Abstract
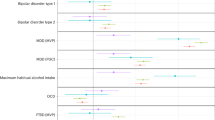
The effect of assortative mating on offspring is often not considered. Here, we present data on illness in the spouse and the parents of patients with bipolar disorder as they affect illness in the offspring. A history of psychiatric illness (depression, bipolar disorder, suicide attempt, alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and “other” illness) was elicited for the parents, spouse, and the offspring of 968 patients with bipolar disorder (540 of whom had children) who gave informed consent for participation in a treatment outcome network. Assortative mating for a mood disorder in the spouse and parents in those from the United States (US) was compared to those from the Netherlands and Germany and related to illnesses in the offspring. There was more illness and assortative mating for a mood disorder in both the spouse and patient’s parents from the US compared to Europe. In the parents of the US patients, assortative mating for a mood disorder was associated with more depression, bipolar disorder, alcohol, and “other” illness in the offspring. Compared to the Europeans, there was more assortative mating for mood and other disorders in two generations of those from the US. This bilineal positivity for a parental mood disorder was related to more depression a second generation later in the patients’ offspring. In clinical assessment of risk of illness in the offspring, the history of psychiatric illness in the spouse and patient’s parents might provide additional information.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelson D, Goldstein B, Goldstein T, Monk K, Yu H, Hickey MB, Sakolsky D, Diler R, Hafeman D, Merranko J, Iyengar S, Brent D, Kupfer D, Birmaher B (2015) Diagnostic precursors to bipolar disorder in offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: a longitudinal study. Am J Psychiatry 172(7):638–646. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14010035
Rasic D, Hajek T, Alda M, Uher R (2014) Risk of mental illness in offspring of parents with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of family high-risk studies. Schizophr Bull 40(1):28–38. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbt114
Goldstein BI, Shamseddeen W, Axelson DA, Kalas C, Monk K, Brent DA, Kupfer DJ, Birmaher B (2010) Clinical, demographic, and familial correlates of bipolar spectrum disorders among offspring of parents with bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(4):388–396
Lapalme M, Hodgins S, LaRoche C (1997) Children of parents with bipolar disorder: a metaanalysis of risk for mental disorders. Can J Psychiatry Revue canadienne de psychiatrie 42(6):623–631. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674379704200609
Gottesman II, Laursen TM, Bertelsen A, Mortensen PB (2010) Severe mental disorders in offspring with 2 psychiatrically ill parents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(3):252–257. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.1
McMahon FJ, Stine OC, Chase GA, Meyers DA, Simpson SG, DePaulo JR Jr (1994) Influence of clinical subtype, sex, and lineality on age at onset of major affective disorder in a family sample. Am J Psychiatry 151(2):210–215
Nordsletten AE, Larsson H, Crowley JJ, Almqvist C, Lichtenstein P, Mataix-Cols D (2016) Patterns of nonrandom mating within and across 11 major psychiatric disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 73(4):354–361. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.3192
Plomin R, Krapohl E, O’Reilly PF (2016) Assortative mating-a missing piece in the jigsaw of psychiatric genetics. JAMA Psychiatry 73(4):323–324. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.3204
Weissman MM, Wickramaratne P, Nomura Y, Warner V, Pilowsky D, Verdeli H (2006) Offspring of depressed parents: 20 years later. Am J Psychiatry 163(6):1001–1008. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.6.1001
Post RM, Leverich GS, Kupka R, Keck P Jr, McElroy S, Altshuler L, Frye MA, Luckenbaugh DA, Rowe M, Grunze H, Suppes T, Nolen WA (2014) Increased parental history of bipolar disorder in the United States: association with early age of onset. Acta Psychiatr Scand 129(5):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/acps.12208
Post RM, Leverich GS, Kupka RW, Keck PE Jr, McElroy SL, Altshuler LL, Frye MA, Luckenbaugh DA, Rowe M, Grunze H, Suppes T, Nolen WA (2010) Early-onset bipolar disorder and treatment delay are risk factors for poor outcome in adulthood. J Clin Psychiatry 71(7):864–872. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.08m04994yel
Post RM, Altshuler LL, Frye MA, Suppes T, Keck PE Jr, McElroy SL, Leverich GS, Luckenbaugh DA, Rowe M, Pizzarello S, Kupka RW, Grunze H, Nolen WA (2010) Complexity of pharmacologic treatment required for sustained improvement in outpatients with bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 71(9):1176–1186. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.08m04811yel(quiz 1252–1173)
Post RM, Altshuler L, Kupka R, McElroy S, Frye MA, Rowe M, Leverich GS, Grunze H, Suppes T, Keck PE Jr, Nolen WA (2014) More pernicious course of bipolar disorder in the United States than in many European countries: implications for policy and treatment. J Affect Disord 160:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.02.006
Post RM, Altshuler LL, Kupka R, McElroy SL, Frye MA, Rowe M, Leverich GS, Grunze H, Suppes T, Keck PE Jr, Nolen WA (2015) Verbal abuse, like physical and sexual abuse, in childhood is associated with an earlier onset and more difficult course of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 17(3):323–330. https://doi.org/10.1111/bdi.12268
Post RM, Leverich GS, Kupka R, Keck PE Jr, McElroy SL, Altshuler LL, Frye MA, Rowe M, Grunze H, Suppes T, Nolen WA (2015) Increases in multiple psychiatric disorders in parents and grandparents of patients with bipolar disorder from the USA compared with The Netherlands and Germany. Psychiatr Genet 25(5):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/YPG.0000000000000093
Post RM, Altshuler LL, Kupka R, McElroy SL, Frye MA, Rowe M, Grunze H, Suppes T, Keck PE, Leverich GS, Nolen WA (2015) More illness in offspring of bipolar patients from the U.S. compared to Europe. J Affect Disord 191:180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.11.038
Duffy A (2010) The early natural history of bipolar disorder: what we have learned from longitudinal high-risk research. Can J Psychiatry Revue canadienne de psychiatrie 55(8):477–485. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371005500802
Duffy A, Alda M, Hajek T, Sherry SB, Grof P (2010) Early stages in the development of bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 121(1–2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2009.05.022
Hillegers MH, Reichart CG, Wals M, Verhulst FC, Ormel J, Nolen WA (2005) Five-year prospective outcome of psychopathology in the adolescent offspring of bipolar parents. Bipolar Disord 7(4):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5618.2005.00215.x
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Monk K, Kalas C, Goldstein B, Hickey MB, Obreja M, Ehmann M, Iyengar S, Shamseddeen W, Kupfer D, Brent D (2009) Lifetime psychiatric disorders in school-aged offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: the Pittsburgh Bipolar Offspring study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66(3):287–296. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2008.546
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Goldstein B, Monk K, Kalas C, Obreja M, Hickey MB, Iyengar S, Brent D, Shamseddeen W, Diler R, Kupfer D (2010) Psychiatric disorders in preschool offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: the Pittsburgh Bipolar Offspring Study (BIOS). Am J Psychiatry 167(3):321–330. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09070977
Chang KD, Steiner H, Ketter TA (2000) Psychiatric phenomenology of child and adolescent bipolar offspring. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(4):453–460. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200004000-00014
Nurnberger JI Jr, McInnis M, Reich W, Kastelic E, Wilcox HC, Glowinski A, Mitchell P, Fisher C, Erpe M, Gershon ES, Berrettini W, Laite G, Schweitzer R, Rhoadarmer K, Coleman VV, Cai X, Azzouz F, Liu H, Kamali M, Brucksch C, Monahan PO (2011) A high-risk study of bipolar disorder. Childhood clinical phenotypes as precursors of major mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68(10):1012–1020. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.126
Van Meter AR, Moreira AL, Youngstrom EA (2011) Meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies of pediatric bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 72(9):1250–1256. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.10m06290
Mesman E, Birmaher BB, Goldstein BI, Goldstein T, Derks EM, Vleeschouwer M, Hickey MB, Axelson D, Monk K, Diler R, Hafeman D, Sakolsky DJ, Reichart CG, Wals M, Verhulst FC, Nolen WA, Hillegers MH (2016) Categorical and dimensional psychopathology in Dutch and US offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: a preliminary cross-national comparison. J Affect Disord 205:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.06.011
Simpson SG, Folstein SE, Meyers DA, DePaulo JR (1992) Assessment of lineality in bipolar I linkage studies. Am J Psychiatry 149(12):1660–1665. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.149.12.1660
Wickramaratne P, Gameroff MJ, Pilowsky DJ, Hughes CW, Garber J, Malloy E, King C, Cerda G, Sood AB, Alpert JE, Trivedi MH, Fava M, Rush AJ, Wisniewski S, Weissman MM (2011) Children of depressed mothers 1 year after remission of maternal depression: findings from the STAR*D-Child study. Am J Psychiatry 168(6):593–602. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10010032
Post RM, Chang K, Frye MA (2013) Paradigm shift: preliminary clinical categorization of ultrahigh risk for childhood bipolar disorder to facilitate studies on prevention. J Clin Psychiatry 74(2):167–169. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.12com08136
Miklowitz DJ, Schneck CD, Singh MK, Taylor DO, George EL, Cosgrove VE, Howe ME, Dickinson LM, Garber J, Chang KD (2013) Early intervention for symptomatic youth at risk for bipolar disorder: a randomized trial of family-focused therapy. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 52(2):121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2012.10.007
Fristad MA, Verducci JS, Walters K, Young ME (2009) Impact of multifamily psychoeducational psychotherapy in treating children aged 8 to 12 years with mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66(9):1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.112
Kessing LV, Hansen HV, Hvenegaard A, Christensen EM, Dam H, Gluud C, Wetterslev J (2013) Treatment in a specialised out-patient mood disorder clinic v. standard out-patient treatment in the early course of bipolar disorder: randomised clinical trial. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci 202(3):212–219. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.112.113548
Bale TL (2014) Lifetime stress experience: transgenerational epigenetics and germ cell programming. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 16(3):297–305
Dias BG, Ressler KJ (2014) Parental olfactory experience influences behavior and neural structure in subsequent generations. Nat Neurosci 17(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3594
Szutorisz H, DiNieri JA, Sweet E, Egervari G, Michaelides M, Carter JM, Ren Y, Miller ML, Blitzer RD, Hurd YL (2014) Parental THC exposure leads to compulsive heroin-seeking and altered striatal synaptic plasticity in the subsequent generation. Neuropsychopharmacology 39(6):1315–1323. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.352
Vassoler FM, Byrnes EM, Pierce RC (2014) The impact of exposure to addictive drugs on future generations: Physiological and behavioral effects. Neuropharmacology 76(Pt B):269–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.016
McGorry PD, Nelson B, Goldstone S, Yung AR (2010) Clinical staging: a heuristic and practical strategy for new research and better health and social outcomes for psychotic and related mood disorders. Can J Psychiatry Revue canadienne de psychiatrie 55(8):486–497. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371005500803
Amminger GP, Schafer MR, Schlogelhofer M, Klier CM, McGorry PD (2015) Longer-term outcome in the prevention of psychotic disorders by the Vienna omega-3 study. Nat Commun 6:7934. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8934
Merikangas KR, He JP, Brody D, Fisher PW, Bourdon K, Koretz DS (2010) Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders among US children in the 2001–2004 NHANES. Pediatrics 125(1):75–81. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-2598
Anderson LE, Chen ML, Perrin JM, Van Cleave J (2015) Outpatient visits and medication prescribing for US children with mental health conditions. Pediatrics 136(5):e1178–e1185. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-0807
Shonkoff JP, Garner AS, Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of C, Family H, Committee on Early Childhood A, Dependent C, Section on D, Behavioral P (2012) The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics 129 (1):e232–e246. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2663
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Post, R.M., Altshuler, L.L., Kupka, R. et al. More assortative mating in US compared to European parents and spouses of patients with bipolar disorder: implications for psychiatric illness in the offspring. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270, 237–245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0934-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0934-y