Abstract
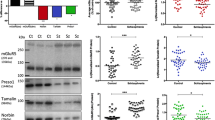
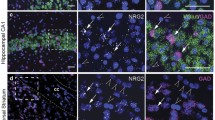
The evidence underlying the so-called glutamatergic hypothesis ranges from NMDA receptor hypofunction to an imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory circuits in specific brain structures. Among all glutamatergic system components, metabotropic receptors play a main role in regulating neuronal excitability and synaptic plasticity. Here, we investigated, using qRT-PCR and western blot, consequences in the hippocampus and prefrontal/frontal cortex (PFC/FC) of mice with a genetic deletion of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5), addressing key components of the GABAergic and glutamatergic systems. We found that mGlu5 knockout (KO) mice showed a significant reduction of reelin, GAD65, GAD67 and parvalbumin mRNA levels, which is specific for the PFC/FC, and that is paralleled by a significant reduction of protein levels in male KO mice. We next analyzed the main NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits, namely GluN1, GluN2A, GluN2B and GluA1, and we found that mGlu5 deletion determined a significant reduction of their mRNA levels, also within the hippocampus, with differences between the two genders. Our data suggest that neurochemical abnormalities impinging the glutamatergic and GABAergic systems may be responsible for the behavioral phenotype associated with mGlu5 KO animals and point to the close interaction of these molecular players for the development of neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia. These data could contribute to a better understanding of the involvement of mGlu5 alterations in the molecular imbalance between excitation and inhibition underlying the emergence of a schizophrenic-like phenotype and to understand the potential of mGlu5 modulators in reversing the deficits characterizing the schizophrenic pathology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lieberman JA, Bymaster FP, Meltzer HY, Deutch AY, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Aprille JR, Dwyer DS, Li XM, Mahadik SP, Duman RS, Porter JH, Modica-Napolitano JS, Newton SS, Csernansky JG (2008) Antipsychotic drugs: comparison in animal models of efficacy, neurotransmitter regulation, and neuroprotection. Pharmacol Rev 60:358–403
Balu DT, Coyle JT (2011) Neuroplasticity signaling pathways linked to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:848–870
Molteni R, Calabrese F, Racagni G, Fumagalli F, Riva MA (2009) Antipsychotic drug actions on gene modulation and signaling mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 124:74–85
Neill JC, Barnes S, Cook S, Grayson B, Idris NF, McLean SL, Snigdha S, Rajagopal L, Harte MK (2010) Animal models of cognitive dysfunction and negative symptoms of schizophrenia: focus on nmda receptor antagonism. Pharmacol Ther 128:419–432
Bubenikova-Valesova V, Horacek J, Vrajova M, Hoschl C (2008) Models of schizophrenia in humans and animals based on inhibition of nmda receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:1014–1023
du Bois TM, Deng C, Han M, Newell KA, Huang XF (2009) Excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission is chronically altered following perinatal nmda receptor blockade. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19:256–265
Lewis DA, Gonzalez-Burgos G (2006) Pathophysiologically based treatment interventions in schizophrenia. Nat Med 12:1016–1022
Lewis DA, Moghaddam B (2006) Cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia: convergence of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate alterations. Arch Neurol 63:1372–1376
Homayoun H, Moghaddam B (2007) Nmda receptor hypofunction produces opposite effects on prefrontal cortex interneurons and pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 27:11496–11500
Lewis DA, Curley AA, Glausier JR, Volk DW (2012) Cortical parvalbumin interneurons and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci 35:57–67
Moghaddam B, Javitt D (2012) From revolution to evolution: the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and its implication for treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:4–15
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
Nicoletti F, Bockaert J, Collingridge GL, Conn PJ, Ferraguti F, Schoepp DD, Wroblewski JT, Pin JP (2011) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: from the workbench to the bedside. Neuropharmacology 60:1017–1041
Mannaioni G, Marino MJ, Valenti O, Traynelis SF, Conn PJ (2001) Metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 and 5 differentially regulate ca1 pyramidal cell function. J Neurosci 21:5925–5934
Pisani A, Gubellini P, Bonsi P, Conquet F, Picconi B, Centonze D, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2001) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 mediates the potentiation of n-methyl-d-aspartate responses in medium spiny striatal neurons. Neuroscience 106:579–587
Perroy J, Raynaud F, Homburger V, Rousset MC, Telley L, Bockaert J, Fagni L (2008) Direct interaction enables cross-talk between ionotropic and group i metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Biol Chem 283:6799–6805
Brody SA, Dulawa SC, Conquet F, Geyer MA (2004) Assessment of a prepulse inhibition deficit in a mutant mouse lacking mglu5 receptors. Mol Psychiatry 9:35–41
Brody SA, Conquet F, Geyer MA (2004) Effect of antipsychotic treatment on the prepulse inhibition deficit of mglur5 knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 172:187–195
Gray L, van den Buuse M, Scarr E, Dean B, Hannan AJ (2009) Clozapine reverses schizophrenia-related behaviours in the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 knockout mouse: association with n-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor up-regulation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:45–60
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Lipina T, Weiss K, Roder J (2007) The ampakine cx546 restores the prepulse inhibition and latent inhibition deficits in mglur5-deficient mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:745–756
Lu YM, Jia Z, Janus C, Henderson JT, Gerlai R, Wojtowicz JM, Roder JC (1997) Mice lacking metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 show impaired learning and reduced ca1 long-term potentiation (ltp) but normal ca3 ltp. J Neurosci 17:5196–5205
Wijetunge LS, Till SM, Gillingwater TH, Ingham CA, Kind PC (2008) Mglur5 regulates glutamate-dependent development of the mouse somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci 28:13028–13037
Jia Z, Lu Y, Henderson J, Taverna F, Romano C, Abramow-Newerly W, Wojtowicz JM, Roder J (1998) Selective abolition of the nmda component of long-term potentiation in mice lacking mglur5. Learn Mem 5:331–343
Ridder S, Chourbaji S, Hellweg R, Urani A, Zacher C, Schmid W, Zink M, Hortnagl H, Flor H, Henn FA, Schutz G, Gass P (2005) Mice with genetically altered glucocorticoid receptor expression show altered sensitivity for stress-induced depressive reactions. J Neurosci 25:6243–6250
Inta D, Monyer H, Sprengel R, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Gass P (2010) Mice with genetically altered glutamate receptors as models of schizophrenia: a comprehensive review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:285–294
Impagnatiello F, Guidotti AR, Pesold C, Dwivedi Y, Caruncho H, Pisu MG, Uzunov DP, Smalheiser NR, Davis JM, Pandey GN, Pappas GD, Tueting P, Sharma RP, Costa E (1998) A decrease of reelin expression as a putative vulnerability factor in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15718–15723
Pesold C, Impagnatiello F, Pisu MG, Uzunov DP, Costa E, Guidotti A, Caruncho HJ (1998) Reelin is preferentially expressed in neurons synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid in cortex and hippocampus of adult rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3221–3226
Berretta S (2012) Extracellular matrix abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 62:1584–1597
Hashimoto T, Arion D, Unger T, Maldonado-Aviles JG, Morris HM, Volk DW, Mirnics K, Lewis DA (2008) Alterations in gaba-related transcriptome in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Mol psychiatry 13:147–161
Kawaguchi Y, Kubota Y (1997) Gabaergic cell subtypes and their synaptic connections in rat frontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 7:476–486
Rudy B, Fishell G, Lee S, Hjerling-Leffler J (2011) Three groups of interneurons account for nearly 100% of neocortical gabaergic neurons. Dev Neurobiol 71:45–61
Kinney GG, Burno M, Campbell UC, Hernandez LM, Rodriguez D, Bristow LJ, Conn PJ (2003) Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors modulate locomotor activity and sensorimotor gating in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:116–123
Kotecha SA, MacDonald JF (2003) Signaling molecules and receptor transduction cascades that regulate nmda receptor-mediated synaptic transmission. Int Rev Neurobiol 54:51–106
Coyle JT, Tsai G, Goff D (2003) Converging evidence of nmda receptor hypofunction in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:318–327
Gordon JA (2010) Testing the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci 13:2–4
Kantrowitz JT, Javitt DC (2010) N-methyl-d-aspartate (nmda) receptor dysfunction or dysregulation: the final common pathway on the road to schizophrenia? Brain Res Bull 83:108–121
Meador-Woodruff JH, Healy DJ (2000) Glutamate receptor expression in schizophrenic brain. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:288–294
Corti C, Xuereb JH, Crepaldi L, Corsi M, Michielin F, Ferraguti F (2011) Altered levels of glutamatergic receptors and Na+/k+ atpase-alpha1 in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 128:7–14
Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW (2005) Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:312–324
Mellios N, Huang HS, Baker SP, Galdzicka M, Ginns E, Akbarian S (2009) Molecular determinants of dysregulated gabaergic gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 65:1006–1014
Guidotti A, Auta J, Davis JM, Di-Giorgi-Gerevini V, Dwivedi Y, Grayson DR, Impagnatiello F, Pandey G, Pesold C, Sharma R, Uzunov D, Costa E (2000) Decrease in reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase67 (gad67) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a postmortem brain study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:1061–1069
Liu WS, Pesold C, Rodriguez MA, Carboni G, Auta J, Lacor P, Larson J, Condie BG, Guidotti A, Costa E (2001) Down-regulation of dendritic spine and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 expressions in the reelin haploinsufficient heterozygous reeler mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3477–3482
Campo CG, Sinagra M, Verrier D, Manzoni OJ, Chavis P (2009) Reelin secreted by gabaergic neurons regulates glutamate receptor homeostasis. PLoS One 4:e5505
Gonzalez-Burgos G, Fish KN, Lewis DA (2011) Gaba neuron alterations, cortical circuit dysfunction and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Neural Plast 2011:723184
Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P (2007) Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:45–56
Keefe RS, Fenton WS (2007) How should dsm-v criteria for schizophrenia include cognitive impairment? Schizophr Bull 33:912–920
Barnes SA, Pinto-Duarte A, Kappe A, Zembrzycki A, Metzler A, Mukamel EA, Lucero J, Wang X, Sejnowski TJ, Markou A, Behrens MM (2015) Disruption of mglur5 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons induces core features of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol psychiatry 20:1161–1172
Pietraszek M, Nagel J, Gravius A, Schafer D, Danysz W (2007) The role of group i metabotropic glutamate receptors in schizophrenia. Amino Acids 32:173–178
Olney JW, Farber NB (1995) Nmda antagonists as neurotherapeutic drugs, psychotogens, neurotoxins, and research tools for studying schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:335–345
Tamminga CA (1998) Schizophrenia and glutamatergic transmission. Crit Rev Neurobiol 12:21–36
Mohn AR, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Koller BH (1999) Mice with reduced nmda receptor expression display behaviors related to schizophrenia. Cell 98:427–436
Belforte JE, Zsiros V, Sklar ER, Jiang Z, Yu G, Li Y, Quinlan EM, Nakazawa K (2010) Postnatal nmda receptor ablation in corticolimbic interneurons confers schizophrenia-like phenotypes. Nat Neurosci 13:76–83
Sprengel R (2006) Role of ampa receptors in synaptic plasticity. Cell Tissue Res 326:447–455
Kopec CD, Real E, Kessels HW, Malinow R (2007) Glur1 links structural and functional plasticity at excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 27:13706–13718
Inta D, Vogt MA, Elkin H, Weber T, Lima-Ojeda JM, Schneider M, Luoni A, Riva MA, Gertz K, Hellmann-Regen J, Kronenberg G, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Sprengel R, Gass P (2014) Phenotype of mice with inducible ablation of glua1 ampa receptors during late adolescence: relevance for mental disorders. Hippocampus 24:424–435
Wiedholz LM, Owens WA, Horton RE, Feyder M, Karlsson RM, Hefner K, Sprengel R, Celikel T, Daws LC, Holmes A (2008) Mice lacking the ampa glur1 receptor exhibit striatal hyperdopaminergia and ‘schizophrenia-related’ behaviors. Mol psychiatry 13:631–640
Bertani M, Lasalvia A, Bonetto C, Tosato S, Cristofalo D, Bissoli S, De Santi K, Mazzoncini R, Lazzarotto L, Santi M, Sale A, Scalabrin D, Abate M, Tansella M, Rugger M (2012) The influence of gender on clinical and social characteristics of patients at psychosis onset: a report from the Psychosis Incident Cohort Outcome Study (PICOS). Psychol Med 42:769–780
Matta JA, Ashby MC, Sanz-Clemente A, Roche KW, Isaac JT (2011) Mglur5 and nmda receptors drive the experience- and activity-dependent nmda receptor nr2b to nr2a subunit switch. Neuron 70:339–351
Sullivan EM, O’Donnell P (2012) Inhibitory interneurons, oxidative stress, and schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 38:373–376
Timms AE, Dorschner MO, Wechsler J, Choi KY, Kirkwood R, Girirajan S, Baker C, Eichler EE, Korvatska O, Roche KW, Horwitz MS, Tsuang DW (2013) Support for the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction hypothesis of schizophrenia from exome sequencing in multiplex families. JAMA Psychiatry 70:582–590
Matosin N, Fernandez-Enright F, Fung SJ, Lum JS, Engel M, Andrews JL, Huang XF, Weickert CS, Newell KA (2015) Alterations of mGluR5 and its endogenous regulators Norbin, Tamalin and Preso1 in schizophrenia: towards a model of mGluR5 dysregulation. Acta Neuropathol 30:119–129
Iasevoli F, Tomasetti C, Buonaguro EF, de Bartolomeis A (2014) The glutamatergic aspects of schizophrenia molecular pathophysiology: role of the postsynaptic density, and implications for treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:219–238
Garcia RA, Vasudevan K, Buonanno A (2000) The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3596–3601
Hahn CG, Wang HY, Cho DS, Talbot K, Gur RE, Berrettini WH, Bakshi K, Kamins J, Borgmann-Winter KE, Siegel SJ, Gallop RJ, Arnold SE (2006) Altered neuregulin 1-erbB4 signaling contributes to NMDA receptor hypofunction in schizophrenia. Nat Med 12:824–828
Conn PJ, Lindsley CW, Jones CK (2009) Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors as a novel approach for the treatment of schizophrenia. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:25–31
Balu DT, Li Y, Takagi S, Presti KT, Ramikie TS, Rook JM, Jones CK, Lindsley CW, Conn PJ, Bolshakov VY, Coyle JT (2016) An mglu5-positive allosteric modulator rescues the neuroplasticity deficits in a genetic model of nmda receptor hypofunction in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:2052–2061
Inta D, Vogt MA, Luoni A, Filipovic D, Lima-Ojeda JM, Pfeiffer N, Gasparini F, Riva MA, Gass P (2013) Significant increase in anxiety during aging in mglu5 receptor knockout mice. Behav Brain Res 241:27–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (IN-168/3-1) to D.I. and P.G. and by Ministry of Health, Italy—Ricerca Sanitaria Finalizzata, GET UP Project Code H61J08000200001 to P.B., M.R. and M.A.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luoni, A., Gass, P., Brambilla, P. et al. Altered expression of schizophrenia-related genes in mice lacking mGlu5 receptors. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 268, 77–87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-016-0728-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-016-0728-z