Abstract
Purpose
Serum decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) level increases in chronic inflammatory diseases. The present study aimed to examine serum DcR3 and IL-6 levels in male patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and acute exacerbation of the disease and correlations between these markers and airflow limitation.
Methods
We measured serum DcR3 and IL-6 levels in 60 COPD patients [30 stable COPD (SCOPD), and 30 acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD)], and 30 control subjects and assessed their correlations with airflow limitation according to the COPD stage indicated by the global initiative for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (GOLD) criteria, peripheral O2 saturation (SpO2), and COPD assessment test (CAT) score. We also tested associations between serum DcR3 levels and COPD patients’ clinical parameters.
Results
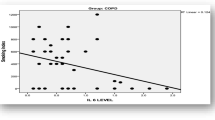
Both serum DcR3 and IL-6 levels increased with increasing severity of airflow limitation in SCOPD and AECOPD groups (P < 0.01 to 0.001). These markers also increased in patients with AECOPD compared with subjects in SCOPD group in GOLD stages III–IV (P < 0.05 to 0.001). In addition, there was a significant positive correlation between serum DcR3 level and IL-6, CAT score and smoking history (per year).
Conclusion
The study revealed that serum DcR3 level elevated with increasing severity of airflow limitation in male COPD patients, particularly in acute exacerbation phase. This increase was associated with a reduced quality of life and increased severity of hypoxia. These results suggest that DcR3 may be associated with the underlying pathophysiology of COPD in male patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh D, Agusti A, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J, Celli BR, Criner GJ, Frith P, Halpin DM, Han M (2019) Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease: the GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00164-2019
Celli BR, Barnes PJ (2007) Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J 29(6):1224–1238. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00109906
Wouters EF, Groenewegen KH, Dentener MA, Vernooy JH (2007) Systemic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the role of exacerbations. Proc Am Thorac Soc 4(8):626–634. https://doi.org/10.1513/pats.200706-071TH
Hurst JR, Perera WR, Wilkinson TM, Donaldson GC, Wedzicha JA (2006) Systemic and upper and lower airway inflammation at exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173(1):71–78. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200505-704OC
Lin W-W, Hsieh S-L (2011) Decoy receptor 3: a pleiotropic immunomodulator and biomarker for inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 81(7):838–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.011
Cheng C-P, Sytwu H-K, Chang D-M (2011) Decoy receptor 3 attenuates collagen-induced arthritis by modulating T cell activation and B cell expansion. J Rheumatol 38(12):2522–2535. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.110245
Chang Y-C, Hsu T-L, Lin H-H, Chio C-C, Chiu AW, Chen N-J, Lin C-H, Hsieh S-L (2004) Modulation of macrophage differentiation and activation by decoy receptor 3. J Leukoc Biol 75(3):486–494. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0903448
Mueller AM, Pedré X, Killian S, David M, Steinbrecher A (2009) The Decoy Receptor 3 (DcR3, TNFRSF6B) suppresses Th17 immune responses and is abundant in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 209(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.01.024
Hung SC, Hsu TW, Lin YP, Tarng DC (2012) Decoy receptor 3, a novel inflammatory marker, and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7(8):1257–1265. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.08410811
Yang C-R, Hsieh S-L, Ho F-M, Lin W-W (2005) Decoy receptor 3 increases monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells via NF-κB-dependent up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, VCAM-1, and IL-8 expression. J Immunol 174(3):1647–1656. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.174.3.1647
Schrijvers DM, De Meyer GR, Kockx MM, Herman AG, Martinet W (2005) Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages is impaired in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1256–1261. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000166517.18801.a7
Chen M-H, Kan H-T, Liu C-Y, Yu W-K, Lee S-S, Wang J-H, Hsieh S-L (2017) Serum decoy receptor 3 is a biomarker for disease severity in nonatopic asthma patients. J Formos Med Assoc 116(1):49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2016.01.007
Gao L, Yang B, Zhang H, Ou Q, Lin Y, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Kim S, Wu B, Wang Z, Fu L, Lin J, Chen R, Lan R, Chen J, Chen W, Chen L, Zhang H, Han D, Chen J, Okunieff P, Lin J, Zhang L (2018) DcR3, a new biomarker for sepsis, correlates with infection severity and procalcitonin. Oncotarget 9(13):10934–10944. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23736
Chen C-Y, Yang K-Y, Chen M-Y, Chen H-Y, Lin M-T, Lee Y-C, Perng R-P, Hsieh S-L, Yang P-C, Chou T-Y (2009) Decoy receptor 3 levels in peripheral blood predict outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit 180(8):751–760. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200902-0222OC
Funke B, Autschbach F, Kim S, Lasitschka F, Strauch U, Rogler G, Gdynia G, Li L, Gretz N, Macher-Goeppinger S, Sido B, Schirmacher P, Meuer SC, Roth W (2009) Functional characterisation of decoy receptor 3 in Crohn's disease. Gut 58(4):483–491. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.148908
Dong Y, Shi D, Li M, Dai P, Wang X, Xie M (2015) Elevated serum levels of decoy receptor 3 are associated with disease severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Intern Emerg Med 10(5):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1195-7
Lee CS, Hu CY, Tsai HF, Wu CS, Hsieh SL, Liu LC, Hsu PN (2008) Elevated serum decoy receptor 3 with enhanced T cell activation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 151(3):383–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03579.x
Chang T-Y, Hsu C-Y, Huang P-H, Chiang C-H, Leu H-B, Huang C-C, Chen J-W, Lin S-J (2015) Usefulness of circulating decoy receptor 3 in predicting coronary artery disease severity and future major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 116(7):1028–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.06.041
Hsieh SL, Lin WW (2017) Decoy receptor 3: an endogenous immunomodulator in cancer growth and inflammatory reactions. J Biomed Sci 24(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-017-0347-7
Zhou A, Zhou Z, Peng Y, Zhao Y, Duan J, Chen P (2018) The role of CAT in evaluating the response to treatment of patients with AECOPD. Int J Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis 13:2849–2858. https://doi.org/10.2147/copd.s175085
Amani M, Ghadimi N, Aslani MR, Ghobadi H (2017) Correlation of serum vascular adhesion protein-1 with airflow limitation and quality of life in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med 132:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2017.10.011
Hogg JC (2004) Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 364(9435):709–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16900-6
Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, Buzatu L, Cherniack RM, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Coxson HO, Pare PD (2004) The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 350(26):2645–2653. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa032158
Barnes PJ (2016) Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(1):16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.011
Liang R, Zhang W, Song YM (2013) Levels of leptin and IL-6 in lungs and blood are associated with the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in patients and rat models. Mol Med Rep 7(5):1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1377
Foschino Barbaro MP, Carpagnano GE, Spanevello A, Cagnazzo MG, Barnes PJ (2007) Inflammation, oxidative stress and systemic effects in mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 20(4):753–763. https://doi.org/10.1177/039463200702000411
Kim S, McAuliffe WJ, Zaritskaya LS, Moore PA, Zhang L, Nardelli B (2004) Selective induction of tumor necrosis receptor factor 6/decoy receptor 3 release by bacterial antigens in human monocytes and myeloid dendritic cells. Infect Immun 72(1):89–93. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.72.1.89-93.2004
Ortiz A, Lorz C, Justo P, Catalan MP, Egido J (2001) Contribution of apoptotic cell death to renal injury. J Cell Mol Med 5(1):18–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2001.tb00135.x
Watz H, Waschki B, Meyer T, Magnussen H (2009) Physical activity in patients with COPD. Eur Respir J 33(2):262–272
Watz H, Waschki B, Kirsten A, Muller KC, Kretschmar G, Meyer T, Holz O, Magnussen H (2009) The metabolic syndrome in patients with chronic bronchitis and COPD: frequency and associated consequences for systemic inflammation and physical inactivity. Chest 136(4):1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.09-0393
Acknowledgements
This is a report of a database from the study “Evaluation of serum levels of Decoy receptor 3 and IL-6 in COPD patients” registered in Research Committee of the Ardabil University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MRA, NH, and HG: Literature search, Proposal writing, Data collection, Analysis of data, Interpretation of data, Manuscript preparation, Review of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghobadi, H., Hosseini, N. & Aslani, M.R. Correlations Between Serum Decoy Receptor 3 and Airflow Limitation and Quality of Life in Male Patients with Stable Stage and Acute Exacerbation of COPD. Lung 198, 515–523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00348-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00348-z