Abstract
Background
Our previous data have demonstrated that the number of IL-9-producing CD4+ T cells (Th9 cells) in malignant pleural effusion (MPE) was significantly increased when compared with that in blood. The aim of the present study was to investigate the mechanism by which Th9 cells were recruited into MPE and the phenotypic characteristics of pleural Th9 cells.
Methods
The expression patterns of chemokine receptors (CCRs) on Th9 cells and the chemoattractant activity of chemokine CCL20 for Th9 cells in vitro were observed. The phenotypic features of Th9 cells in MPE were determined by flow cytometry.
Results
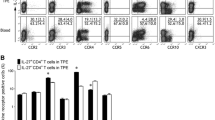
We found that Th9 cells in both MPE and blood expressed a high level of CCR6 on their surface. An in vitro migration assay confirmed that both MPE and supernatants of cultured pleural mesothelial cells could induce the migration of Th9 cells, and anti-CCL20 mAb significantly inhibited the ability of MPE or supernatants to stimulate Th9 cell chemotaxis. We also noted that pleural Th9 cells expressed high levels of CD45RO and very low levels of CD45RA and CD62L, displaying the phenotype of effector memory cells.
Conclusions
Our data revealed that recruitment of Th9 cells into MPE could be induced by pleural CCL20 and that the majority of Th9 cells in MPE displayed the phenotype of effector memory cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts ME, Neville E, Berrisford RG, Antunes G, Ali NJ, BTS Pleural Diseases Guideline Group (2010) Management of a malignant pleural effusion: British Thoracic Society Pleural Disease Guideline 2010. Thorax 65(Suppl 2):ii32–ii40
Maskell NA, Lee YC, Gleeson FV, Hedley EL, Pengelly G, Davies RJ (2004) Randomized trials describing lung inflammation after pleurodesis with talc of varying particle size. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:377–382
Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, Martin B, Wilhelm C, Stockinger B (2008) Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper two cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol 9:1341–1346
Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos G, Gao W, Sobel RA, Mitsdoerffer M, Strom TB, Elyaman W, Ho IC, Khoury S, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2008) IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9 + IL-10 + Foxp3(−) effector T cells. Nat Immunol 9:1347–1355
Stassen M, Schmitt E, Bopp T (2012) From interleukin-9 to T helper 9 cells. Ann NYAcad Sci 1247:56–68
Jäger A, Dardalhon V, Sobel RA, Bettelli E, Kuchroo VK (2009) Th1, Th17, and Th9 effector cells induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with different pathological phenotypes. J Immunol 183:7169–7177
Chang HC, Sehra S, Goswami R, Yao W, Yu Q, Stritesky GL, Jabeen R, McKinley C, Ahyi AN, Han L, Nguyen ET, Robertson MJ, Perumal NB, Tepper RS, Nutt SL, Kaplan MH (2010) The transcription factor PU.1 is required for the development of IL-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat Immunol 11:527–534
Horka H, Staudt V, Klein M, Taube C, Reuter S, Dehzad N, Andersen JF, Kopecky J, Schild H, Kotsyfakis M, Hoffmann M, Gerlitzki B, Stassen M, Bopp T, Schmitt E (2012) The tick salivary protein sialostatin L inhibits the Th9-derived production of the asthma-promoting cytokine IL-9 and is effective in the prevention of experimental asthma. J Immunol 188:2669–2676
Ye ZJ, Yuan ML, Zhou Q, Du RH, Yang WB, Xiong XZ, Zhang JC, Wu C, Qin SM, Shi HZ (2012) Differentiation and recruitment of Th9 cells stimulated by pleural mesothelial cells in human Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS One 7:e31710
Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, Yin W, Yuan ML, Yang WB, Xiong XZ, Zhang JC, Shi HZ (2012) Differentiation and immune regulation of interleukin 9-producing CD4+ T cells in malignant pleural effusion. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:1168–1179
Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, Gu YY, Qin SM, Ma WL, Xin JB, Tao XN, Shi HZ (2010) Generation and differentiation of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells in malignant pleural effusion. J Immunol 185:6348–6354
Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, Yuan ML, Du RH, Yang WB, Xiong XZ, Huang B, Shi HZ (2012) Differentiation and recruitment of IL-22-producing helper T cells stimulated by pleural mesothelial cells in tuberculous pleurisy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185:660–669
Qin XJ, Shi HZ, Huang ZX, Kang LF, Mo WN, Wu C (2005) Interleukin-16 in tuberculous and malignant pleural effusions. Eur Respir J 25:605–611
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (1999) Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 401:708–712
Stathopoulos GT, Kalomenidis I (2012) Malignant pleural effusion. Tumor–host interactions unleashed. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:487–492
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grant from National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (No. 30925032), and in part by Grants (No. 81272591 and No. 81270149) from National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X.-N. Bu and Q. Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, XN., Zhou, Q., Zhang, JC. et al. Recruitment and Phenotypic Characteristics of Interleukin 9-Producing CD4+ T Cells in Malignant Pleural Effusion. Lung 191, 385–389 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9474-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9474-4