Abstract
Background
There is little conclusive data regarding the effect of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) on glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). An earlier meta-analysis included two randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and found no significant effect of CPAP on HbA1c. The meta-analysis presented here was conducted to include all relevant observational studies and RCTs on the effect of CPAP on HbA1c.
Methods
We searched the PubMed database for all studies published prior to March 2012 for trials of the effect of CPAP on HbA1c. Data from observational studies and RCTs that met the inclusion criteria were extracted for pre- and post-treatment HbA1c.
Results
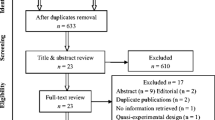
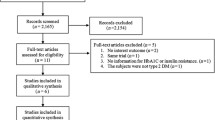
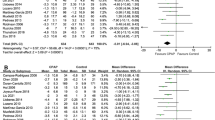
A total of nine studies that included 151 subjects met the inclusion criteria. The duration of the studies ranged from 41 days to 6 months. The mean net change in the HbA1c was −0.06 % [95 % CI: −0.24, 0.12] (p = 0.5). Five of the nine studies, with a total of 112 subjects, comprised patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2. The mean net change in HbA1c for the subjects with DM type 2 was 0.08 % [95 % CI: −0.26, 0.42] (p = 0.65). The mean net change in HbA1c for subjects with DM type 2 in studies that were at least 3 months in duration was 0.16 % [95 % CI: −0.26, 0.58] (p = 0.45).
Conclusions
This meta-analysis found that CPAP does not reduce HbA1c levels when used in the short term.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ (2002) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(9):1217–1239
Ip MS, Lam B, Ng MM, Lam WK, Tsang KW, Lam KS (2002) Obstructive sleep apnea is independently associated with insulin resistance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(5):670–676
Punjabi NM, Beamer BA (2009) Alterations in glucose disposal in sleep-disordered breathing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(3):235–240
Punjabi NM, Shahar E, Redline S, Gottlieb DJ, Givelber R, Resnick HE (2004) Sleep-disordered breathing, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance: the Sleep Heart Health Study. Am J Epidemiol 160(6):521–530
Punjabi NM, Sorkin JD, Katzel LI, Goldberg AP, Schwartz AR, Smith PL (2002) Sleep-disordered breathing and insulin resistance in middle-aged and overweight men. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165(5):677–682
Levy P, Bonsignore MR, Eckel J (2009) Sleep, sleep-disordered breathing and metabolic consequences. Eur Respir J 34(1):243–260
Spiegel K, Tasali E, Leproult R, Van Cauter E (2009) Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and obesity risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5(5):253–261
Aronsohn RS, Whitmore H, Van Cauter E, Tasali E (2010) Impact of untreated obstructive sleep apnea on glucose control in type 2 diabetes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181(5):507–513
Okada M, Takamizawa A, Tsushima K, Urushihata K, Fujimoto K, Kubo K (2006) Relationship between sleep-disordered breathing and lifestyle-related illnesses in subjects who have undergone health-screening. Intern Med 45(15):891–896
Papanas N, Steiropoulos P, Nena E, Tzouvelekis A, Maltezos E, Trakada G et al (2009) HbA1c is associated with severity of obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome in nondiabetic men. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:751–756
Steiropoulos P, Papanas N, Bouros D, Maltezos E (2010) Obstructive sleep apnea aggravates glycemic control across the continuum of glucose homeostasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182(2):286
Babu AR, Herdegen J, Fogelfeld L, Shott S, Mazzone T (2005) Type 2 diabetes, glycemic control, and continuous positive airway pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Intern Med 165(4):447–452
Shpirer I, Rapoport MJ, Stav D, Elizur A (2012) Normal and elevated HbA1C levels correlate with severity of hypoxemia in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and decrease following CPAP treatment. Sleep Breath 16(2):461–466
Steiropoulos P, Papanas N, Nena E, Tsara V, Fitili C, Tzouvelekis A et al (2009) Markers of glycemic control and insulin resistance in non-diabetic patients with obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome: does adherence to CPAP treatment improve glycemic control? Sleep Med 10(8):887–891
Dawson A, Abel SL, Loving RT, Dailey G, Shadan FF, Cronin JW et al (2008) CPAP therapy of obstructive sleep apnea in type 2 diabetics improves glycemic control during sleep. J Clin Sleep Med 4(6):538–542
Harsch IA, Schahin SP, Bruckner K, Radespiel-Troger M, Fuchs FS, Hahn EG et al (2004) The effect of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on insulin sensitivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Respiration 71(3):252–259
Hassaballa HA, Tulaimat A, Herdegen JJ, Mokhlesi B (2005) The effect of continuous positive airway pressure on glucose control in diabetic patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 9(4):176–180
Smurra M, Philip P, Taillard J, Guilleminault C, Bioulac B, Gin H (2001) CPAP treatment does not affect glucose-insulin metabolism in sleep apneic patients. Sleep Med 2(3):207–213
West SD, Nicoll DJ, Wallace TM, Matthews DR, Stradling JR (2007) Effect of CPAP on insulin resistance and HbA1c in men with obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes. Thorax 62(11):969–974
Hecht L, Mohler R, Meyer G (2011) Effects of CPAP-respiration on markers of glucose metabolism in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ger Med Sci 9:Doc20
Yang D, Liu Z, Yang H, Luo Q (2012) Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on glycemic control and insulin resistance in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. doi: 10.1007/s11325-012-0680-8
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283(15):2008–2012
Comondore VR, Cheema R, Fox J, Butt A, John Mancini GB, Fleetham JA et al (2009) The impact of CPAP on cardiovascular biomarkers in minimally symptomatic patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a pilot feasibility randomized crossover trial. Lung 187(1):17–22
Sharma SK, Agrawal S, Damodaran D, Sreenivas V, Kadhiravan T, Lakshmy R et al (2011) CPAP for the metabolic syndrome in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 365(24):2277–2286
Selvin E, Steffes MW, Zhu H, Matsushita K, Wagenknecht L, Pankow J et al (2010) Glycated hemoglobin, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in nondiabetic adults. N Engl J Med 362(9):800–811
Pallayova M, Donic V, Tomori Z (2008) Beneficial effects of severe sleep apnea therapy on nocturnal glucose control in persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 81(1):e8–11
Barcelo A, Barbe F, de la Pena M, Martinez P, Soriano JB, Pierola J et al (2008) Insulin resistance and daytime sleepiness in patients with sleep apnoea. Thorax 63(11):946–950
Lindberg E, Berne C, Elmasry A, Hedner J, Janson C (2006) CPAP treatment of a population-based sample–what are the benefits and the treatment compliance? Sleep Med 7(7):553–560
Murri M, Alcazar-Ramirez J, Garrido-Sanchez L, Linde F, Alcaide J, Cardona F et al (2009) Oxidative stress and metabolic changes after continuous positive airway pressure treatment according to previous metabolic disorders in sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome patients. Transl Res 154(3):111–121
Nguyen PK, Katikireddy CK, McConnell MV, Kushida C, Yang PC (2010) Nasal continuous positive airway pressure improves myocardial perfusion reserve and endothelial-dependent vasodilation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 12:50
Conflict of interest
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest with any companies/organizations whose products or services may be discussed in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iftikhar, I.H., Blankfield, R.P. Effect of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Hemoglobin A1c in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Lung 190, 605–611 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-012-9404-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-012-9404-x