence or presence of hydrogen recorded by the ‘hydrogen sensor’ olivines embedded in the aggregate allows the estimation of bounds on this characteristic distance. Results presented here suggest that hydrogen effective diffusion coefficients are only one order of magnitude faster (~10−9 m2s−1 at 1,000°C) than in an olivine single crystal along the [100] axis. Resulting diffusion coefficients for hydrogen in grain boundary are four orders of magnitude faster than in a single crystal, but this diffusivity is not fast enough to affect hydrogen mobility in mantle rocks with grain sizes greater than ~1 mm. Thus, very limited chemical homogenization would occur using grain boundaries diffusion in mantle hydrous peridotite for incompatible and volatile element, such as hydrogen.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aines RD, Rossman GR (1984) Water in minerals? A peak in the infrared. J Geophys Res (B6) 89:4059–4071
Aucouturier M (1982) Grain boundary segregations and hydrogen embrittlement. J Physique 43(C6–12):C6–C175
Bahr K, Simpson F (2002) Electrical anisotropy below low- and fast- plates: paleoflow in the upper mantle? Science 295:1270–1272
Balluffi RW, Allen SM, Carter WC (2005) Kinetics of materials. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Bedini MR, Bodinier JL, Dautria J-M, Morten L (1999) Evolution of LILE-renriched small melt fractions in the lithospheric mantle: a case study of the East African Rift. Earth Planet Sci Lett 153:67–83
Béjina F, Jaoul O, Liebermann RC (2003) Diffusion in minerals at high pressure: a review. Earth Planet Sci Lett 139:3–20
Bell D, Rossman G (1992) Water in earth’s mantle: the role of nominally anhydrous minerals. Science 255:1391–1397
Bell D, Rossman G, Maldener J, Endisch D, Rauch F (2003) Hydroxide in olivine: a quantitative determination of the absolute amount and calibration of the IR spectrum. J Geophys Res 108(B2). doi: 1029/2001JB000679
Berry A, Hermann J, O’Neill HSC, Foran GJ (2005) Fingerprinting the water site in mantle olivine. Geology 33:869–872
Bolfan-Casanova N (2005) Water in the earth’s mantle. Mine Mag 69:229–257
Bolfan-Casanova N, Keppler H, Rubie DC (2000) Water partitioning between nominally anhydrous minerals in the MgO–SiO2–H2O system up to 24 GPa: implications for the distribution of water in the earth’s mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 182:209–221
Brady JB (1983) Intergranular diffusion in metamorphic rocks. Am J Sci 283-A:181–200
Brenan JM, Watson EB (1987) Fluids in the lithosphere, 1. Experimentally-determined wetting characteristics of CO2–H2O fluids and their implications for fluid transport, host-rock physical properties, and fluid inclusion formation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 85:497–515
Chakraborty S, Farver JR, Yund RA, Rubie DC (1994) Mg tracer diffusion in synthetic forsterite and San carlos olivine as a function of P, T and fO2. Phys Chem Miner 21:489–500
Chen S, Hiraga T, Kohlstedt DL (2006) Water weakening of clinopyroxene in the dislocation creep regime. J Geophys Res 111:B08203. doi:10.1029/2005JB003885
Chopra PN, Paterson MS (1984) The role of water in the deformation of dunite. J Geophys Res 89:7861–7876
Costa F, Chakraborty S (2008) The effect of water in Si and O diffusion rates in olivine and implications for the transport properties and processes in the upper mantle. Phys Earth Planet Inter 166:11–29
Demouchy S, Mackwell SJ (2003) Water diffusion in synthetic iron-free forsterite. Phys Chem Miner 30:486–494
Demouchy S, Mackwell S (2006) Mechanisms of hydrogen incorporation and diffusion in iron-bearing olivine. Phys Chem Miner 33:347–355
Demouchy S, Jacobsen SD, Gaillard F, Stern CR (2006) Rapid magma ascent recorded by water diffusion profiles in mantle olivine. Geology 34:429–432
Demouchy S, Mackwell SJ, Kohlstedt DL (2007) Influence of hydrogen on Fe–Mg interdiffusion in (Mg, Fe)O and implications for earth’s lower mantle. Contrib Miner Petrol 154:279–289
Dixon JE, Leist L, Langmuir C, Schilling J-G (2002) Recycled dehydrated lithosphere observed in plume-influenced mid-ocean ridge-basalt. Nature 420:385–389
Harrison LG (1961) Influence of dislocations on diffusion kinetics in solids with particular reference to the alkali halides. Trans Faraday Soc 57:1191–1199
Hayden LA, Watson EB (2007) A diffusion mechanism for core-mantle interaction. Nature 450:709–712
Hayden LA, Watson EB (2008) Grain boundary mobility of carbon in earth’s mantle: a possible carbon flux from the core. Proceed Nat Acad Sci 105(25):8537–8541
Heidelbach F, Terry MP, Bystricky M, Holzapfel C, McCammon C (2009) A simultaneous deformation and diffusion experiments: quantification of the role of deformation in enhancing metamorphic reactions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 278:386–394
Hier-Majumder S, Anderson IM, Kohlstedt DL (2004) Influence of protons on Fe–Mg interdiffusion in olivine. J Geophys Res 110. doi: 10.1029/2004JB003292
Hiraga T, Kohlstedt DL (2007) Equilibrium interface segregation in the diopside-forsterite system I: analytical techniques, thermodynamics, and segregation characteristics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:1266–1280
Hiraga T, Kohlstedt DL (2009) Systematic distribution of incompatible elements in mantle peridotite: importance of intra and—inter-granular melt-like component. Contrib Miner Petrol 158:149–167
Hiraga T, Anderson IM, Kohlstedt DL (2003) Chemistry of grain boundaries in mantle rocks. Am Miner 88:1015–1019
Hiraga T, Anderson IM, Kohlstedt DL (2004) Grain boundaries as reservoirs of incompatible elements in the earth’s mantle. Nature 427:699–703
Hiraga T, Hirschmann MM, Kohlstedt DL (2007) Equilibrium interface segregation in the diopside-forsterite system 2: applications of interface enrichment to mantle geochemistry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:1281–1289
Hirth G, Kohlstedt DL (1996) Water in the oceanic upper mantle: implications for rheology, melt extraction and the evolution of the lithosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144:93–108
Holzapfel C, Rubie DC, Mackwell SJ, Frost DJ (2003) Effect of pressure on Fe–Mg interdiffusion in (Fe x Mg1−x )O, ferropericlase. Phys Earth Planet Inter 139:21–34
Huang X, Xu Y, Karato S-I (2005) Water content in the transition zone from electrical conductivity of wadsleyite and ringwoodite. Nature 434:746–749
Ingrin J, Skogby H (2000) Hydrogen in nominally anhydrous upper-mantle minerals: concentration levels and implications. Eur J Miner 12:543–570
Jacobsen SD, Smyth JR, Spetzler HA, Frost DJ (2004) Sound velocities and elastic constant of iron-bearing hydrous ringwoodite. Phys Earth Planet Inter 143–144:47–56
Joesten R (1991) Grain boundary diffusion kinetics in silicate and oxide minerals. In: Ganguly J (ed) Diffusion, atomic ordering and mass transport, vol 8. Advances in physical geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, pp 345–395
Karato S-I (1990) The role of hydrogen diffusivity in the electrical conductivity of the upper mantle. Nature 347:272–273
Karato S-I (2008) Deformation of earth material. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 463 p
Keppler H, Bolfan-Casanova N (2006) Thermodynamics of water solubility and partitioning. In: Keppler H, Smyth JR (eds) Water in nominally anhydrous minerals, 62. American Mineralogical Society Geochemical Society, Chantilly (Vir.), pp 193–230
Kirchheim R (2001) Solubility and diffusivity of hydrogen in complex materials. Phys Scripta T94:58–62
Kohlstedt DL (2006) The role of water in high-temperature rock deformation. In: Keppler H, Smyth JR (eds) Water in Nominally Anhydrous Minerals, 62. American Mineralogical Society Geochemical Society, Chantilly (Vir.), pp 377–396
Kohlstedt DL, Mackwell SJ (1998) Diffusion of hydrogen and intrinsic point defects in olivine. Z Phys Chem 207:47–162
Kohlstedt DL, Keppler H, Rubie DC (1996) Solubility of water in the α, β and γ phases of (Mg, Fe)2SiO4. Contrib Miner Petrol 123:345–357
Kröger FA, Vink HJ (1956) Relation between the concentrations of imperfections in crystallines solids. Academy Press, New York
Le Roux V, Tommasi A, Vauchez A (2008) Feedback between melt percolation and deformation in an exhumed lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Earth Planet Sci Lett 274:401–413
Libowitzky E, Rossman GR (1997) An IR absorption calibration for water in minerals. Am Miner 82:1111–1115
Mackwell SJ, Kohlstedt DL (1990) Diffusion of hydrogen in olivine: implications for water in the mantle. J Geophys Res 95(B4):5079–5088
Mackwell SJ, Kohlstedt DL, Paterson (1985) The role of water in the deformation of olivine single crystals. J Geophys Res 90(B13):11,319–11333
Mackwell SJ, Dimos D, Kohlstedt DL (1988) Trancient creep of olivine: point-defect relaxation times. Philos Mag A 57(5):779–789
Mackwell SJ, Bystricky M, Sproni C (2005) Fe–Mg interdiffusion in (Mg,Fe)O. Phys Chem Miner. doi:10.1007/s00269-005-0013-6
Matveev S, O’Neill HS, Ballaus C, Taylor WR, Green DH (2001) Effect of silica activity on OH− IR spectra of olivine: implications for Low-aSiO2 mantle metasomatism. J Petrol 42(4):721–729
McCaig A, Covey-Crump SJ, Ben Ismail W, Lloyd GE (2006) Fast diffusion along mobile grain boundaries in calcite. Contrib Miner Petrol. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0138-8
McCammon CA (2005) The paradox of mantle redox. Science 308:807
Mei S, Kohlstedt DL (2000) Influence of water on plastic deformation of olivine aggregates 2. Dislocation creep regime. J Geophys Res 105(B9):21,471–21481
Miller GH, Rossman GR, Harlow GE (1987) The natural occurence of hydroxide in olivine. Phys Chem Miner 14:461–472
Misener DJ (1974) Cationic diffusion in olivine at 1400°C and 35 kbar. In: Hoffman AW et al (eds) Geochemical transport and kinetics. Carnegie Inst, Washington, DC, pp 117–129
Müller T, Dohmen R, Chakraborty S (2009) Modelling infiltration driven reactions using experiments: coupled dissolution-precipitation and exchange reaction between spinel grains in the presence of water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:A915
Mütschele T, Kirchheim R (1987) Segregation and diffusion of hydrogen in grain boundaries of Palladium. Scripta Metal 21:135–140
Nakamura A, Schmalzried H (1983) On the nonstoichiometry and point defects of olivine. Phys Chem Miner 10:27–37
Nakamura A, Schmalzried H (1984) On the Fe2+-Mg2+-interdiffusion in olivine (II). Ber. Bunsenges. Phys Chem 88:140–145
Nakamura M, Watson EB (2001) Experimental study of aqueous fluid infiltration into quartzite: implications for the kinetics of fluid redistribution and grain growth driven by interfacial energy reduction. Geofluids 1:73–89
Nakamura M, Watson EB (2005) Grain growth control of isotope exchange between rocks and fluids. Geology 33:829–832
O’Neill HS, Wall V (1987) The olivine-orthopyroxene-spinel oxygen geobarometer, the nickel precipitation curve, and the oxygen fugacity of Earth’s upper mantle. J Petrol 28:1169–1191
Paterson M (1982) The determination of hydroxyl by infrared absorption in quartz, silicate glasses and similar materials. Bull Minér 105:20–29
Paterson MS (1990) Rock deformation experimentation. In: Duba A et al (eds) The brittle-ductile transition in rocks: the Head, vol 56. Geophys Monogr Ser, AGU, Washington, DC, pp 187–194
Pawley AR, Wood BJ (1995) The high-pressure stability of talc and 10 A phase: potential storage site of H2O in subduction zones. Am Min 80:998–1003
Pedersen A, Jònsson H (2009) Simulation of hydrogen diffusion at grain boundaries in aluminium. Acta Mater 57:4036–4045
Pitzer KS, Sterner SM (1994) Equations of state valid continuously from zero to extreme pressures for H2O and CO2. J Chem Phys 101:3111–3116
Sato H (1986) High temperature a.c. electrical properties of olivine single crystal with varying oxygen partial pressure: implications for the point defect chemistry. Earth Planet Inter 41:269–282
Schmalzried H (1981) Solid state reactions. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim 254 pp
Soustelle V, Tommasi A, Demouchy S, Ionov D (2010) Deformation and fluid-rock interactions in supra-subduction mantle: microstructures and water contents in peridotite xenoliths from the Avacha volcano, Kamchatka. J Petrol 51:363–394
Sutton AR, Balluffi RW (1995) Interfaces in crystalline materials. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, 819 p
Van Orman J, Grove T, Shimizu N (2001) Rare earth element diffusion in diopside: influence of temperature, pressure, and ionic radius, and an elastic model for diffusion in silicates. Contrib Miner Petrol 141:687–703
Van Orman JA, Grove TL, Shimizu N, Layne GD (2002) Rare earth element diffusion in a natural pyrope single crystal at 2.8 GPa. Contrib Miner Petrol 142:416–424
Van Orman JA, Fei Y, Hauri E, Wang Y (2003) Diffusion in MgO at high pressures: constraints on deformation mechanisms and chemical transport at the core-mantle boundary. Geophys Res Lett 30. doi: 10.1029/2002GL016343
Wang Z, Hiraga T, Kohlstedt DL (2004) Effect of H+ on Fe–Mg interdiffusion in olivine, (Fe–Mg)2SiO4. Appl Phys Lett 85:209–211
Wang J, Mookherjee M, Xu Y, Karato S (2006) The effect of water on the electrical conductivity of olivine. Nature 443:977–980
Wernet P, Testemale D, Hazeman J-L, Argoud R, Glatzel P, Petersson LGM, Nilsson A, Bergmann U (2005) Spectroscopic characterization of microscopic hydrogen-bounding disparities in supercritical water. J Chem Phys 123:154503
Yoshino T, Matsuzaki T, Yamashita S, Katsura T (2006) Hydrous olivine unable to account for conductivity anomaly at the top of the asthenosphere. Nature 443:973–976
Zhao Y, Ginsberg S, Kohlstedt D (2004) Solubility of hydrogen in olivine: dependence on temperature and iron content. Contrib Miner Petrol 147:155–161
Acknowledgments
SD is thankful to Takehiko Hiraga and Tony Withers for numerous and enthusiastic discussions at the very early stage of the project, as well as to Bruce Watson and two reviewers for helpful comments. Christophe Nevado and Doriane Delmas are thanked for providing high-quality thin sections. Joel Oustry is thanked for his precious assistance and patience in the mechanical workshop. Electron microprobe analyses were carried out with the help of Claude Merlet and Bernard Boyer at the Electron Microprobe Lab ‘SUD’, and FTIR analyses were performed with the help of David Maurin at the Lab. Colloids, Verre et Nanomateriaux, both facilities located at Université Montpellier 2, France. CNRS supported this study trough INSU and its SEDIT 2008 program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. L. Grove.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demouchy, S. Hydrogen diffusion in spinel grain boundaries and consequences for chemical homogenization in hydrous peridotite. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160, 887–898 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-010-0512-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-010-0512-4